![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a neuron? |
A specialized cell that can transmit nerve impulses |
|
|
Name the components of a typical neuron. |
Dendrites- tiny projections that relay information to the cell body Axon- the long arm that transmits a signal to other neurons, muscles or glands Cell body- processes signals and maintains neurons Myelin sheath- a protective layer wrapping axons that also helps propagate signals |
|
|
What are glial cells? Name the different types of these cells. |
Glial cells- collective term for cells that support neurons and its functions (4 types) - astrocytes - oligodendrites/Schwann cells - Microglia - Ependymal cells |
|
|
What is the function of an astrocyte? |
-supply nutrients to nerves -create a structural framework to support cells -maintains homeostatic environment within brain |
|
|
What is the function of an oligodendrite/Schwann cell? |
- forms myelin sheath around axons that assist in propagation of electrical/chemical signal -oligodendrites are in CNS only Schwann cells are in PNS only |
|
|
What is the function of microglia? |
-acts as the immune system for the brain |
|
|
What is the function of ependymal cells? |
-produce and regulate cerebrospinal fluid |
|
|
What is a synapse? |
Synapse- at structure that allows a neuron to pass an electrical/chemical signal to another cell |
|
|
What is a chemical synapse composed of? |
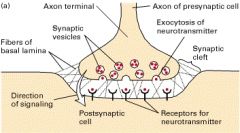
-pre-synaptic membrane -synaptic cleft -post-synaptic membrane |
|
|
What occurs at the pre-synaptic membrane? |
1. An electrochemical excitation occurs (action potential) is triggered in a nerve and travels down the axon to the pre-synaptic membrane
2. The action potential triggers the release of neurotransmitters collected in vesicles from the pre-synaptic membrane into the synaptic cleft |
|
|
What occurs in the synaptic cleft? |
Neurotransmitters travel from the pre-synaptic membrane through the synaptic cleft until it reaches the post-synaptic membrane. |
|
|
What occurs in the post-synaptic membrane? |
1. Some neurotransmitters attach to receptors located on the post-synaptic membrane. 2. The receptors modify the post-synaptic membrane in some way to recreate the action potential from the presynaptic cell and continue to pass it along. |
|
|
How does an electrical synapse propagate? |
Between two axons via gap junctions.-rarer in body and more rapid than a chemical synapse. |

