![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
104 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the GCS |
motor - Obays commands, Localizes to pain, Flexes to pain, Decorticate, Decerebrate, none
speech - Orientated, Confused, words, noise, none
Eye- Spontaneous, Verbal , Pain, None
(Normal = 15 , Coma =8, Minimum =3)
|
|
|
If a pt has a GCS 8 , what do they usually present like ? |
No eye opening or obeying commands
makes noises |
|
|
What are the signs of base of skull # ? |
racoon's eyes
Battle's signs
CSF leakage from ear/nose |
|
|
What is racoon's eyes |
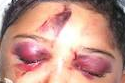
Periorbital ecchymosis |
|
|
What is Battle's sign? |
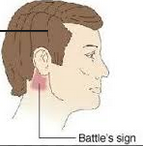
postauricular ecchymosis |
|
|
If there is a risk of base of skull # , what is contraindicated ? |
Nasopharyngeal tube ! |
|
|
In a person with a head injury , what are the indications for CT scan ? |
GCS < 13
suspicion of Skull #
Focal neurological signs
Vomitting > 1
Seizure |
|
|
How would you manage a pt with head injury ? |
Supportive
If seizures -> diazepam
If Hydrocephalus - CSF drainage (via ventricles) , mannitol |
|
|
What is important to look for on examination in a patient with head injury ? |
Head lacerations Skull # CSF leak from nose/ear
Palpate the posterior neck for tenderness |
|
|
What do non-missile injuries involve ?
|
Coup & Contracoup injury |
|
|
How does diffuse axonal injury occur ?
What are the complications ?
|
Non-missile injury --> acceleration/deceleration -> damage to white matter -> widespread axonal injury
Complications - coma |
|
|
What occurs during diffuse axonal injury ??
How do you manage it ? |
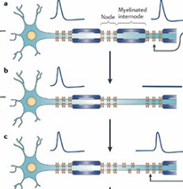
Injury -> decreased myelin sheath -> increased exposure of neurons -> increased Na/Ca exchange by neurons -> increased Ca in neurons -> toxicity -> apoptosis
Rx- Induce coma ( to stop Ca influx) |
|
|
What are the types of brain herniations |
Falcine/Cingulate - under falx cerebri
Tentorial/uncal - under tentorium cerebelli
Cerebellar/tonsillar (through foramen magnum)
transcalvarium (defect in the skull) |
|
|
What are the criteria for brainstem death ? |
2x doctors for confirmation
Irreversible damage Not caused by Dx Normothermia exclude - Coma, Apnoea, Vascular/metabolic/endocrine dx |
|
|
What is hydrocephalus ?
What is Evan's ratio ? |
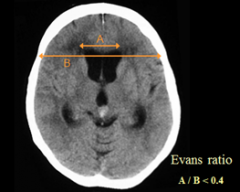
excess fluid within ventricles
Evan's ratio = Ventricular width/ biparietal width (Normal <0.4) |
|
|
What are the Rx options for hydrocephalus ? |
Shunting
ventriculostomy
(May use furosemide/acetazolamide) |
|
|
What are the different types of hydrocephalus ? (give e.g) |
Communicating (no obstruction b/w ventricles & subarachnoid granules) -e.g Normal pressure hydrocephalus, hydrocephalus ex vacuo
Non-communicating (obstruction ) e.g tumor, abscess, SAH |
|
|
What is hydrocephalus ex-vacuo ? |
Enlarged ventricles due to cerebral atrophy -e.g alzheimer's |
|
|
What are the characteristics of normal pressure hydrocephalus ? |
Normal CSF pressure + enlarged ventricles
(wet, wacky, wobbly)
Incontinence Confusion Ataxia |
|
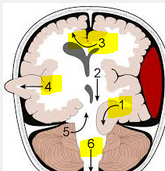
Describe the herniations |
1 - Uncal/transtentorial 3- falcine/cingulate 4- Transcalvarium 6- Cerebellar/tonsillar |
|
|
What is the cerebral herniation through the foramen magum ? |
Cerebellar /tonsillar |
|
|
What is the commonest tumor in the brain ? |
Metastasis ! |
|
|
Where do brain metastasis come from ? |
Lung Renal Breast Prostate |
|
|
Brain tumors are usually benign, why do they cause problems ? |
Space occupying lesion -> raised ICP |
|
|
What are the types of primary intracranial tumors ?
(describe their associations ) |
Astrocytoma - commonest
Medulloblastoma - children
Meningioma |
|
|
describe the progression of an astrocytoma ? |
Pilocytic astrocytoma -> diffuse -> anaplastic -> Glioblastoma |
|
|
If a glioblastoma appears in a pt < 50yrs, what does that indicate ? |
Likely a progression from astrocytoma
(Bad prognosis- 8 months) |
|
|
If a glioblastoma appears in a pt > 50 yrs , what does that indicate ? |
Likely primary glioblastoma
(WORSE prognosis - 5 months) |
|
|
For Primary brain malignancies , which is better - Chemo or radiotherapy ? & why ? |
Radiotherapy ( b/c chemo doesn't penetrate through the BBB) |
|
|
What is cerebral palsy ?
When does it occur ? |
Non progressive
Movement & postural disorder
Occurs during developmental growth period |
|
|
What are the risk factors for cerebral palsy ? |
Preterm Low birth weight
periventricular leukomalacia TORCHes Asphyxia intraventricular hemorrhage birth trauma , cerebral malformation |
|
|
What are common associated symptoms of cerebral palsy ? |
Seizures
Disturbance in vision, hearing, sensarion, language |
|
|
What is periventricular leukomalacia?
Caused by ? |
Necrosis of white matter tracts lateral to the ventricles
-caused by Neonatal CMV infection & prematurity/low birth weight |
|
|
What are the types of cerebral palsies ( what structures are damaged ) ? |
Spastic (Cerebral cortex/Corticospinal ) - commonest
Dyskinetic (basal ganglia)
Ataxic ( cerebellum) - most severe |
|
|
Describe the features of spastic cerebral palsy |
UMN - spasticity, weakness, hyperreflexia , hypertonia, Clonus
babinski sign
|
|
|
What are the types of distribution of cerebral palsy ? |
paraplegic (lower limbs)
Diplegic (lower limbs + others..)
Hemiparesis (unilateral body)
Quadriplegic (all 4 limbs) |
|
|
Which type of spastic cerebral palsy is associated w/ periventricular leukomalacia ? |
Paraplegic or diplegic (due to location on the homunculus) |
|
|
Which type of spastic cerebral palsy is associated w/ cognitive dysfunction ? |
Quadriplegic |
|
|
What Rx are available for spasticity ? |
Baclofen
dantrolene ( muscle relaxant) |
|
|
What are the characteristics of dyskinetic/athetoid cerebral palsy ? |
Involuntary movement (chorea/athetosis)
NOT ASSOCIATED W/ COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT |
|
|
What are the characteristics of ataxic cerebral palsy ? |
most severe
all 4 limbs affected
DANISH
Associated w/ developmental delay, mental retardation |
|
|
What are seizure mimics ? |
Hypoglycemia
Cardiac arrhythmias, prolonged QT
Migraine
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of syncope ? |
LOC preceded by a trigger (prolonged standing/heat)
DOES NOT OCCUR LYING DOWN
-Prodrome: Lightheadedness, dizziness, blurry vision , Pallor -Flaccidity -quick recovery w/ no deficit
May be associated w/ incontinence & myoclonus |
|
|
What are the characteristics of vertigo ? |
Illusion of rotatory movement
-N&V -Worsen w/ movement . Relieved by sitting/lying |
|
|
If vertigo + hearing loss, what are your DDx ? |
Labyrynthitis (post-infection + acute)
Menieres (recurrent episodes + low pitch hearing loss) |
|
|
What commonly triggers epilepsy ? |
Bright lights
poor sleep
Stress (physical)
Alcohol
menstruation |
|
|
describe the characteristics of focal/partial epilepsy ?
Age group? caused by what type of pathology Subtypes ? |
Commonly in adults
Due to structural etiology
localizing S/S Associated w/ Prodrome
Focal --> secondary generalized
Subtypes - Simplex ( conscious) or Complex (unconscious) |
|
|
Hippocampal sclerosis is caused by what ?
What type of epilepsy is it associated with ? |
Caused by CNS infection (?viral)
temporal lobe epilepsy |
|
|
for generalized epilepsy, describe
-Age group -Predisposing factor -Subtypes ? |
Children
due to genetic factors
LOC
Subtypes - tonic clonic, myoclonic, absent, atonic
NOT ASSOCIATED W/ AURA |
|
|
What are the characteristics of tonic-clonic seizure ? |
Stiffness -> jerks. Acute onset LOC |
|
|
What are the characteristics of myoclonic seizures ? |
Violent limb movements |
|
|
What are the characteristics of absent seizures ? |
Brief <10s
Stops mid-sentence |
|
|
What are other features of seizures ? |
Tongue biting Cyanosis Incontinence Pro-ictal confusion/weakness (i.e Todd's Paresis) Residual focal neurological signs |
|
|
What Ix can be performed for a seizure ? |
blood glucose, ECG
Video MRI EEG- 3hrtz spike wave in absent seizures
if head injury -> CT scan |
|
|
Describe where the lesion is with these types of prodromal auras
-Somatosensory -Visual -Automatism -Auditory/language -vertiginous |
-Somatosensory -> parietal -Visual -> occipital -Automatism -> temporal -Auditory/language-> temporal -vertiginous -> temporal
|
|
|
If a seizure is bilateral & the pt is conscious , what type of seizure is it ? |
Non-epileptic |
|
|
How do you Rx partial or generalized seizures ? |
Partial - > carbamazepine
Generalized -> sodium valproate |
|
|
If i had my first seizure , how long can't i drive for ? |
6 months
HGV ( 5 yrs) |
|
|
If i have epilepsy & i have another seizure, how long can't i drive for ? |
12 months
HGV (10 yrs) |
|
|
what are the typical features of a temporal lobe epilepsy ?
what is it associated with ? |
Automatism (lip smacking, plucking ) Olfactory hallucination gustatory hallucinations
Associated w/ hippocampal sclerosis |
|
|
What is juvenile myoclonic epilepsy
Rx? |
Teen w/ Myoclonic + tonic clonic + absent seizures
Worsenned w/ sleep deprivation, alcohol
Rx- Sodium valproate
|
|
|
what are the side effects of sodium valproate ? |
(vALPROATE) Appetite increased Liver dx Pancreatitis Reversible alopecia Oedema Ataxia Thrombocytopenia/tremor/teratogenic Encephalopathy |
|
|
What are the side effects of carbamazepine ?
|
Ataxia
Agranulocytosis Teratogenic , SJS, SIADH, Enzyme inducer (alters OCP) |
|
|
What are the side effects of phenytoin ? |
Gum hypertrophy hirsutism
Megaloblastic anemia , Leucopenia cerebellar S/S Osteoporosis
Enzyme inducer (alters OCP) |
|
|
What are the side effects of lamotrigine ? |
-SJS
(slow onset ) |
|
|
What are the side effects of topiramate ? |
weight loss Sedation Renal stones Parasthesia Psychosis
Enzyme inducer |
|
|
What are the side effects of levetiracetam ? |
Mood swings |
|
|
Which AED are safe in pregnancy ? |
Lamotrigine (but need to begin prior to pregnancy due to slow onset)
Levetiracetam |
|
|
Which AED causes reversible alopecia ? |
Valproate |
|
|
Which AED causes SIADH ? |
Carbamazepine |
|
|
Which AED causes liver disease ? |
Valproate |
|
|
Which AED are teratogenic ? |
Valproate Carbamazepine |
|
|
Which AED causes SJS ? |
Carbamazepine
Lamotrigine |
|
|
Which AED are Enzyme inducers ? |
Carbamazepine
Phenytoin
topiramate |
|
|
Which AED causes ataxia ? |
Valproate
carbamazepine
phenytoin |
|
|
Which AED causes hirsutism ? |
Phenytoin |
|
|
Which AED causes megaloblastic anemia |
phenytoin |
|
|
Which AED causes diplopia |
Carbamazepine |
|
|
Which AED causes pancreatitis |
Sodium valproate |
|
|
If a pt with epilepsy becomes pregnant , what dose of folic acid should they receive ?
What is the normal folic acid prescription ? |
If epileptic = 5mg
Normal = 400mcg |
|
|
When do you treat a seizure ? |
@ 10 mins of symptoms |
|
|
what are the types of status epilepticus ? |
Generalized convulsive
Epilepsia partialiss continua (simple focal )
Non-convulsive (Absent ) |
|
|
How do you Rx status epilepticus in the community |
-Buccal midazolam -Rectal diazepam |
|
|
How do you Rx status epilepticus in the hospital ? |
IV lorazepam x2 IV phenytoin |
|
|
Do you Rx non-epileptic fits ? |
NO! reassurance is needed |
|
|
How would you counsel someone with non-epileptic fits ? |
Explain that :
Not intentional No control Non-psychiatric No explanation
No Rx required |
|
|
Febrile seizures are common in which age groups ? |
3months -5 yrs |
|
|
What are the types of febrile seizures |
Simple - generalized <15 mins . No recurrence (within same febrile episode)
Complex - focal seizure >15 mins. Recurrence within febrile episode |
|
|
How would you manage a febrile seizure in a child ? |
lie on floor in recovery position
Rx if > 5 mins -If <2 yrs or <10kg -> Rectal diazepam -If > 2 yrs -> Buccal midazolam |
|
|
In febrile seizures, when should Rx be stopped ? |
If > 5 yrs
If 2 yrs of unused Rx |
|
|
Which is more important , REM or Non REM sleep ? |
Non REM
(REM is more important for development) |
|
|
What are the characteristics of Non REM sleep ?
What parasomnias are associated with Dysfunctional Non-REM sleep ? |
Partial paralysis Non-narrative dreaming
Sleep walking Sleep terrors |
|
|
What are the characteristics of REM sleep ?
What parasomnias associated with dysfunctional REM sleep ? |
Total paralysis Narrative dreaming
REM sleep behavior disorder - (loss of atonia -> vigorous movements -> injury )
|
|
|
What is REM sleep disorder associated with ? |
Parkinson disease
Narcolepsy |
|
|
What are the S/S of narcolepsy |
-Poor night sleep -Excessive sudden daytime sleep
Cataplexy REM Sleep disorder Hypnagogic hallucinations |
|
|
What are the consequences of poor sleep ? |
RTA |
|
|
What is considered chronic headache? |
>3 months ( > 15 x month) |
|
|
What do you need to exclude in a pt with a headache (describe their characteristics) |
GCA- temporal tenderness, jaw claudication
Acute glaucoma
Brain lesion - Raised ICP - Papilloedema, focal neurological signs, vomitting w/o nausea, LR6 palsy
Head injury
SAH
Meningitis (Meningism - fever, nuchal rigidity )
|
|
|
a patient taking the OCP if they have a migraine &...? |
> 35 yrs old
Aura
|
|
|
What are the S/S for tension type headache ? |
(30mins-days )
Bilateral tight band around head Non-throbbing Photophobia OR phonophobia
None of: aggravation by activity, aura, N&V |
|
|
What are the S/S of migraine ? |
(4hrs-days)
Unilateral throbbing pain Worse w/ activity Aura
Photophobia/ phonophobia OR N&V |
|
|
What is the Rx for tension headache ?
Prophylaxis ? |
1. Aspirin OR paracetamol 2.Aspirin & paracetamol
Prophylaxis 1. Amitriptylline (TCA) 2. Venlafaxine (SNRI) 3. Mirtaapine (NaSSA) |
|
|
What is the Rx for migraine ?
Prophylaxis? |
1. NSAIDS + Antiemetics 2.Sumatriptan PO
Prophylaxis 1. Propanolol 2. Topiramate 3. Amitriptylline |
|
|
Sumatriptan is contraindicated in what ? |
CVS dx - MI/angina
HTN
(b/c it vasoconstricts!) |

