![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In the brainstem, what is the artery that is more commonly affected by strokes?
|
Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
|
|
|
Describe what the oculomotor nerve innervates
|
1. extrinsic eye muscles: medial, superior and inferior rectus
2. inferior oblique 3. levator palebrae (also has SNS innervation) PSNS fibres -> constrictor pupillae and ciliary muscles -> accommodation |
|
|
What does damage to the oculomotor nerve result in?
|
Diplopia, ptosis and outward deviation of the eye.
Dilated pupil and decreased accommadation |
|
|
Describe what the trochlear nerve innervates
|
Superior oblique muscle
|
|
|
What does damage to the trochlear nerve result in?
|
Upward deviation and diplopia
|
|
|
Describe what the trigeminal nerve innervates
|
1. General sensory to the face
2. Muscles of mastication 3. tensor tympani 4. tensor palati 5. digastric 6. opthalmic branch -> sensory to cornea |
|
|
What does damage to the trigeminal nerve result in ?
|
Decrease sensitivity to the face, asymmetric chewing and wasting of jaw muscles with asymmetric chewing. Loss of corneal reflex
|
|
|
Describe what the abducens nerve innervates
|
Lateral rectus muscles
|
|
|
What does damage to the abducens nerve result in?
|
Inward deviation
Diplopia |
|
|
Describe what the facial nerve innervates
|
1. Muscles of facial expression
2. Stapedius 3. Taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue 4. Lacrimal gland (PSNS supply) 5. Salivary glands |
|
|
What does damage to nVII result in?
|
1. Paralysis of facial expression
- orbicularis oris + buccinator = dropping mouth and drooling 2. Loss of taste to the ant. 2/3 of tongue 3. Effect orbularis oculi -> unable to close eyes and loss of corneal reflex |
|
|
What does the nVIII innervate?
|
1. Vestibular apparatus
2. Cochlear |
|
|
What does damage to nVIII result in?
|
1. Deafness
2. Disequilibrium |
|
|
What does nIX innervate?
|
1. Post. 1/3 of tongue
2. Sensation to palate 3. stylopharyngeal muscle |
|
|
What does damage to nIX result in?
|
1. Pain spasms in posterior pharynx
2. Loss of taste in post. 1/3 of tongue |
|
|
What does nX innervate
|
Carries PSNS fibres to and gets sensory information from: visera,
heart, muscles of pharynx and larynx supplies motor to pharynx and larynx |
|
|
What does damage to nX result in?
|
1. Hoarseness
2. Poor swallowing 3. Loss of gag reflex |
|
|
What does nXI innervate?
|
1. Trapezius
2. SCM |
|
|
What does damage to nXI result in?
|
Wasting in neck with weak neck rotation
Can't shrug |
|
|
What does XII innervate?
|
1. Intrinsic muscles of the tongue
2. Hypoglossus 3. Styloglossus 4. Genioglossus |
|
|
What does damage to nXII result in?
|
1. Tongue deviation to the side of the lesion on protrusion
2. Wasting of tongue |
|
|
Name the embryological vesicle (from the 3 vesicle stage) in which the BS originates from
|
Rhombencephalon
|
|
|
True or false
BS contains nuclei that contributes to nIII-XII |
true
|
|
|
What tract passes through both cerebral peduncles and pyramids?
|
Corticospinal tract (CsT)
|
|
|
When does CsT become lateral CsT?
|
Lower medulla = pyramidal decussation
|
|
|
What is the function of the olivary nuclei?
|
supplies motor control information to the cerebellum
role in the coordination of movement |
|
|
What is the position of the olives in relation to the cerebellar peduncles?
|
Inferior
|
|
|
What does the terms "open medulla" and "closed medulla" refer to?
|
Closed medulla: sections of the brainstem taken below the level of the rhomboid fossa
Open medulla: Sections of the brainstem that cut through the lower end of the rhomboid fossa |
|
|
What tract does the red nucleus receive and where do the tracts proceed from there?
|
Fibres from the cerebellum -> superior cerebellar peduncle -> midbrain -> red nucleus -> Thalamus
Fibres about motor coordination from the cerebellum to thalamus |
|
|
What synapses with the Gracile and Cunate nuclei?
|
Dorsal column tract (sensory)
|
|
|
What is the medial lemniscus?
|
the DCT after it has synapsed with the gracile and cunate nuclei and have crossed the midline.
Carries sensory information from the SC -> thalamus -> cerebral cortex |
|
|
What fibres do the inferior cerebellar peduncles carry?
|
ScT -position and balance
|
|
|
Describe the pontine nuclei
1) main input 2) axons/tracts that originate from it 3) location |
location: in the pons, scattered amongst bundles of corticofugal axons that make up LPT ( at this level
main input: CsT Tracts: Longitudinal pontine tract (mainly corticospinal axons) and pontocerebellar axons |
|
|
True or false
The ponto cerebellar axons decussate before MCP |
True
|
|
|
What tract makes up the pryamids?
|
LPT (mostly corticospinal)
|
|
|
In the pons where is the tegmentum
|
dorsal to pontocerebellar axons
|
|
|
Is the ML still apparent at the level of the pons?
|
Yes
|
|
|
At what level does the auditory decussation happen?
|
Pons
|
|
|
Where would you find substantia nigra pars compacta and reticulata? and which is more medial?
|
Caudal midbrain
Pars compacta |
|
|
1) What are the main arteries?
2) What are they branches off? 3) Through what structure do they enter the skull? 4) When they unite, what do they form? |
1) vertebral arteries
2) subclavian artery 3) foramen magnum 4) join at caudal boarder of pons -> basilar artery |
|
|
What are the branches of the basilar artery?
|
1) AICA
2) SCA 3) 2 PCA |
|
|
What is the PICA a branch of?
|
vertebral artery
|
|
|
What does the PICA supply?
|
(medulla)
lateral medulla (dorsolateral to olive + ICP) ventral surface of cerebellum |
|
|
What is the medial BS medulla supplied by?
|
small branches of the vertebral artery
|
|
|
What is the pons supplied by?
|
AICA and SCA
(Boys Still Pose in AIS = basilar artery supplies pons (by) anterior inferior and superior arteries) |
|
|
What is the midbrain and cerebral peduncles suppled by?
|
2 PCA
|
|
|
Which vertebral artery is usually smaller and whys that important?
|
Right < Left usually
= most of the vertebral flow is through the left artery |
|
|
name the arteries
|
|
|
|
name the arteries
|
|
|

name the arteries
|
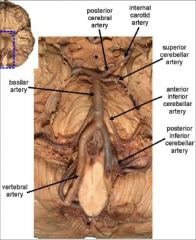
|
|
|
name the blood supply to these areas
|
|
|
|
name the blood supply to these areas
|
|
|
|
name the blood supply to these areas
|
|

