![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
111 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is demyelination |
Loss of myelin that is already formed and initially normal |
|
|
What is primary demyelination |
Myelin sheath selectively affected and the axon remains intact |
|
|
What is primary demyleination a feature of |
Canine dystemper Visna Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis Virus |
|
|
What is secondary demyelination a feature of |
Loss of myelin following damage to the azon |
|
|
In which type of neuronal response to damage does demyelination occur |
Wallerian degeneration |
|
|
What is dysmyelination |
Abnormal myelination |
|
|
What does vasculat disease usually cause |
Partial or complete blockage of blood flow Ischaemia |
|
|
What do the consequences of ischaemia depend on? |
Duration of and degree of ischaemia Size and type of vessel involved Susceptability to hypoxia |
|
|
What are the consequences of ischaemia |
Acute neuronal necrosis Vasogenic oedema (may be simultaneous if vasuclar damage is present) Infarct |
|
|
What is an infarct |
Necrosis of a tissue following obstruction of its blood supply |
|
|
What are the causes of infarction |
Thrombosis - dic and sepsis Embolism - bone marrow following fractures Fibrocartillaginous embolic myelopathy Vasculitis |
|
|
What is FCEM |
Common in large breed dogs Causes non progressive disease Fibrocartillagenous thrombi in small vessels 60% have had previous trauma |
|
|
What is the definition of malacia |
Grossly appreciable softening of the brain or spinal cord |
|
|
What infections can cause vasculitis |
Hog cholera/CSF Malignant catarrhal fever Oedema disease Vasculitis caused by E.Coli Toxin |
|
|
What can malacia mean on a microscopic level |
Softening |
|
|
When can malacia occur |
During infarcts and other diseases such as hypoxia, toxicosis, nutritional deficiency, metabolic disease or infection |
|
|
What agents cause symmetrical malacia |
Nutritional, Toxic, Metabolic, Genetic |
|
|
What agents cause assymetrical malacia |
Infectious Vascular Trauma |
|
|
What are the routes of entry |
Haematogenous Direct implantation Peripheral nerves within axoplasm Local extension |
|
|
What are the components of the BBB |
Endothelial cells, astrocytes and pericytes
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of bbb endothelium |
Not fenestrated Tight junctions Fewer transport vesicles |
|
|
What does fibrinous exudate indicate |
Bacteria including mycoplasma |
|
|
What does suppurative exudate indicate |
Becaria including mycoplasma and fungi |
|
|
What does granulomatous exudate indicates |
Bacteria or funghi |
|
|
Lymphoplasmacytic exudate indicates |
Viruses |
|
|
Haemorrhagic exudate indicates |
Septicaemia or infarcts |
|
|
Sneaky infection examples |
Rabies - via nerve axoplasm Mycobacterium in macrophages |
|
|
Where can infection extend from |
nasal cavity middle ear paranasal sinuses |
|
|
Where can infection become established |
Epidural space Subdural space Leptomeninges Brain parenchyma |
|
|
What does epidural/subdural inflammation result in |
absecesses which are uncommon |
|
|
Types of leptomeningitis |
Suppurative Eosinophillic Lymphocytic Granulomatous |
|
|
Causes of suppurative leptomeningitis |
Bacterial |
|
|
Gross lesions with suppurative leptomeningitis |
Swollen brain Opaque meninges Petechiae Glassy membrane |
|
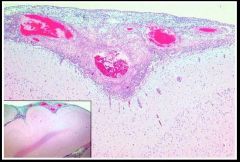
|
Histological appearence of suppurative leptomeningitis |
|
|
Causes of eosinophillic meningioencephalitis |
Porcine salt poisoning Water deprivation |
|
|
Appearence of eosinophillic meningioencephalitis |
Perivascular cuffing with eosinophils
|
|
|
What generally causes lymphocytic leptomeningitis |
Viral infection |
|
|
What generally causes granulomatous leptomeningitis |
Idiopathic - sterile meningitis Fungal diseases Mycobacteria |
|
|
What are the 3 types of virus affecting the nervous system |
Neurotrophic Endotheliotrophic Pantrophic |
|
|
What are the types of enecphalitis |
Bacterial Viral Prion |
|
|
What is encephalitis |
Inflammation of the cerebral parenchyma |
|
|
What does bacterial encephalitis generally result in |
Abscesses - macro or micro Single or multiple depending on route Central liquefied cavity May be encapsuative - compressive |
|
|
What are the hallmark lesions of viral CNS infections |
Neuronal necrosis Gliosis Perivascular cuffing with lymphocytes and plasma cells |
|
|
What is gliosis |
Glial cell responses to infection Proliferation and hypertrophy |
|
|
Neurotrophic viruses |
Rabies - rhabdovirus Aujeskys disease Visna - ovine virus |
|
|
What are the endotheliotrophic viruses |
Infectious canine hepatitis Classical swine fever Equine herpes virus type 1 |
|
|
Feature of EHV 1 |
Spinal cord haemorrhage |
|
|
What is pantropic |
has a tropisn for all neural tissue nonspecific |
|
|
What viruses are pantrophic |
Canine distember Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis |
|
|
Pathogenesis of listeria |
Oral mucosa Trigeminal nerve Trigeminal ganglion |
|
|
Signs of cns listeriosis |
circling facial n drooling pharyngeal paralysis recumbancy paddling death |
|
|
What are TSE |
neurogenerative diseases including BSE, scrapie, CJD, chronic wasting disease |
|
|
What is the aetiology of prion disease |
PrP sc comprise the infectous agents, lack substantial nucleic acid PrP sc changes the structure of the host encoded PrP to abnormal isoform Accumulates in abnormal fibrils - amyloid like |
|
|
What are the microscopic lesions of scrapie |
Spongiform change Astrogliodsis Amyloid plaques |
|
|
Concussion |
Temporary loss of consciousness following head trauma |
|
|
What is contusion |
focal haemorrhage |
|
|
What is the difference between coup and contrecoup |
Head is suddenly stopped by object, brain doesnt stop and hits inside at the skull at first point of impact (coup) The brain moves in the cranium streching and tearing vessels and nerves at the opposite side to the impact |
|
|
What is laceration |
Tearing of the CNS by bone within the skull Fracture or penetrating objects |
|
|
Haemorrhage occurs due to |
Contusion endothelial damage |
|
|
Responses of the spinal cord to injury |
compression contusion concussion haemorrhage |
|
|
Causes of spinal cord compression |
abscess fracture neoplasm malformation |
|
|
Extramedullary compression ecampled |
Neoplasm of meninges Vertebral bone fracture or malfromation |
|
|
Intramedullary compression example |
Neoplasm or abscess intervertebral disk disease |
|
|
What breeds are predisposed to idd |
Beagle Dachsund Basset |
|
|
What is wobblers syndrome |
Stenoic myelopathy Vertebral canal narrows due to malformation and malarticulation of the cervical vertebra C3-4 |
|
|
Gross lesions associated with compression |
Intentation or flattening Malacia |
|
|
Microscopic lesions associated with spinal cord compression |
Myelin sheath ballooning in all funiculi with axonal swelling.oss Wallerian degeneration Removal of myelin in macrophages with myelin digestion chambers Neuronal and glial loss |
|
|
Causes of congenital malformation |
Enviromental - during gestation Inherited |
|
|
What are the types of cranial malformation |
Hydrocephalus Cerebellar defects
|
|
|
Anencephaly |
Absence of brain May be small foci of germinal tissue |
|
|
Lissencephaly |
No gyri/sulchi |
|
|
What is hydrocephalus |
Increase accumulation of fluid in the cranial cavity |
|
|
What are the types of hydrocephalus |
Internal External Communicating Hydrocephalus ex vacuo |
|
|
Internal hydrocephalus |
Within venticles Congenital or acquired |
|
|
CSF circulation |
Choroid plexus Lateral ventricles 3rd 4th |
|
|
External hydrocephalus |
within the arachnoid space |
|
|
Communicating hydrocephalus |
within the ventricles and the arachnoid space |
|
|
Compensatory hydrocephalus |
Secondary to loss of cerebral tissue - also known as compensatory hydrocephalus |
|
|
Aquired hydrocepahlus |
Due to obstruction - inflammation or compression Space occupying lesions INrlammation of meninges or ependymal cells |
|
|
Congenital hydrocephalus |
Malformed mesencephalic aquaduct may be involved but often obstructive lesion not found Common in brachycephalics |
|
|
What are the 2 main cerebellar defects |
Cerebellar hypoplasia and cerebellar abiotrophy |
|
|
What is cerebellar hypoplasia |
Occurs in all domestic spp Inherited or environmental |
|
|
What teratogens cause cerebellar hypoplasia |
BVD Feline parvo Pestivirus Panleukopaenia Schmallenberg Hog cholera |
|
|
Layers of the cerebellum |
Molecular Purkinje Granular |
|
|
What is cerebellar abiotrophy |
Premature or accellerated degeneration of nervous tissue after they have been formed |
|
|
In what animals is inherited cerebellar hypoplasia common |
arab foals jersey cettle chows corriedale sheep |
|
|
What are the primary neoplasms of the briain |
Meningioma Glial tumours Primative neuroectodermal tumours
|
|
|
What are the features of meningioma |
Common in cats and dogs in the falx region Compressive space occupying which seldom invades Well demarcated and can be removed |
|
|
What are the types of glial tmours |
Astrocytoma Oligodendroglioma Ependymoma choroid plexus tumours |
|
|
Astrocytoma features |
Most commmon Brachycephalic Solid firm gray/white mottled with necrosis |
|
|
Oligodendroglioma |
Most common in dogs - brachycephalics Soft grey to pink/red Gelatinous |
|
|
Ependymoma |
Occur mainly within the ventricles May spread to the ventricular system via the CSF Expansile but can be invasive and destructive |
|
|
Choroid plexus tumours |
Papillomas or carcinomas (epithelial) Rare Mainly in dogs and generally in the 4th ventricle |
|
|
What causes idiopathic epilepsy |
Small group of neurons spontaneously depolarise This can occur due to structural, biochemical or unknown causes |
|
|
Structural epilepsy |
Neoplasm INflammation trauma |
|
|
Biochemical epillepsy |
Hypocalcaemia Hypoglycaemia Hepatic enephalopathy |
|
|
Secondary malignancies that can seed in the brain |
Haemangiosarcoma Lymphosarcoma (Lymphoma) Mammary/Pulmonary carcinoma |
|
|
What adjacent tissue tumours can invade the brain |
Pituitary or nasal carcinomas |
|
|
Why are some peripheral nerves predisposed to injurt |
Superficial location Close proximity to bone Dyscoia - obturator nerce Proximity to injection sites |
|
|
What are the types of truma that can occur to peripheral nerves |
Avulsion Crushing Slicing |
|
|
How does neospora caninum affect peripheral nerves |
Predilection for dorsal root (afferent) |
|
|
Equine gutteral pouch mycosis causes what |
Laryngeal hemiplegia due to recurrant laryngeal nerve paralysis and damage |
|
|
What is macaw wasting disease |
caused by borna disease virus Non suppurative inflammation in the autonomic nervous system (enteric is particularly affected) CNS also affected - neurological signs Wasting anorexia and depression Proventricular dilation syndrome |
|
|
What is coonhound paralysis |
Polyradiculoneuritis Linked to racoon bites Quadriplegia Lesions in ventral roots of spinal nerves - efferent |
|
|
Equine laryngeal hemiplegia |
Idiopathic degeneration of (95% left) recurrent laryngeal nerve leading to atropy of left dorsal cricoarytenoid nuscle Inability to abduct arytenoids Inspiratory obstruction leading to noise and reduced performance |
|
|
Toxic causes of neuropathy |
Heavy metals Lead damages schwann cells - peripheral demyelination Mercury targets neuronal cell bodies - secondary axonal degeneration in peripheral nerves |
|
|
Copper deficiency causes what |
Swayback in newborn lambs Enzootic ataxia in older lambs
|
|
|
What metabolic states are associated with neuropathies |
Diabetes mellitis and hypothyroidism |
|
|
What is a lysosomal storage disease |
Inherited - lesions in both cns and pns Enzyme change in conformation and either works less well or not at all |
|
|
Krabbes disease |
Galactocerebrosidase mutation Myelin -> galactocerebroside -> (enzyme)-> breakdown products Accumulation of galactocerebroside and psychosine in tissues |
|
|
What does psychosidase accumution cause |
Demyelination toxic to olidodendrocytes |

