![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
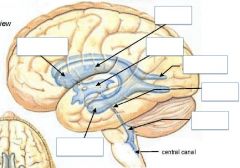
Name the structures
|
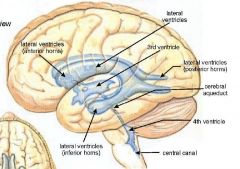
|
|
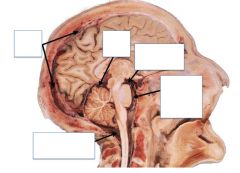
Name the structures
|
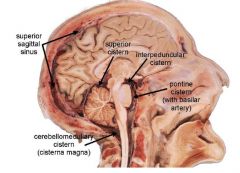
|
|
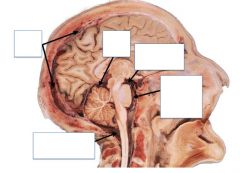
Name the structures
|
|
|
|
What is the percentage of epidural hematoma that is from a venous origin?
|
10%
|
|
|
When do you typically see an epidural hematoma?
|
blows to the side of the head that ruptures a middle meningeal artery
|
|
|
Most bleeds into the subarachnoid space are from?
|
aneurysms from the Circle of Willis
|
|
|
How would a stroke occur after a subarachnoid haemorrhage?
|
blood in the subarachnoid space mixes with the CSF and coats the pia. RBCs then die and release their contents which are vasoconstrictive and decrease arterial diameter which may lead to a stroke
|
|
|
Via which foramina does the 3rd ventricle communicate with the lateral ventricles
|
Foramina Munro
|
|
|
What is the name of the aqueduct that transverses the midbrain?
|
Mesencephalic (cerebral) aquaduct
|
|
|
Describe the structures around the 4th ventricle
|
Sandwiched between: cerebellum, pons and rostral medulla.
It's floor = rhomboid fossa It's roof = superior and inferior medullary vela of the cerebellum |
|
|
What are the three apertures in the 4th ventricle?
|
foramen of Magendie
foramina of Luschka |
|
|
How does CSF differ from blood?
|
High in: Na, Mg
Little in: K, Ca Low in: Cells and protein Remains stable |
|
|
Where is CSF made?
|
Choriod plexus (80%) and ependyma cells (line ventricles)
|
|
|
Where is the choriod plexus not found?
|
anterior and posterior horns of the lateral ventricles
Note: important for catheters or measuring pressure. Choriod plexus clogs catheter tip |
|
|
How much CSF is made per day?
|
500ml
|
|
|
How many times is CSF replaced in a day?
|
4 times
|
|
|
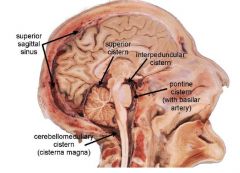
Which Cistern contains he Circle of Willis?
|
Interpeduncular Cistern
|
|
|
Which Cistern is of radiological improtance and why?
|
Superior Cistern
Contains: 1. great cerebral vein of Galen 2. pineal gland 3. continues rostrally into transverse fissure |
|
|
True of False:
When the pressure is high in the Subarachnoid space, it follows down it's concentration gradient into the dorsal venous sinuses (e.g. Superior Sagittal Sinus) and when the pressure is high in the sinuses, CSF flows back down its concentration gradient into the subarachonoid space |
False
The flow is unidirectional, due to valves in the arachnoid villi |
|
|
Where are the three main blood-brain-barriers?
|
1. Arachnoid
2. Choroid Plexus 3. Cerebral Capillaries |
|
|
How does the arachnoid act as a BBB?
|
Passive functions
1. ependymal cells fold over themselves 2. tight junctions 3. impermeable to hydrophilic substances |
|
|
How does the Choroid Plexus act as a BBB?
|
Selectively permeable -prevent most macromolecules from entering CSF
1. Microvilli on CSF side -allows CSF out 2. Tight junctions -keep most things from getting in More permeable than the other BBBs |
|
|
How does the Cerebral Capillaries act as a BBB?
|
1. Non fenestrated
2. Tight Junctions of endothelial cells |
|
|
When might the BBB break down?
|
1. infection
2. Trauma 3. Stroke 4. Tumour |
|
|
What type of Spina Bifida does the following features describe?
Defect in the lumbosacral region, where the SC, spinal roots and meningitis protrude into a sac/cysts and there is constant leakage of CSF |
Spina bifida cystica -myelomeningocele
|
|
|
When does myelomeningocele usually occur in gestation and what is it due to?
|
Usually 4th week of gestation
Due to failure of posterior neuropore closure |
|
|
When should folate supplement be given to a woman preparing to have a child and why?
|
before 3-4 weeks of gestation (before neural tube is programmed to close)
Reduces the risk of myelomeningocele by 80% |
|
|
What are the reasons for a child born with myelomeningocele developing hydrocephalus?
|
1. abnormal part of the SC tethering to the vertebral column. Which pulls the medulla into the foramen magnum
2. CSF is escaping through the opened neural tube, however after surgery, hydrocephalus can occur due to the above mentioned reason |
|
|
At what level does spina bifida occult usually occur?
|
the arch of a single vertebra is opened usually either at LV5 or SV1
|
|
|
When does spina bifida occult occur during gestation and why?
|
Occurs: 5-12 weeks of gestation
Why: failure of the vertebral precursor cells to migrate around the SC |
|
|
True or False
Spina Bifida Occulta isn't associated with any clinical features because the SC is normal? |
True
Only a defect of the vertebral column which is often marked hy a tuft of hair, pigmented nevus or a dimple |
|
|
What is the only difference between Spina Bifida Occulta and Spina Bifida Cystica -meningocele?
|
Several vertebrae are involved in meningocele.
Meningocele is rare malformation |
|
|
What is a common herniation?
|
Herniation across the temporal lobe/over tentorium cerebelli
Causes: 1. paresis of IIIn 2. contralateral UMN symptoms (due to compression of cerebral peduncle against tentorium) |
|
|
What type of herniation is life threatening and why?
|
Tonsillar herniation
because it compresses vital centres in the BS --> coma |

