![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
prosencephalon |
telencephalon (cerebral hemispheres, cortex, basal ganglia) and diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus) |
|
|
mesencephalon (midbrain) |
peduncles, tectum, tegmentum |
|
|
rhomebencephalon |
metencephalon (pons, cerebellum) and myelencephalon (medulla) |
|
|
development of the neural tube |
neural plate>neural groove>neural crest>neural tube |
|
|
spina bifida |
incomplete development of the laminae and/or spinous processes of the vertebrae with incomplete closure of surface |
|
|
3 vesicle stage |
prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon |
|
|
5 vesicle stage |
telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon, myelencephalon |
|

|
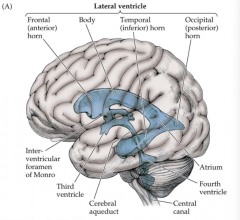
|
|
|
choroid plexus function and location |
secretes CSF in lateral ventricles fenestrated |
|
|
blood brain barrier |
have tight junctioned capillary endothelial cells |
|
|
brain parenchyma |
transport from intra to extracellular space |
|
|
plasma vs. CSF |
plasma = protein, Ca+, K+ CSF = Na+, Cl-, H+ |
|
|
hydrocephalus |
enlarged ventricles in brain |
|
|
circumventricular organs |
detect blood chemicals
pineal, neurohypophysis, area postrema, subfornical organ, median eminence |
|
|
area postrema |
chemotactic trigger zone monitors blood for poisons causes mouth to open when vomiting |
|
|
pericyte |
astrocyte (glial cell) wraps around blood vessels |
|
|
cistern |
where csf is pooled |
|
|
multi-drug resistance proteins
|
enzymes in bbb that sit on neural cells and remove unwanted particles |
|
|
dura mater layers |
periosteal layer (top) meningeal layer (bottom) |
|
|
cauda equina |
the bottom of the spine where there is no spinal cord (nerves only) |
|
|
vertebrae are different due to... |
gap patterns of expression hox genes |
|
|
mesoderm |
muscle |
|
|
ectoderm |
central nervous system |
|
|
lateral motor pathways |
lateral corticospinal rubrospinal |
|
|
medial motor pathways |
anterior corticospinal tract vestibulospinal tract tectospinal tract reticulospinal tract |
|
|
potential epidural space |
between periosteal dura and the skull |
|
|
lateral corticospinal tract |
cortex>corona radiata>internal capsule>peduncles>pyramid (deccusates)>lateral columns in scord |
|
|
rubrospinal tract |
red nuclei>ventral tegmental decussation>cervical ventral horn>arms
|
|
|
posterior column-medial lemniscal pathway |
-synapses in nucleus gracilis and cuneatus -crosses over via internal arcuate fibers -primary synapses in ventral posterior lateral nucleus of the thalamus (VPLN) -senses touch -ipsilateral until bstem |
|
|
splanchnic nerve |
paired visceral nerve can be para or symp |
|
|
white and grey ramus |
white = inside (first) grey = outside (second) |
|
|
anterolateral pathway |
goes through VPLN of thalamus then to cortex synapses in dorsal horn
crosses in anterior commissure of scord
senses pain |
|
|
periaqueductal grey |
takes pain away from receptors pain modulation |
|
|
which tract senses body pain? |
the spinothalamic tract (part of anterolateral pathway) |
|
|
peduncles |
inferior (input)--| -- cerebellar cortex middle (input)---| superior (output) - cerebral deep nuclei |
|
|
intermediate hemisphere of cerebellum (medial) |
motor to limbs
active during motion
|
|
|
lateral hemisphere of cerebellum |
planning of motion to limbs
active before motion
lateral corticospinal tract
|
|
|
vermis of cerebellum |
balance, vestibuloocular reflexes
MLF |
|
|
cortex to cerebellum pathway |
cortex>pons (synapses)>pontocerebellar fibers>middle cerebellar peduncle>cerebellar cortex (purkinje fiber) |
|
|
fibers in middle and inferior cerebellar peduncles |
= mossy fibers |
|
|
fibers from inferior olive |
= climbing fibers |
|
|
purkinje cells |
project to deep cerebellar nuclei > cerebellar outputs |

