![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
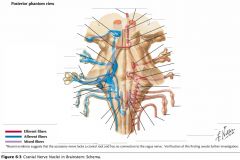
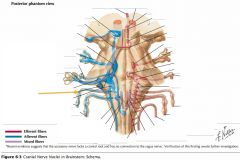
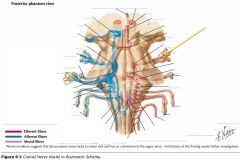
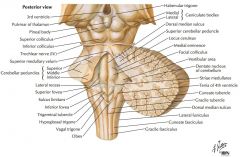
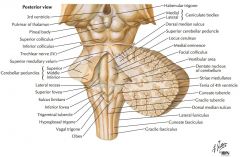
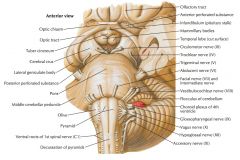
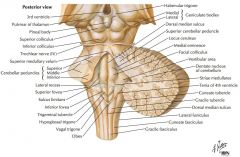
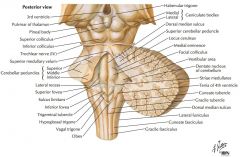
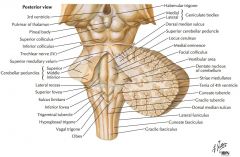
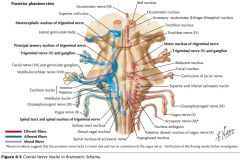
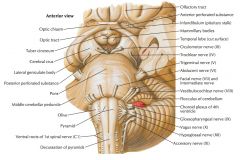
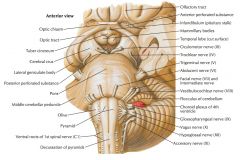
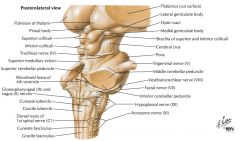
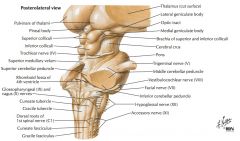
Which cranial nerves exit the Medulla Oblongata? |
CN IX, X, XI, XII. |
|
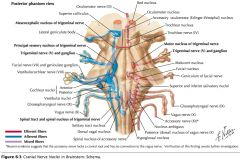
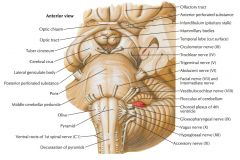
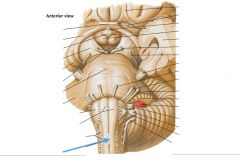
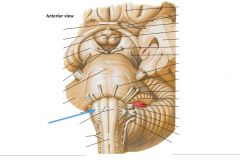
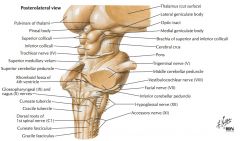
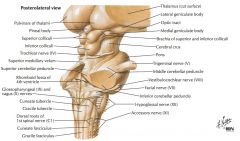
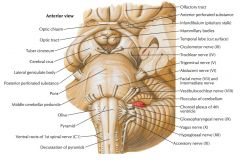
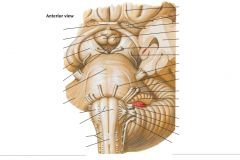
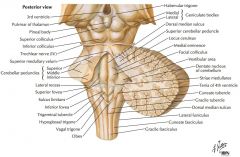
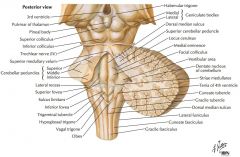
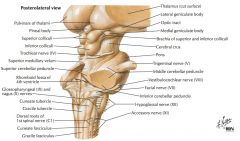
What cranial nerve is indicated by the orange arrow? |
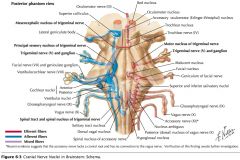
CN IX, the Glossopharyngeal Nerve. |
|
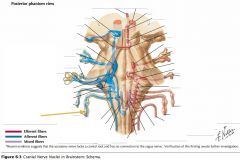
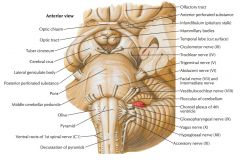
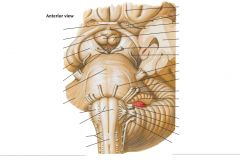
What cranial nerve is indicated by the orange arrow? |
CN X, the Vagus Nerve. |
|
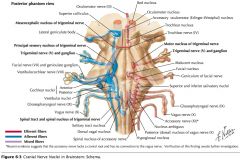
What cranial nerve is indicated by the orange arrow? |
CN XI, the Spinal Accessory Nerve. |
|
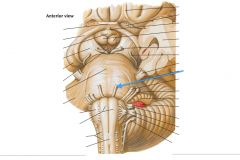
What cranial nerve is indicated by the orange arrow? |
The Trigeminal Nerve, CN V |
|
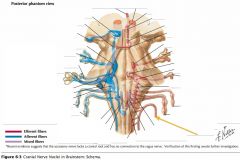
What cranial nerve is indicated by the orange arrow? |
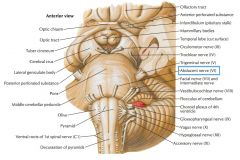
CN IV, the Abducens Nerve |
|
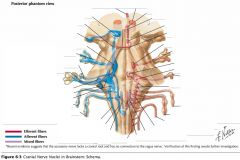
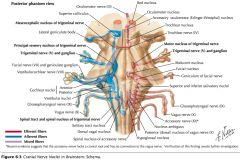
What is the function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX)? |
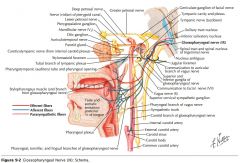
CN IX conveys general and taste sensation from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue, and innervates the pharyngeal muscles and the parotid gland. |
|
|
Where does CN IX exit the brainstem? |
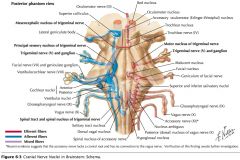
The Glossopharyngeal Nerve exits the Medulla Oblongata just caudal to its junction with the Pons and dorsal to the Inferior Olive. |
|
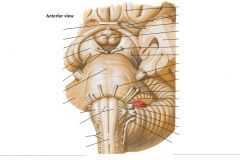
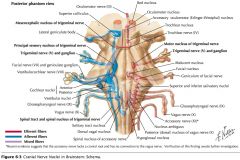
Which cranial nerves exit the Pons? |
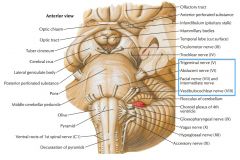
CNs V, VI, VII, VIII. |
|
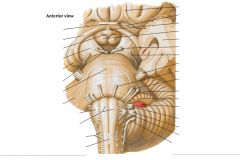
Which cranial nerves exit the Mesencephalon? |
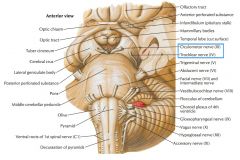
CNs III, IV |
|
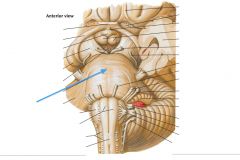
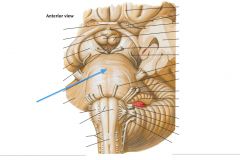
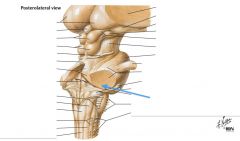
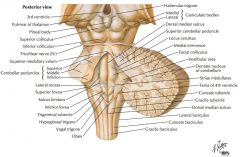
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Basilar Pons (or just pons) |
|
What does the anterior surface of the Pons consist of? |
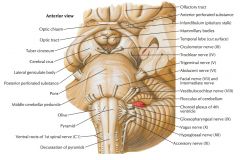
Transversely arranged fibers which arise as axons of neurons in the pontine nuclei. |
|
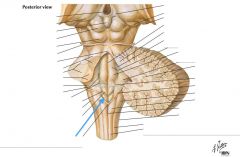
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Vagal Trigone |
|
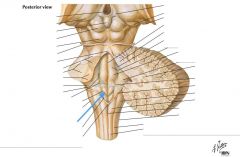
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Hypoglossal Trigone |
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Decussation of the Pyramids |
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Olive |
|
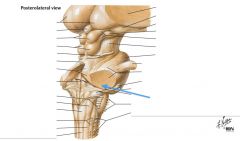
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
An Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle. |
|
What are the Inferior Cerebellar Peduncles composed of? |
They consist chiefly, but not exclusively, of pathways afferent to the cerebellum. |
|
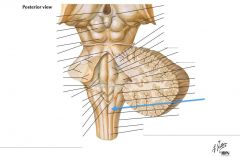
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
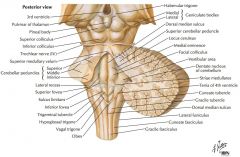
The Nucleus Gracilis (Gracile Tubercle) |
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
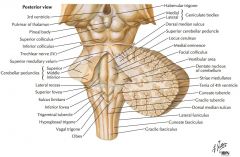
The Fasciculus Gracilis |
|
What information is carried by the fasciculi gracilis and cuneatus? |
They transfer information concerning proprioception, fine touch and vibration sense. |
|
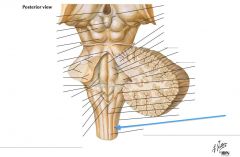
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Fasciculus Cuneatus |
|
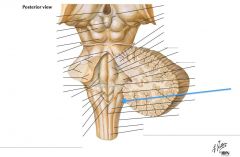
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Nucleus Cuneatus (Cuneate Tubercle) |
|
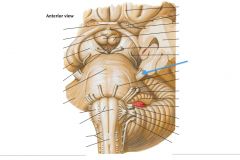
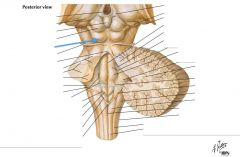
What nerve is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) |
|
Where does CN V arise? |
From the region where the fibers of the Basilar Pons become continuous with the Middle Cerebellar Peduncle. |
|
What does CN V supply? |
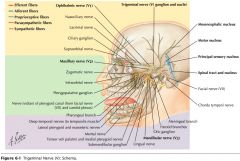
It supplies motor innervation to the muscles of mastication and sensory innervation to the structures of the face and mouth. |
|
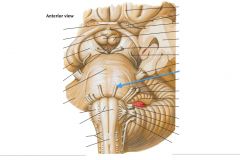
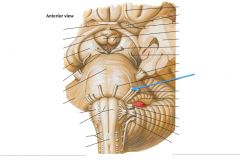
What nerve is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Abducens Nerve (CN VI) |
|
What nerve is indicated by the blue arrow? |
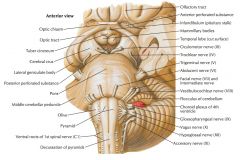
The Facial Nerve (CN VII) |
|
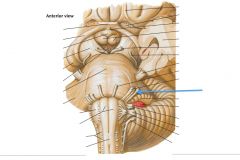
What nerve is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Vestibulo-cochlear Nerve (CN VIII) (also called the Auditory Nerve) |
|
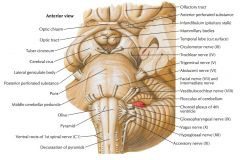
What nerve is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Oculomotor Nerve (CN III) |
|
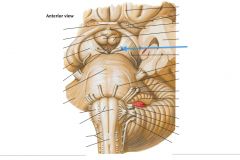
What nerve is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Trochlear Nerve (CN IV) |
|
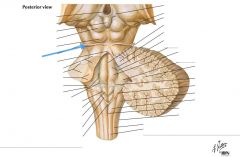
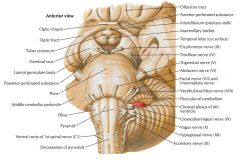
What nerve is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Trochlear Nerve (CN IV) |
|
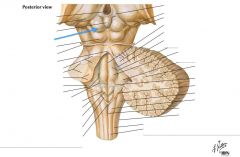
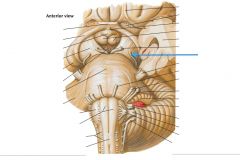
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
One of the Superior Colliculi of the Corpora Quadrigemina. |
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
One of the Inferior Colliculi. |
|
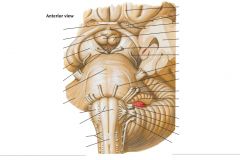
What is the function of the Abducens Nerve? |
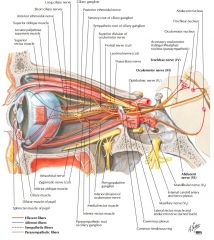
It provides motor innervation to the lateral rectus muscle of the eye. |
|
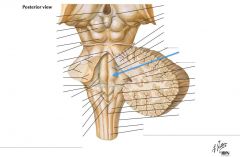
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
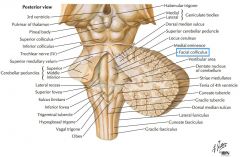
The Facial Colliculus. |
|
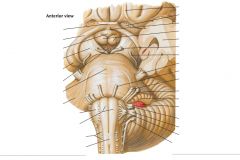
What does the Facial Nerve innervate? |
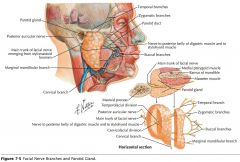
It provides taste to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue and motor innervation to the muscles of facial expression (among other things). |
|
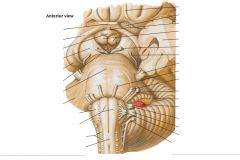
What is the function of the Vestibulocochlear Nerve? |
The Vestibular Root conveys information of balance and the position of the head. |
|
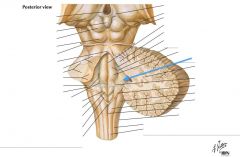
What area is indicated by the blue arrow? |
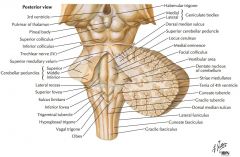
The Vestibular Area |
|
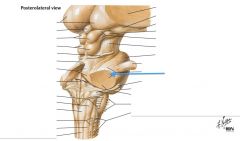
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Middle Cerebellar Peduncle |
|
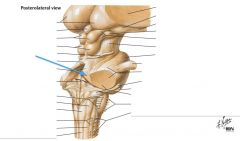
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow? |
The Superior Cerebellar Peduncle |
|
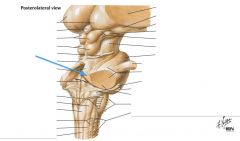
What type of information is carried on the Superior Cerebellar Peduncle? |
It largely carries efferent fibers from the Cerebellum. |

