![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The purpose an organism has for being here is his .... |
niche |
|
|
The abiotic factors under which an organism lives makes up his ____ niche. |
fundamental |
|
|
The biotic and abiotic factors under which an organism lives make up his ____ niche. |
realized |
|
|
When we can't exactly determine what purpose an organism serves, we often say he has _____ value to us -- value for its own sake. |
intrinsic |
|
|
When we can see some useful purpose for an organism we often say it has _____ value. |
instrumental |
|
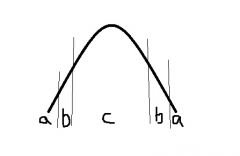
The optimum conditions for an organism living in this niche is zone.... |
C |
|
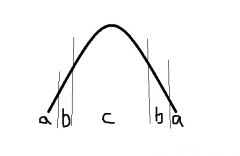
An organism in survival mode, under bad conditions, is in zone.... |
A |
|
|
Organisms that are not picky about their niche, and can tolerate about anything are said to be.... |
generalists |
|
|
Organism that are picky about their niche, and can only tolerate a narrow range of conditions are said to be.... |
specialists |
|
|
A ____ is the type of organism likely to be around after the environment has changed so much that other organisms have gone extinct. |
generalist |
|
|
When a species dies out, we say it has gone.... |
extinct |
|
|
Right now, earth is experience a man-caused, sixth _____. |
extinction |
|
|
Our present mass extinction is mostly due to.... |
overharvesting, climate change, habitat destruction, invasive species |
|
|
Gause discovered that no two species can coexist in the same niche at the same place and time. We refer to this as the .... |
competitive exclusion principle |
|
|
If two different species are going after the same limiting resource (in the same niche), one of them will be the better competitor, in which case one of them survives and the other one.... |
dies or moves away |
|
|
Species that live in close association with each other, whether it's good or bad, are said to have a ____ relationship. |
symbiotic |
|
|
A symbiotic relationship where two species struggle to attain the same resource, are said to be in... |
competition |
|
|
A symbiotic relationship where two species both benefit from the relationship are experiencing .... |
mutualism |
|
|
A symbiotic relationship where one species benefits but is neither harmful nor beneficial to the other species is experiencing.... |
commensalism |
|
|
When one animal seeks and eats another animal in order to survive, we call it ___, where the seeker is the _____, and the one eaten is the ____. |
predation, predator, prey |
|
|
When one organism "eats" another organism by living in or on another organism, we call it... |
parasitism |
|
|
When animals eat plants, we call this activity... |
herbivory |
|
|
When multiple similar species occupy the same niche, but do their business in a slightly different way by their behavior or morphology, in order to coexist, then they are doing.... |
resource partitioning |
|
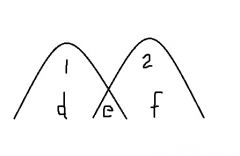
Organisms in niches 1 & 2 are competing for limiting resource labelled as .... |
E |
|
|
A species in an ecosystem that is not necessarily in large abundance but is responsible for providing stability to the entire ecosystem is called a.... |
keystone species |
|
|
Examples of keystone species include.... |
beavers, sea otters, sea stars, prairie dogs, gopher tortoises |

