![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are 3 functions of the nervous system
|
Input, integration, output
|
|
|
What are the divisions of the NS?
|
Peripheral and Central
Peripheral --> somatic and autonomic Autonomic--> parasympathetic and sympathetic |
|
|
What are the 3 portions of the brainstem?
|
Midbrain, pons, and medulla
|
|
|
What is special about the cranial nerves 1 and 2?
|
They are outgrowths of the CNS
|
|
|
What are the 3 main subcortical structures??
|
Diencephalon
Basal Ganglia Cerebellum |
|
|
What two areas make up the diencephalon?
|
Thalamus and hypothalamus
|
|
|
Where does the spinal cord technically end?
|
T12, and then cauda equina to S5
|
|
|
What is white matter?
|
myelinated axons
|
|
|
What is grey matter?
|
cell bodies
|
|
|
What are the two main areas of white matter in the brain?
|
Internal capsule and corpus callosum
|
|
|
What does EPSP stand for?
What does IPSP stand for? |
Excitatory post-synaptic potential
Inhibatory post-synaptic potential |
|
|
What does the limbic system do, and what are its 5 parts?
|
Plays a role in memory and emotion
1) cingulate sulcus and gyrus, 2) parahippocampal gyrus, 3) Uncus, 4) Isthmus, 5) Amygdala |
|
|
What are the 5 lobes of the brain?
|
Frontal lobe
Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Occipital lobe Limbic lobe |
|
|
What are the two major white matter formations in the brain?
|
Corpus collosum
Internal capsule |
|
|
What does EPSP and IPSP stand for?
|
Excitatory post synaptic potential
Inhibitory post synaptic potential |
|
|
What does the insular lobe do?
|
Responds to very foul smells and situations, strongly negative feelings
|
|
|
Where are perkinje cells located?
|
cerebellar cortex
|
|
|
Where are pyramidal cells found?
|
cerebral cortex
|
|
|
Where are bipolar cells located?
|
Olfactory bulb and retina
|
|
|
Where are pseudounipolar neurons located?
|
peripheral NS
|
|
|
What is morphogenesis?
|
Process by which nervous system takes its shape
|
|
|
What is histogenesis?
|
Process by which nervous tissue differentiates and makes connections/communications
|
|
|
What is gastrolation and when does it begin?
|
Begins 3 weeks after conception, and it is when a 2 layered disc divides into 3 germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
|
|
|
What does the endoderm become?
|
Organs of respiration, digestion, and cardiopulm
|
|
|
What does the mesoderm become?
|
musculoskeletal
|
|
|
What does the ectoderm become?
|
Skin, nervous system
|
|
|
What is neurolation and when does it begin?
|
During 3rd week, ectoderm forms neural plate, folds and inward and becomes the neural tube, tube closes from the center moving up and down--> CNS
|
|
|
What does the notocord become
|
vertebral bodies
|
|
|
What are neuro crest cells?
|
go on to become PNS
|
|
|
What is the sulcus limitans
|
groove that appears in middle of neural tube that differentiates motor (anterior) and sensory (posterior)
|
|
|
What is vesciculation?
|
bulges and flexures in neural tube as it differentiates into 3 brain areas
|
|
|
What does the prosencephalon become?
|
Telencephalon --> Cerebral cortex
Diencephalon --> Thalamus, hypothalamus |
|
|
What does the mesencephalon become?
|
Midbrain
|
|
|
What does the cephalic flexure separate?
|
Prosencephalon and mesencephalon
|
|
|
What does the rhombencephalon become?
|
Metencephalon --> cerebellum and pons
Myelincephalon --> medulla |
|
|
What does fractionation of movement mean?
|
moving isolate muscles
|
|
|
Where is the T10 dermatomal line?
|
umbelicus
|
|
|
Where is the T4 dermatomal line?
|
nipples
|
|
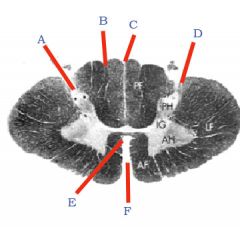
|
A) Posterolateral sulcus
B) Posterior intermediate sulcus C) Posterior median fissure D) Lissauer's tract E) Anterior white commissure F) Anterior median fissure |
|
|
What runs through the anterior median fissure?
|
anterior spinal artery
|
|
|
What is unique about the posterior intermediate sulcus?
|
It is only found in cervical vertebrae
|
|
|
What is the fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus?
|
Gracilis- is in the posterior medial column containing LE sensory
Cuneatus- is in the posterior lateral column containing UE sensory |
|
|
What are the 2 grey matter subdivision
|
1) Lamina of rexed- 10 subdivision based on histological differences
2) Posterior, anterior horns and intermediate grey |
|
|
What is found in the intermediate frey?
|
Autonomic neurons and interneuron cell bodies
|
|
|
Understand what happens in terms of differentiation of the motor/autonomic/sensory in the spinal cord and brain stem
|
Spinal cord- A/P- Motor, autonomic, sensory
Brainstem- M/L- (becomes squished) Motor, autonomic, sensory |
|
|
What is the reticular formation?
|
Where respiration, consciousness, and complex motor patterns are found
|
|
|
Where is the 4th ventricle located?
|
Between pons and cerebellum and extending down to rostral medulla
|
|
|
What do the basil pons and pyramids do and where are they each located?
|
Motor control
BP located in pons Pyramids located in medulla |
|
|
What things are unique about CN IV?
|
only CN that innervates the contralateral side.
Also only CN that exits the brainstem posteriorly |
|
|
What are the major sensory modalities?
|
olfaction, touch, temperature, proprioception, nociception
|
|
|
What is the receptor potential refer to?
|
it is something that increases or decreases the likelihood that an action potential will occur
|
|
|
What is Weber's law?
|
Size of just noticeable difference is a constant proportion of the original stimulus value. i.e. shouting to hear each other in a loud bar
|
|
|
What are receptive fields and what changes at different areas in the body?
|
i.e. two point discrimination
smaller receptive field distally (hands) larger receptive field proximally |
|
|
What are some types of pain?
|
Nociceptive
Neuropathic Acute Chronic Cutaneous Musculoskeletal |
|
|
What are the 2 types of pain fibers?
|
A-delta: sharp prickling pain, thinly myelinated, first stage of pain
C-fibers: Dull, aching, diffusely localized, unmyelinated, chemo and thermoreceptors, associated with autonomic and emotional responses |
|
|
What is Substance P?
|
Inflammation induced substance that causes vasodilation and release of mast cells (i.e. histamine), lowers pain threshold
|
|
|
What is allodynia?
|
When pain threshold is lowered, a non-painful stimuli is perceived as pain. Due to the release of Substance P
|
|
|
When are hot and cold receptors activated?
|
Hot and cold are both activated during middle tempuratures, but during extreme cold, only cold receptors are activated, and vice versa. They are communicated through A-delta and C fibers
|
|
|
What does the spinothalamic tract carry?
|
Pain and temperature information
|
|
|
Where are the 3 nuclei in the spinothalamic tract?
|
1) DRG
2) Substantia gelatinosa 3) VLP in thalamus |
|
|
Where does the spinothalamic tract decussate?
|
Anterior white commissure
|
|
|
How is the spinothalamic tract tested?
|
sharp-dull test
|
|
|
Where does the spinothalamic tract end?
|
post-central gyrus in parietal lobe, with collateral branches going to hypothalamus, and reticular formation
|
|
|
What is the significance of Lissauer's tract?
|
primary afferent neuron enters at dermatomal level and fans out in lissaur's tract (up and down a few levels) before communicated with 2nd order neurons in SG
|
|
|
What doe muscle spindles do and where are they?
|
Located in muscle belly
Detect muscle length change Triggered in DTR's Stimulated by Gamma motor neurons Sensory component that sends afferent info about muscle length |
|
|
What are gamma motor neurons?
|
Signals to keep muscle spindle taut relative to muscle fibers. There is a co-activation between alpha and gamma motor neurons so that when muscle cells contract, so do muscle spindles
|
|
|
What are golgi tendon organs and where are they found?
|
Detects muscle tension, found in musculo-tendinous junction.
Communicate through 1b afferent |

