![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
define neuroglia?
|
major supporting and nurturing component of the nervous system
|
|
|
what are the three classifications of neurons?
|
multipolar, bipolar, unipolar (pseudo)
|
|
|
do dendrites release or recieve NT?
|
receive
|
|
|
gray matter is composed of what?
|
nerve nuclei (cell bodies of the CNS)
|
|
|
where would grey matter be found in the spinal cord? the brain?
|
interior of the spinal cord, exterior of brain
|
|
|
what type of neurons makeup sensory cells? interneurons? motor neurons?
|
pseudounipolar and bipolar, multipolar, and multipolar
|
|
|
aside from neuron polarity, what other classification criteria is used?
|
type of NT, excitatory vs. inhibitory, length of axon (golgi type I or II, projection neuron)
|
|
|
what occurs at the synaptic end bulb?
|
NT release
|
|
|
these are angular granule bodies found in the cell body of a neuron.
|
nissl material
|
|
|
what is the chemical composition and function of acetylcholine?
|
it is a non-amino acid derived small molecule transmitter. It is used at myoneural junctions, all parasymp. synapses, and preganglionic sympathetic synapses
|
|
|
what is the chemical quality and function of NE as a NT?
|
it is a small molecule NT, biogenic amine, and catecholamine that is used in post ganglionic symp. synapses except for sweat glands
|
|
|
what is the chemical qualities and function of the NT glutamic acid?
|
it is a small molecule transmitter and amino acid that is used in presnaptic sensory and cortex neurons and it is the most common excitatory NT of the CNS
|
|
|
what is the chemical quality and function of the NT gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA)
|
it is a small molecule transmitter and amino acid that is the most common inhibitory NT of the CNS
|
|
|
what is the chemical quality and function of the NT dopamine?
|
it is a small molecule transmitter, a biologic amine and catecholamine. It is used as inhibitory NT in the basal ganglia of the CNS
|
|
|
what is the chemical quality and function of the NT serotonin?
|
it is a small molecule transmitter and biologic amine that inhibits pain, controls mood, and regulates sleep
|
|
|
what is the chemical quality and function of the NT glycine?
|
it is a small molecule transmitter and biologic amine. It is inhibitory and in the spinal cord
|
|
|
what is the chemical qualities and functions of endorphins?
|
it is a neuropeptide and opiod peptide that is an analgesic (unsure of transmission)
|
|
|
what are the chemical qualities and functions of enkephalins?
|
they are neuropeptides and opiod peptides that are analgesic
|
|
|
distinguish between protoplasmic and fibrous astrocytes.
|
protoplasmics are found in the grey matter of the CNS and have more processes while the fibrous astrocytes are found in the white matter of the CNS
|
|
|
what are the functions of astrocytes?
|
NT metabolism, ion balance for AP's, brain development, help form blood brain barrier, supporting network for neurons, and provide a link between neurons and blood vessels
|
|
|
these are the most common glial cells in the CNS with relatively fewer processes and a round/ oval cell body.
|
oligodendrites
|
|
|
what is the function of oligodendrites?
|
support neurons, produce myelin (each cell wraps myelin around several axons
|
|
|
these glial cells have few processes, are derived from monocytes, and can migrate to the site of injury.
|
microglia
|
|
|
what are the functions of microglia?
|
macrophages of the CNS
|
|
|
describe ependymal cells (not function)
|
epithelial cells arranged in a single layer that can be squamos or columnar, many are ciliated
|
|
|
what is the function of ependymal cells?
|
they form a continuous epithelial lining for the ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord. They secrete CSF and possibly assist in circulation of CSF in these areas
|
|
|
what are the neuroglia found in the CNS?
|
ependymal cells, astrocytesl, microglia, and oligodendrocytes
|
|
|
what are the neuroglia found in the PNS?
|
schwann cells and satellite cells
|
|
|
what are the function and structure of schwann cells?
|
they are flattened cells arranged around the axons in the PNS that produce the myelin sheath around a single axon in the PNS
|
|
|
what is the function and structure of the satellite cells?
|
they are flattened cells surrounding the cell bodies of neurons in the ganglia (thus in PNS) and they are used to support these neurons
|
|
|
what neuroglia have perivascular feet?
|
astrocytes
|
|
|
how do schwann cells form the myelin sheaths?
|
the cell circles the axon many times, squezing the cytoplasm out with each circle (note oligodendrocytes do this the same way except around mutliple axons instead of just one)
|
|
|
what are the four types of synapses?
|
axodendritic, axosomatic, axoaxonic, and dendrodendritic
|
|
|
1. axon
2. axolemma 3. mitochondria 4. glial process 5. synaptic vessicles 6. synaptic cleft 7. presynaptic density 8. postsynaptic density 9. postsynaptic cell |
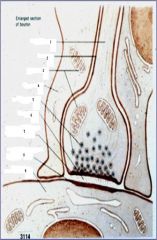
label
|
|
|
1. epineurium
2. perineurium 3. endoneurium 4. schwann cells 5. axon |
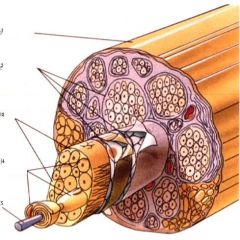
label
|
|
|
bipolar sensory neurons detect what kinds of senses?
|
sepcial such as vision, hearing, smell, balance...
|
|
|
psedounipolar neurons detect what kind of sensation?
|
in all nonspecial (taste, hearing, vision, etc) sensation of the cord and the cranial nerves
|
|
|
what are the roles of golgi type I, type II and projection neurons?
|
I are long axons, thpe II are short, usually used to communicate in the same spinal segment, projection project to the cortex or from the cortex
|

