![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Antibodies in patients with Graves Disease
|
Thyroid stimulating antibodies (TSAb)
Thyroid stimulating blocking antibodies (TSBAb) Anti-thyroid peroxidase (TPOAb) Anti-TGAb (anti-thyroglobulin antibodies) Anti-iodide symporter Anti-components of eye muscle and/ or fibroblasts Antibodies to DNA Antibodies to parietal cells (infrequent) Antibodies binding to platelets |
|
|
Three diseases share same immunological changes, histology & genetic predisposition:
1) graves 2) ? 3) ? |
Graves dis, AITD, idiopathic failure
(AITD, characterized by goiter and various degrees of hypothyroidism Idiopathic “atrophic” hypothyroidism is a result of AITD, and myxedema is most advanced form of disease) |
|
|
In the three diseases, antibodies & cell-mediated immunity are directed against:
|
TSH receptor (megalin), thyroid peroxidase& thyroglobulin
|
|
|
In pts with ophthalmopathy, antibodies against components of _____ _____ and fibroblasts are formed
|
orbital muscles
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of Graves Disease:
Three sets of antibodies are produced: |
TSAb: thyroid-stimulating & acts similar to TSH
TSBAb: thyroid stimulating blocking antibody – blocks binding of TSH, but not stimulatory by itself Third set neither blocks nor stimulates thyroid function (TBII: thyrotropin binding inhibitory immunoglobulins TSAb mediates the thyroid activity and hypersecretion seen in Graves Dis |
|
|
B cells produce what antibodies to cause Graves disease?
|
anti-TSH receptor IgG
|
|
|
What is the thyroid hormone feedback circuit?
|
thyroid hormone tells pituitary to stop production of TSH.
|
|
|
Describe the onycholysis of thyrotoxicosis
|
Distal separation of the nail plate from the nail bed (Plummner's nails)
|
|
|
Thyroid gland, acropachy (clubbing of fingers)
|
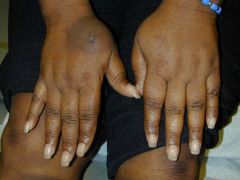
?
|
|
|
Pretibial myxedema
|
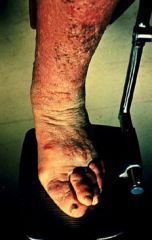
?
|
|
|
Thyroid gland, Localized myxedema (pretibial)
|

?
|
|
|
Other Causes of Hyperthyroidism
|
Toxic nodular goiter
Follicular adenoma Solitary “hot” nodule TSH-mediated thyrotoxicosis Pituitary tumor Pituitary resistance to thyroid hormone HCG-mediated hyperthyroidism Hydatidiform mole Choriocarcinoma Other HCG-related tumors Thyroid carcinoma (rare) |
|
|
Thyroid gland, nodular goiter, hyperthyroidism
|

?
|
|
|
Heart problem assoc with Graves
|
pericardial effusion
acute necrosis of myocardium |
|
|
Autoimmune thyroiditis. Note: Clusters of Hurthle cells
in sea of lymphocytes |

?
|
|
|
Bands of fibrous tissue in autoimmune thyroiditis.
|

?
|
|
|
Autoimmune thyroiditis in nodular goiter
|

?
|
|
|
What causes collections of lymphocytes in the gland and is responsible for epithelial cell damage?
|
thyroid autoimmunity
|
|
|
Progression of disease can change picture from “goitrous” hypothyroidism to “_______” thyroiditis (known as primary hypothyroidism)
|
atrophic
|
|
|
Alternative cause of “atrophic” hypothyroidism is development of ________ Abs
|
thyroid stimulation blocking antibodies (TSBAb)
|
|
|
thyroid stimulation blocking antibodies (TSBAb) Prevents TSH binding to TSH-R, but do not stimulate thyroid cells to produce _____
|
hyperthyroidism
|
|
|
Proposed that TSBAb binds to one end of TSH-R, while thyroid stimulating antibodies (TSAb) bind to ______
|
opposite end of TSH-R
|
|
|
A predominant TSAb response results in ______
|
hyperthyroidism
|
|
|
A predominant TSBAB response results in _______
|
hypothyroidism
|
|
|
HLA antigens of hypothyroid pts with TSAb were different from pts with Hashimoto thyroiditis & idiopathic myxedema and more similar to pts with ______ disease
|
Graves
|
|
|
Thyroid dysfunction may be induced by ______-mediated apoptosis of thyroid epithelial cells
|
cytokine
|
|
|
___ lymphocytes may not be directly involved in thyrocyte cell death
|
T
|
|
|
______ DNA, a feature of apoptosis, was found frequently in autoimmune thyroiditis
|
Fragmented
|
|
|
Ligand for Fas (Fas L), expressed on thyrocytes, induced by IL-1alpha, which is abundantly produced in thyroid gland of Hashimoto thyroiditis, induces ___ expression on thyrocytes
|
Fas
|
|
|
_______ interaction on thyrocytes may induce apoptosis & destruction of thyroid cells
|
Fas-FasL
|
|
|
Fas & FasL strongly stained in follicular cells which suggests that cytokines induce up-regulation of ______-
|
apoptosis
|
|
|
Increased serum TSH may inhibit ____-mediated apoptosis of thyrocytes
|
Fas
|
|
|
In contrast, _____ blocks inhibitory action of Fas-mediated apoptosis and induces thyroid atrophy
|
TSBAb
|
|
|
In relation to Fas-FasL system, mutations of Fas, which induce loss of function, found in thyroid lymphocytes of 38% of pts with ______ thyroiditis
|
Hashimoto
(Additionally, in 64% of pts with malignant lymphoma) |
|
|
There is a relationship of AIT to malignant ______
|
lymphoma
|
|
|
Antithyroglobulin autoantibody stains colloid
|

?
|
|
|
Antimicrosomal antibody stains follicular epithelium
|

?
|
|
|
Most common cause of hypothyroidism in American women
|
Autoimmune Thyroiditis (AIT)
|
|
|
Etiology of AIT?
|
Etiology unknown
|
|
|
Who is affected by AIT?
|
Affects older women (45-65 yrs), usually asymptomatic, with goiters (diffuse, non-nodular)
|
|
|
Lab findings in early AIT?
|
Early laboratory changes: decreased T4, increased TSH
|
|
|
Treatment of AIT?
|
Lifetime replacement with thyroid hormone
|
|
|
Cancer risk after AIT?
|
Slightly increased risk for malignant lymphoma of thyroid gland
|
|
|
95% of malignant ______ arise within autoimmune thyroiditis
|
lymphomas
|
|
|
However, only 5% of patients with AIT are at risk for malignant _____
|
lymphomas
|
|
|
Radiogram of thyroid of pt
Thyroid is not taking up iodine |

?
|
|
|
Thyroid gland, granulomatous thyroiditis. Note: partial involvement of gland
|

?
|
|
|
Thyroid gland, granulomatous thyroiditis.
Note: giant cells & smaller stromal cells |

?
|
|
|
Thyroid gland, granulomatous thyroiditis, giant cell engulfing colloid
|

?
|
|
|
Thyroid gland, granulomatous thyroiditis. Inflammatory reaction
against colloid |

?
|
|
|
Thyroid gland, granulomatous thyroiditis, giant cell reaction to colloid
|

?
|
|
|
Thyroid gland, FNA, granulomatous thyroiditis, giant cell
|

?
|
|
|
Clinical findings to thyroiditis
|
Severe pain, extreme tenderness in region of thyroid gland.
Malaise, fatigue, myalgia & arthralgia, common Mild to moderate fever Disease may peak in 3-4 days & subside within a week More typical. Onset over 1-2 weeks & continues for 3-6 wks Symptoms may also extend over many months Thyroid gland enlarged 2-3 times normal Tender to palpation About ½ of pts present with symptoms of thyrotoxicosis: nervousness, heat intolerance, tremors, increased sweating Thyroid function returns to normal <10% of pts develop permanent hypothyroidism |
|
|
Lab findings of thyroiditis
|
Laboratory findings: striking elevation of ESR
Elevated C-reactive protein High serum T3, T4, thyroglobulin, low radionuclide uptake, absent or low TG antibodies |
|
|
Thyroid gland, radionuclide scan, granulomatous thyroiditis
|
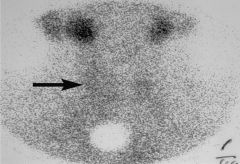
?
|

