![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
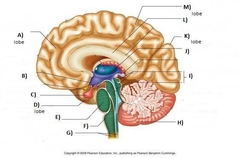
Label this diagram |
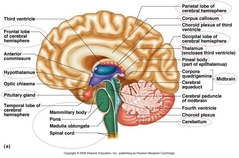
|
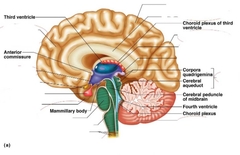
|
|
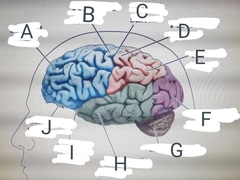
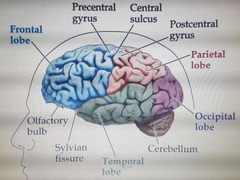
Label diagram |
|
|
|
|
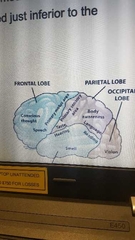
Where are the 1° visual, gustatory, auditory & olfactory areas located respectively? |
Posterior tip of the occipital lobe, inferior to 1° somatosensory area, superior part of temporal lobe, inferomedial temporal love |
|
|
|
Difference between generalised, partial and absence epilepsy. |
G: entire cerebral, complete behaviour disruption, consciousness loss P: circumscribed (restricted within limits) cerebral, abnormal sensation/aura A: Like generalised but under 30 secs. |
Full, partial, less full. |
|
|
What does DLPFC stand for? |
Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex |
|
|
|
Main constituents of limbic system? |
Amygdala, hippocampus, cingulate gyrus, fornix |
A, HC, CG, FX |
|
|
3 sub categories of brain |
Forebrain, mesencephalon, hindbrain |
|
|
|
2 subcategories of forebrain |
Telencephalon and diencephalon |
|
|
|
2 subcategories of hindbrain |
Metencephalon, myelencephalon |
|
|
|
Constituents of telencephalon |
Isocortex, basal ganglia, limbic system |
|
|
|
Diencephalon constituents |
Thalamus and hypothalamus |
|
|
|
Another name for mesencephalon |
Midbrain |
|
|
|
Constituents of metencephalon |
Cerebellum and pons |
|
|
|
What does TRN stand for? |
Thalamic reticular nucleus |
A thalamic division |
|
|
What is the foramen magnum? |
Hole in the base of the skull that spinal cord passes through. |
|
|
|
Body planes |
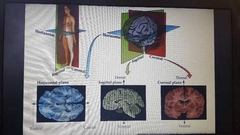
Saggital Coronal Horizontal |
|
|
|
Sympathetic ganglia are found? |
In the CNS |
|
|
|
Parasympathetic ganglia are found? |
In the Peri.NS |
|
|
|
ANS preganglionic neurons are... |
Cholinergic |
|
|
|
Sympathetic postganglionic neurons are... |
Adrenergic |
|
|
|
Parasympathetic postganglionic neurons are... |
Cholinergic |
|
|
|
4 parasympathetic ganglia |
Ciliary Otic Pterygopalatine Submandibular |
|
|
|
8 Sympathetic ganglia |
Superior, middle, inferior cervical Superior, inferior mesenteric Celiac Aorticorenal Renal |
|
|
|
Dopamine expressing neurons from the midbrain originate from... |
Sunstantia nigra |
|
|
|
Serotonin expressing neurons from the midbrain originate from... |
Raphe nuclei |
|
|
|
Noradrenaline expressing neurons from the midbrain originate from... |
Locus coerulus |
|
|
|
ACh expressing neurons from the midbrain originate from... |
Pedunculopontine nucleus |
|
|
|
Inferior colliculus processes... |
Auditory information |
|
|
|
Superior colliculus processes... |
Visual information |
|
|
|
4 diffuse modulator systems |
Raphe nuclei Substantia nigra/ventral tegmental area Locus coerulus Basal forebrain + brain stem complexes |
|
|
|
Raphe nuclei are... |
- Serotonergic - Users of 5HT receptors - associated with mental illnesses, sleep disorders & pain |
|
|
|
# of 5HT receptor classes |
7 |
|
|
|
5HT: ionotropic or metabotropic? Any exceptions? |
Metabotropic, G-protein 5HT3 = ionotropic |
|
|
|
Major dopamine nuclei |
Substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, hypothalamus |
|
|
|
Associates disorders with impaired dopamine regulation |
Parkinson's Psychosis Addiction ADHD Hormonal disorders |
|
|
|
Dopamine receptors, type of receptor and their families |
D1, 2, 3, 4, 5 G protein D1 fam: D1, 5 D2 fam: D2, 3, 4 |
|
|
|
Which 5HT receptors are excitatory/inhibitory |
I: 1-2 E: 4-7 5HT3: excitatory ligand-gated action channels |
|

