![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Brenda Milners work |
Neuropsychological testing, careful observation in generating hypotheses, dissassociation of the right and left hemispheres in perception and memory |
|
|
Clive Wearing |
Amnesia, living moment to moment, infection that damaged temporal and frontal lobes |
|
|
Historical roots of neuropsychology |
1960s-1970s, emerged from neurology in 20th century, movement from veterans returning with focaland non-focal forms of brain damage |
|
|
WW1 vetrans with focal and non focal brain damage |
Recognition of PTSD in 1980s, termed shell shock or battle fatigue |
|
|
Earilest focus on neuropsych was on |
Localising lesions and diagnosis. Brain imaging techniques lead to a change in focus, now it is on cognitive and behavioural expression of brain damage and disease |
|
|
History of psychometrics |
From 1880s to current, focus on quantititive data, systematic observation and testing, impact of test characteristics on outcomes, age effects, intelligence impact of education and occupation |
|
|
History of intelligence assessment |
Established practises for standardised testing tools and techniques, use of normative datasets (how someone deviates from normal standards) |
|
|
Examples of statistical norms |
Percentile ranks, z scores, t scores, weschler IQ, Stanford Binet IQ, Stanine |
|
|
Standard battery approach to neuropsych assessment |
More ridgid to testing and scoring, yeilds staistical outcome to comparento norms, somewhat outdated |
|
|
Process approaches to neuropsych assessment |
Uses hypothesis testing and observational approaches, careful observation as well as normative data considered |
|
|
Topics covered in neuropsych assessments |
Cogniton (intellectual functioning, education and occupation level), general aspects of functioning (attention executive functioning, psychomotor speed), more specific domains (lanugage, visuospatial functions, memory, working memory, emotion processing) |
|
|
Type of assessment overall |
Patient, clinician, observer and performance outcomes |
|
|
Neuropsychological assessment focuses on |
Perfromance outcomes |
|
|
Apart from perfromance, neuropsych assessment focuses on |
Interview and questionnaires to determine how patient is feeling or what they think is wrong. Memory is the common complaint for cognitive ability |
|
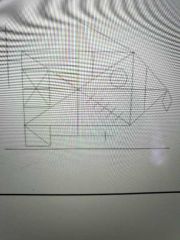
What is this test |
Rey Complex Figure Test: copy, immediate recall and delayed recall |
|
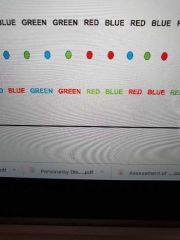
What is this test? |
Stroop test: assesses executive control of interference (attention and cognitive flexibility) |
|
|
Verbal Memory tests |
List learning (what words on list and recognition of words), story memory (tell me the story) |
|

What is this test |
Line Bisection (assesses attention and awareness of visual field, unilateral spatial neglect). Place a line crossing though each line |
|
|
Neuropsychological report entails |
Record of observations, quantitative and qualitiative data, synthesis of results, reccomendations |
|
|
Who ises a neuropsych report |
Patient, family, teachers, other clinicans, legal representatives |
|
|
What is neuropsychological assessment |
The application of assessment principals based on the scientific study of human behaviour across the lifespan as it relates to normal and abnormal functioning of the central nervous system |
|
|
What do neuropsychologists do |
Study changes in thinking and behaviour arising from brain dysfunction (head injury, epilepsy, neurological disease and stroke, drug and alcohol disorders etc) |
|
|
Neuropsychological treatments |
Behvaiour therapy, CBT, relaxation therapy and mindfulness, lifestyle interventions |

