![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Autonomic nervous system |
Sympathetic: T1-L3 (thoracolumbar)
Parasympathetic: cranial nerves and S2-S4 (craniosacral) |
|
|
|
Nicotinic receptors |
🔹Na+/K+ channels 🔹NN: autonomic ganglia and adrenal medulla, blocked by hexamethonium 🔹NM: skeletal muscle, blocked by curare |
|
|
|
GProtein Receptors |
α1 Gq K M1 Gq K α2 Gi I M2 Gi I β1 Gs S M3 Gq CK β2 Gs S |
|
|
|
α1 receptors |
🔹Vascular smooth muscle of the skin and splanchnic regions; 🔹GI and bladder sphincters; 🔹Radial muscle of the iris. |
|
|
|
α2 receptors |
🔹Walls of the GIT (relaxation) 🔹⬇️insulin release |
|
|
|
β1 receptors ❤️ |
⬆️Heart ⬆️SA node, AV node, ventricular muscle. |
|
|
|
β2 receptors |
🔹Vascular smooth muscle of skeletal muscle 💪🏻 🔹Bronchial smooth muscle 🔹Walls of the GIT and bladder |
|
|
|
Muscarinic receptors |
M1: CNS M2: Heart M3: Glands, smooth muscle Antagonist: atropine |
|
|
|
Drugs that act on the ANS |
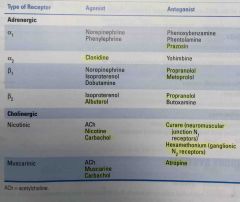
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Effect of the ANS on organ systems |
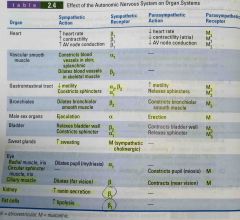
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Nerve fiber types |
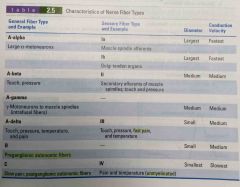
I'm
|
|
|
|
Dorsal column system |
🔹Fine touch, pressure, two-point discrimination, vibration and proprioception. 🔹Group II fibers 🔹Ascend ipsilaterally to the nucleus gracilis and cuneatus of the medulla, where they cross toward the thalamus. |
|
|
|
Anterolateral system |
🔹Temperature, pain and light touch. 🔹Group III and IV fibers 🔹2nd neuron ascends contralaterally to the thalamus |
|
|
|
Nociception |
🔹Receptor: free nerve endings 🔹Substance P: inhibited by opioids 🔹Fast pain: group III fibers (localized) 🔹Slow pain: C fibers (poorly localized) |
|
|
|
Refractive errors |
🔹Hypermetropia: light focuses behind the retina (convex lens) 🔹Miopia: light focuses in front of the retina (biconcave lens) 🔹Astigmatism: curvature of the lens not uniform (cylindric lens). |
|
|
|
Layers of the retina |
🔹Pigment epithelial cells: convert 11-cis retinal to all-trans retinal. 🔹Receptor cells: rods and cones are not present on the optic disk (blind spot).
Receptor cells ➡️ Bipolar cells ➡️ Ganglion cells (optic nerve) |
|
|
|
Functions of Rods and Cones |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Functions of Rods and Cones |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Optic pathways |
Optic nerve ➡️➡️ Lateral geniculate body of the thalamus ➡️➡️ Geniculocalcarine tract ➡️➡️ Occipital lobe of the cortex |
|
|
|
Lesions of the geniculocalcarine tract causes... |
Homonymous contralateral hemianopia, just like lesions of the optic tract, but with macular sparing. |
|
|
|
Lesions of the optic pathways |
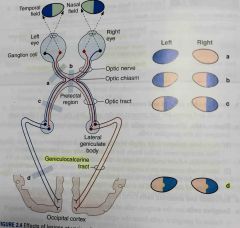
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Photoreception in rods |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Organ of Corti |
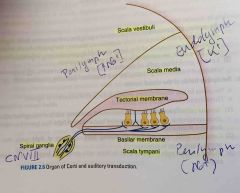
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Central auditory pathways |
Lateral meniscus ➡️ Inferior colliculus ➡️ Medial geniculate nucleus of the thalamus ➡️ Auditory cortex 🔹Fibers may be crossed or uncrossed 🔹Tonotopic representation at all levels of the pathway |
|
|
|
Olfactory receptor cells |
🔹True neurons located in the olfactory epithelium 🔹Basal cells are undifferentiated stem cells that continuously turn over 🔹The only neurons in the adult that replace themselves 🔹Activate G proteins (⬆️cAMP) |
|
|
|
CN I (olfactory) |
🔹Unmyelinated C fibers 🔹Olfactory epithelium inervated by CN V (noxious stimuli, such as ammonia) 🔹Pass through the cribiform plate, whose fracture causes anosmia, but still responds to ammonia. |
|
|
|
Mitral cells in the olfactory bulb |
🔹Second-order neurons 🔹Forms the olfactory tract, which projects to the prepiriform cortex. |
|
|
|
Taste |
🔹Receptors are not neurons 🔹Anterior 2/3 of the tongue: salty, sweet and umami. CN VII 🔹Posterior 1/3 of the tongue: sour and bitter. CN IX 🔹Back of the throat and epiglottis: CN X. 🔹CNs ascend in the solitary tract to solitary nucleus and to taste cortex. |
|
|
|
Muscle spindle |
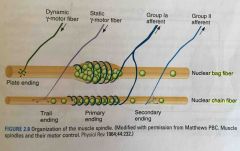
🔹Muscle spindle reflexes oppose increases in muscle length. 🔹ɣ-motoneurons adjust the sensitivity of the muscle spindle so that it will respond appropriately during muscle contraction. |
|
|
|
Muscle reflexes |

Back (Definition) |
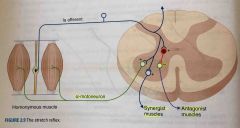
Knee-jerk reflex |
|
|
Spinal shock |
Immediately after transection, there is loss of the excitatory influence from α- and γ-motoneurons. Limbs become flaccid and reflexes are absent. |
|
|
|
Cervical lesions |
C7: loss of sympathetic tone to the heart. ⬇️HR ⬇️ BP C3: disconnection of respiratory muscles. 🚫breathing C1: death (e.g., as a result of hanging) |
|
|
|
Transections above the spinal cord |
⬆️ Lateral vestibular nucleus: decerebrate rigidity (removal of inhibition from higher centers). ⬆️ Pontine reticular formation: decerebrate rigidity (remove of central inhibition) ⬆️ Midbrain: decorticate posturing and intact tonic neck reflexes. |
|
|
|
Cerebellum |
🔹Vestibulocerebellum: balance and eye movement. 🔹Pontocerebellum: planning and initiation of movement. 🔹Spinocerebellum: synergy (rate, force, range) of movement. |
|
|
|
Purkinje cells |
🔹The only output of the cerebelar cortex
🔹Always inhibitory |
|
|
|
Basal ganglia |
🔹Striatum, globus pallidus, subthalamic nuclei and substantia nigra. 🔹Plan and execute smooth movements 🔹Striatum communicates with thalamus by indirect (inhibitory) and direct (excitatory) pathways. |
|
|
|
Dopamine |
🔹Connections between striatum and substantia nigra. 🔹Inhibitory on the indirect pathway (D2 receptors) 🔹Excitatory on the direct pathway (D1 receptors) 🔹 Thus, overall excitatory. |
|
|
|
Lesions of the basal ganglia |
🔹Globus pallidus: inability to maintain postural stability. 🔹Subthalamic nucleus: hemibalismus. 🔹Striatum: uncontrollable movements (Huntington disease). 🔹 Substantia nigra: Parkinson (destruction is inhibitory). |
|
|
|
Language |
Left hemisphere damages:
Wernicke: sensory aphasia Broca: from aphasia |
|
|
|
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) |
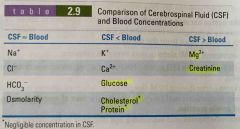
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) |
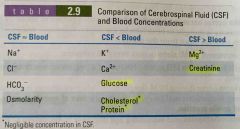
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Temperature regulation |
Heat-loss: anterior hypothalamus
Heat-generation: posterior hypothalamus
IL-1 acts on anterior hypothalamus to increase prostaglandins. |
|
|
|
Drugs that affect Autonomic Activity |
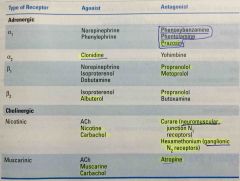
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Chorda tympani |
CN VII: taste 2/3 anterior of the tongue |
|
|
|
Types of muscle fibers |
Extrafusal: alfa-motoneurons, force for contraction Intrafusal: gama-motoneurons, adjust the sensitivity of the muscle spindle |
|
|
|
Muscle spindle reflexes |
Sensory information about muscle length is received by group Ia (dynamic) and group II (static) afferent fibers.
Stretching stimulates alfa-motoneurons to contract. |
|

