![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How much does the cerebral cortex usually weigh?
|
600g
|
|
|
How much do the neurons of the CC usually weigh?
|
180g
|
|
|
what % of the brain is the CC?
|
40% w/ 15b neurons
|
|
|
what are the 6 layers of the NEOCORTEX?
|
1 - molecular layer
2 - external granular layer 3 - external pyramidal layer 4 - internal granular layer 5 - internal pyramidal layer 6 - muliform layer |
|
|
Which layer of the neocortex is this?
axons/dendrites mostly, with few cell bodies |
molecular layer
|
|
|
Which layer of the neocortex is this?
Densely packed stellate cells |
Internal granular layer
|
|
|
Which layer of the neocortex is this?
Stellate/star cells, not as densly packed |
external granular layer
|
|
|
Which layer of the neocortex is this?
Neurons of pyramidal shape |
external pyramidal layer
|
|
|
Which layer of the neocortex is this?
medium pyramidal neurons, also spindle shape cells and stellate cells |
multiform layer
|
|
|
What NT do pyramidal neurons use?
|
GLUTAMATE
|
|
|
Pyramidal neurons are Excitatory or Inhibitory?
|
Excitatory
|
|
|
Pyramidal neurons are afferent or efferent?
|
efferent
|
|
|
Granule neurons use what NT?
|
Glutamate OR GABA
|
|
|
Granule neurons are excitatory or inhibitory?
|
BOTH
|
|
|
What does it mean to be "homotypical cortex"
|
have al 6 layers (of neocortex)
|
|
|
which type of functional layer is common to association areas?
|
homotypical
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of heterotypical corices?
|
Agranular and Koniocortex
|
|
|
What are Agranular (heterotypical corices)
|
Has NO Internal granular layer (IV)
AND Large External pyramidal and Internal pyramidal layers (III and V) |
|
|
What type of functional layer is common to Primary Motor Cortex?
|
Agranular
|
|
|
What are Koniocortex heterotypical cortices?
|
has LARGE internal granular layers and SMALL internal
pyramidal layers |
|
|
What type of functional cortex is common to a sensory corticol area?
|
Keriocortex
|
|
|
What is the paleocortex?
|
Contains olfactory processes
|
|
|
What type of cortex are olfactory processes contained in?
|
Paleocortex
|
|
|
What type of cortex is the hippocampus?
|
archicortex
|
|
|
What is BA 17?
|
VISUAL
|
|
|
What is BA 1,2,3
|
Somatosensory
|
|
|
What is BA 41 and 42?
|
Auditory
|
|
|
What is BA 39?
|
color association
|
|
|
What is BA 6 and 8?
|
motor association
|
|
|
What is BA 21 and 22?
|
Auditory association
|
|
|
What layer of the neocortex receives the majority of thalmic input?
|
4
|
|
|
This BA receives input from what?
BA17 |
Lateral geniculate
|
|
|
This BA receives input from what?
BA 41/42 |
medial geniculate body
|
|
|
This BA receives input from what?
BA 1,2,3 |
Ventral posterior nuclear complex
|
|
|
This BA receives input from what?
BA4 |
ventral lateral/ventral anterior nuclei
|
|
|
Lesions of the Parietal Association cotex result in deficits in what area?
|
Attention
|
|
|
Lesions of hte Temporal association cortex result in deficits in what?
|
Recognition
|
|
|
Lesions of the association cortex result in deficits in what?
|
planning/emotional expression and control
|
|
|
Lateral neglect syndrome usually results from whta?
|
lesion in the parietal association cortex, usually the Right side
|
|
|
If you had to have damage to a parietal association cortex, which side would you have?
|
the left, because the right is dominant and can compensate
|
|
|
What is prosopangosia? what is it a result of?
|
inablitiy to recognize FACES, due to injury to temporal association cortex
|
|
|
what is Agnosia? What is it a result of?
|
inability to recognize familiar items, due to injury to temporal association cortex
|
|
|
An injury to what results in language complications in recognition?
|
Left temporal association cortex
|
|
|
An injury to what results in inability to recognize faces?
|
temporal association cortex
|
|
|
An injury to what would result in a drastic change in personality and behavior pattern?
|
Fronal association cortex
|
|
|
An injury to frontal association cortex results in what?
|
a drastic behavior/personality change
|
|
|
What BA is the visual cortex?
|
17
|
|
|
what BA is the somatosensory cortex?
|
1,2,3
|
|
|
what BA is the auditory cortex?
|
41 and 42
|
|
|
what BA is the color association cortex?
|
39
|
|
|
what BA is the motor association cortex?
|
6 and 8
|
|
|
what BA is the auditory association cortex?
|
21 and 22
|
|
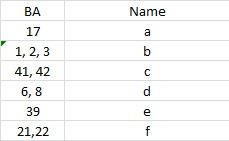
|
a- visual
b - somatosensory c - auditory d - motor association e - color association f - auditory association |
|
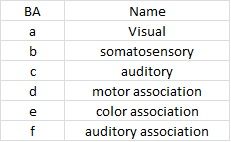
|
a - 17
b - 1,2,3 c - 41, 42 d - 6,8 e - 39 f - 21, 22 |

