![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
203 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Loss of pain + temp sensation in arms, shoulder
Occurs in what disease? |
Syringomyelia
|
|
|
L arm: loss of strength + sensation
What artery is responsible? |
R middle cerebral artery
|
|
|
L leg: loss of strength + sensation
|
R anterior cerebral artery
|
|
|
L leg: spastic paralysis, loss of proprioception
R leg: loss of pain + temp sensation |
hemisection of L spinal cord
|
|
|
Spastic paralysis of both legs
|
total transaction of spinal cord
|
|
|
Pupil dilation can mean 3 things...
|
3AM:
3rd CN palsy Anti-muscarinics (M3)(bethanechol, carbechol, pilocarpine) (muscarininics =>mioisis ="2 little i's" Myotonic pupil (absent/delayed rxn to light + convergence = Holmes-Ardie) |
|
|
Muscle atrophy + fasiculations in arms + legs
|
ALS
|
|
|
L arm, leg, body: paralysis, loss of pain + temp sensation
R lower face: loss of sensation |
Wallenberg syndrome – R lateral medulla (PICA)
|
|
|
Sensory loss at hands + feet
|
Peripheral neuropathy
|
|
|
Impotence + loss of sensation over perineum + buttocks
|
Cauda equina lesion
|
|
|
Knee jerk/Patellar reflex: what dermatome?
|
L4
|
|
|
Ankle jerk reflex: what dermatome?
|
S1
|
|
|
Biceps reflex_: what dermatome?
|
C6 (don says)
|
|
|
Skull: what dermatome?
|
C2
|
|
|
Thumb: what dermatome?
|
C6
|
|
|
Nipple: what dermatome?
|
T5
|
|
|
Belly button: what dermatome?
|
T10
|
|
|
Penis: what dermatome?
|
S3
|
|
|
Middle finger: what dermatome?
|
C7
|
|
|
Pinky: what dermatome?
|
C8
|
|
|
Big toe/medial foot: what dermatome?
|
L4
|
|
|
Lateral foot: what dermatome?
|
L5
|
|
|
Anus: what dermatome?
|
S5
|
|
|
Lesion @ _: post-rotational nystagmus
|
Vestibular
Nystagmus (defined by fast phase) against direction of prior rotation |
|
|
Lesion @ _: caloric nystagmus
|
Vestibular
Nystagmus (defined by fast phase) away from cold ear |
|
|
Lesion @ _: horizontal nystagmus
|
Vestibular
|
|
|
Lesion @ _: vertical nystagmus
|
Brainstem
|
|
|
Respiratory center
|
Cut:
above pons: normal respiration below pons: gasping below medulla: stops breathing Vagotomy: removes afferent input from pulmonary sensory R’s |
|
|
Lesion @ pretectal region of superior colliculus
|
Argyll Robertson Pupil
Due to syphilis Pupil accommodates, doesn’t react |
|
|
Calcified tumor that produces bitemporal hemianopsia
|
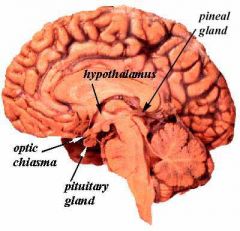
Pituitary tumor mashing optic chiasm
Calcification suggest craniopharyngioma |
|
|
Inability to form new memories
|
Bilateral lesion to hippocampus (temporal lobe)
|
|
|
Visual agnosia
Hyperphagia Hypersexuality Docility |
Kluver-Bucy syndrome
Bilateral lesion to amygdale (anterior temporal lobe) |
|
|
Receptive aphasia:
Fluent Unable to understand speech |
Wernicke’s aphasia (temporal lobe)
|
|
|
Lesion to this area:
Unilateral => slight hearing loss Bilateral => cortical deafness |
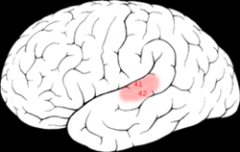
Primary auditory cortex (temporal lobe)
Auditory pathway: Come In My Baritone Cochlear nucleus Inferior colliculus Medial geniculate nucleus Brodmann's 41 = auditory cortex in temporal lobe |
|
|
Contralateral astereognosis + sensory neglect
|
Superior parietal lobule
Astereognosis = inability to recognize objects by touch |
|
|
Contralateral astereognosis + hypoesthesia
|
Sensory cortex (parietal lobe)
Astereognosis = inability to recognize objects by touch |
|
|
Loss of judgement + abstracting ability
|
Prefrontal cortex
|
|
|
Contralateral spastic paralysis
|
Motor/premotor cortex (frontal lobe)
|
|
|
Expressive aphasia:
Understands language Nonfluent aphasia = inability to produce speech. |
Broca’s aphasia
|
|
|
Necrotizing arteriris in caudate, putamen, + thalamus
Ass’d c/ _ infection |
Syndenham’s chorea
Ass’d c/ Strep infection |
|
|
Huntington’s chorea:
Degeneration of _-ergic + _-ergic neurons in _ Chromosome _ Inheritence |
Degeneration of cholinergic + GABAergic neurons in putamen
Chromosome 4 AD inheritence |
|
|
_ is damaged in infants c/ kernicterus
|
Globus pallidus
|
|
|
Wilson’s disease:
Decreased _ à Cu accumulation à _ degeneration Eyes have _ Chromosome _ Autosomal _ |
Decreased ceruloplasmin à Cu accumulation à hepatolenticular degeneration (lenticular nucleus = putamen + globus pallidus)
Eyes have Kayser-Fleisher rings Chromosome 13 Autosomal D |
|
|
Hemiballismus
where is the lesion? |
Unilateral wild, flailing movements of extremities
Subthalamic nucleus = lateral to hypothalamus |
|
|
Internuclear opthalmoplegia
|
Demyelination of medial longitudinal fasiculus
Multiple Sclerosis |
|
|
Eyes can’t open
Eyes deviated down + out |
Oculomotor nerve palsy
|
|
|
Eye’s are deviated down + in
|
Trochlear nerve palsy
|
|
|
Ptosis + meiosis of R eye, following fall on a popsicle stick
Where is the lesion? |
Injury to cervical sympathetic ganglion
|
|
|
Vertical diplopia
|
CN 4 palsy
|
|
|
R eye mydriasis, lid lag, deviation down + out
Pt c/o headache |
CN 3 palsy
Compression by aneurysm (mydriasis = excessive pupil dilation) |
|
|
L eye horizontal diplopia, worse on gaze to L
Recent hx of bacterial meningitis. |
CN 6 palsy => lateral rectus weakness
|
|
|
Bilateral lateral rectus weakness
|
Increased intracranial P
Papilledema usually present |
|
|
Infant c/ paralysis of upward gaze
|
Perinaud’s syn = hydrocephalus secondary to stenosis of Sylvian aquaduct
|
|
|
Oculomotor nerve paralysis after head injury
|
Uncal herniation c/ compression of CN3
|
|
|
Schwannoma in jugular foramen à 3 lesions
|
CN 9: loss of taste in posterior 1/3 of tongue
CN 10: palate weakness, loss of gag reflex, laryngeal paralysis CN11: Trapezius/Sternocleoidmastiod weakness |
|
|
_ syndrome = oculomotor nerve palsy, UMN signs.
Lesion @ _ |
Weber syndrome
Midline midbrain lesion |
|
|
Pituitary craniopharyngioma is derived from _
|
Rathke’s pouch
|
|
|
Inferior quadrantanopia
|
Defect in superior fibers of parietal lobe
|
|
|
C2 transection of fasiculata gracilus
|
Loss of lower extremity vibration, fine touch, proprioception
|
|
|
Superior olivary nucleus does...
Inferior olivary nucleus dies... |
Superior olivary nucleus => SOund localization
Inferior olivary nucleus => sIght localization in medulla |
|
|
Anterior cerebral artery
|
Medial surface of brain
Motor + Sensory to contralateral legs/feet |
|
|
Middle cerebral artery
|
Lateral cortex
Motor + Sensory to contralateral upper body Broca’s + Wernicke’s speech areas Anterior limb of internal capsule |
|
|
Lateral striate arteries (divisions of middle cerebral)
|
internal capsule, caudate, putamen, globus pallidus
“arteries of stroke” |
|
|
Posterior cerebral artery
|
Occipital cortex
Obstruction à contralateral homonymous hemianopsia |
|
|
Anterior communicating artery
|
Visual field deficits
#1 site for Circle of Willis aneurysms |
|
|
Posterior communicating artery
|
CN3 palsy
|
|
|
What artery occlusion?
loss of pain/temp ipsilateral face loss of pain/temp contralateral body loss of taste ipsilateral tongue ipsilateral Horner’s hoarseness, loss of pharyngeal reflex |
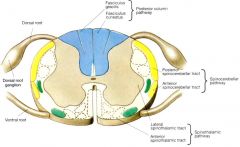
Wallenberg syndrome = lateral medulla infarction due to PICA occlusion
Spinal tract nucleus V => pain/temp ipsilateral face Nucleus solitarius => taste ipsilateral tongue Reticular formation => ipsilateral Horner’s Nucleus ambiguous => hoarseness, loss of pharyngeal reflex Spinothalamic tract => pain/temp contralateral body Posterior inferior cerebellar artery occlusion |
|
|
Pyramidal tract infarction leads to ...
|
contralateral spastic paralysis
|
|
|
Basilar artery
|
Medial upper + lower pons
|
|
|
Location of:
Spinal tract nucleus V Nucleus solitarius Reticular formation Nucleus ambiguous Spinothalamic tract |
Lateral medulla (PICA)
|
|
|
Location of:
hypoglossal nerve medial lemniscus pyramidal tract |
Medial medulla (anterior spinal artery)
|
|
|
_ message --> superior colliculus --> _geniculate body
_ message --> inferior colliculus --> _ geniculate body |
SLIM:
Superior colliculus --> Lateral geniculate Inferior colliculus --> Medial geniculate Music (sound) --> inferior colliculus --> Medial geniculate Light (sight) --> superior colliculus --> Lateral geniculate |
|
|
Medial lower pons infarction:
|
Basilar artery
Nucleus VII => ipsilateral face spastic parálisis Medial longitudinal fasiculus => ipsilateral eye can’t adduct on lateral gaze Nucleus VI => ipsilateral paralysis of lateral rectus Corticospinal tract => spasic paralysis on contralateral body Medial lemniscus => contralateral loss of position + vibration sense |
|
|
Lateral upper pons infarction:
|
Superior cerebellar artery
Motor nucleus V => ipsilateral loss of masseter fx Reticular formation => ipsilateral Horner’s Spinotalamic tract => contralateral loss of pain + sensation |
|
|
Bell's palsy
|
BELLS
abnl Blink reflex Earache Lacrimation (increased/decreased) Loss of taste Sudden onset |
|
|
Anterior circle stroke
|
General sensory + motor dysfx
Aphasia |
|
|
Posterior circle stroke
|
cranial nerve deficits: vertigo, visual changes
coma cerebellar defects: ataxia, intention tremor |
|
|
Anterior choroidal artery
|
Basal ganglia
Hypothalamus Posterior limb of internal capsule |
|
|
Cerebellar artery
|
Cerebellum (obstruction à ataxia)
Lateral brain stem (obstruction à brainstem syndromes) |
|
|
Occlusion of _ => Ipsilateral monocular blindness = “amaurosis fugax”
Contralateral hemiparesis Contralateral hemisensory loss Language disturbance |
Internal carotid
|
|
|
Occlusion of __:
Vertigo Diplopia Ataxia Facial numbness/ weakness Nausea |
Vertebrobasilar
|
|
|
Hemorrhage into __:
contralateral weakness, including face contralateral hemianopsia |
putamen
|
|
|
Hemorrhage into __:
contralateral hemiparesis sensory changes homonymous hemianopsia |
thalamus
|
|
|
Lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus:
Relay of _ |
Visual stimuli
|
|
|
Medial geniculate nucleus of thalamus:
Relay of _ |
Auditory stimuli
|
|
|
Mediodorsal nucleus of thalamus:
_ fx |
Limbic
|
|
|
Hemorrhage into __:
small reactive pupils quadriplegia coma |
pons
|
|
|
Hemorrhage into __:
unsteady gait clumsiness nausea/vomiting |
cerebellum
|
|
|
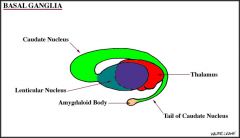
Basal ganglia
|
Caudate
Putamen Globus pallidus Subthalamic nucleus Substantia nigra |
|
|
Striatum
|
Caudate
Putamen +/- Globus pallidus? |
|
|
Neostriatum
|
Caudate
Putamen |
|
|
Paleostriatum
|
Globus pallidus
|
|
|
Lentiform nucleus
|
Putamen
Globus Pallidus |
|
|
Parkinson’s
|
Substania nigra to striatum: loss of dopaminergic input
Bradykinesia = difficulty starting/stopping mvmt Muscle rigidity Pill-rolling tremor |
|
|
Huntington’s
|
Caudate nucleus atrophy
Chorea = involuntary mvmts Personality changes, dementia |
|
|
Wilson’s:
lesion location symptoms |
Lentiform nucleus (putamen + globus pallidus): Cu accumulation
Tremor Spasticity Chorea Bizarre behavior |
|
|
Anterior thalamus
Part of _ system Input: _ Output: _ |
Part of limbic system
Input: mamillary bodies Output: cingula (cortex) |
|
|
Medial thalamus:
Projects to _ |
Projects to frontal cortex
|
|
|
Thalamus:
Major relay station of _ input |
Major relay station of sensory input
Basal ganglia => thalamus => cortex Injury can make pts insensitive to pain, other sensory stimuli |
|
|
_ of brainstem projects to thalamus, determines consciousness.
|
Reticular activating system of brainstem projects to thalamus, determines consciousness.
Pupillary light reflex = crude way to check brainstem fx |
|
|
Ion channel type: _
CNS inhibitory post-synaptic potentials |
Cl- channels
|
|
|
Ion channel type: _
Nicotinic ACh R @ motor endplate |
Cation channels
|
|
|
Ion channel type: _
Dark current of photoreceptors |
Cation channels
|
|
|
Ion channel type: _
Phase 0 of cardiomyocyte AP |
Na+ channels
|
|
|
Ion channel type: _
Phase 0 of cardiac pacemaker cells |
Ca2+ channels
|
|
|
Ion channel type: _
Cardiac plateau phase |
Ca2+ channel (Ca2+ in during cardiac plateau phase)
|
|
|
Where do the trigeminal branches exit the skull?
|
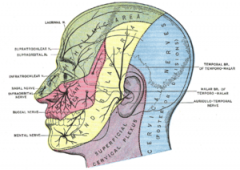
Standing Room Only
V1: Superior orbital fissure V2: foramen Rotundum V3: foramen Ovale |
|
|
specialized CNS macrophages
from hematopoietic precursors (not ectoderm). 15% of cells in CNS. in all regions of brain + spinal cord. mobile in brain. |
Microglia
|
|
|
CNS macroglia
provide myelin to up to 50 axons |
Oligodendrocytes
|
|
|
CNS macroglia
make CSF+ beat their cilia to circulate it line cavities of CNS, make up the walls of ventricles |
Ependymal cells
|
|
|
Brain tumor:
Children. 4th ventricle (infratentorial) à hydrocephalus. Poor prognosis. Perivascular rosettes, rod-shaped blepharoplasts (basal ciliary bodies) near nucleus, |
Ependymoma
|
|
|
CNS macroglia:
Bergmann glia in cerebellum that regulate synaptic plasticity Muller cells in retina that communicate c/ neurons Progenitor cells in developing NS that serve as scaffold for neurons to migrate |
Radial glia
|
|
|
PNS macroglia:
neurolemmocytes provide myelin to one neuron phagocytosis of cellular debris |
Schwann cells
|
|
|
#3 primary brain tumor
Bilateral in neurofibromatosis 2 |
Schwannoma
|
|
|
PNS macroglia: line exterior surface of PNS neurons to regulate external chemical environ.
|
Satellite cells
|
|
|
Brain tumor: in cerebral hemispheres (supratentorial)
can cross corpus callosum => “Butterfly glioma” GFAP = stain “Pseudopalisading” cells border areas of necrosis + hemorrhage |
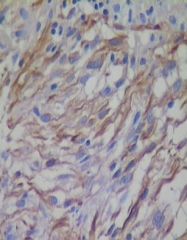
GBM
|
|
|
Decorticate posture:
Injury to _ Legs _ Arms _ |
Cortex injury
Legs extended Arms flexed |
|
|
Decerebrate posture:
Injury to _ Legs _ Arms _ |
Brainstem injury
Legs + arms extended |
|
|
Spinothalamic tract
|
Pain
Temperature |
|
|
Myopia:
Focal point too _ (or eyeball too _) Correct c/ _ lens |

Near-sighted:
Focal point too short (or eyeball too long) Correct c/ concave or (-) lens |
|
|
Hypermetropia:
Focal point too _ (or eyeball too _) Correct c/ _ lens |
Far-sighted:
Focal point too far (or eyeball too short) Correct c/ convex or (+) lens |
|
|
_ = lens has lost elasticity c/ age
Can't shorten focal L Correct c/ _ lens |
Presbyopia
Correct c/ convex or (+) lens |
|
|
Intention tremor in ipsilateral extremities
lesion? What other neuro changes whould one expect? |
cerebellar hemisphere
dysmetria = can't stop mvmts @ desired point adiadochokinesia = can't do smooth rapidly alternating mvmts decomposition of mvmts = can't coordinate mvmts that require several joints @ once |
|
|
Resting tremor, chorea, athetosis, dystonia
lesion? |
basal ganglia
exact lesion depends on location |
|
|
Truncal ataxia, dysarthria
lesion? |
cerebellar vermis
|
|
|
frontal eye field lesion causes…
|
deviation of eyes ipsilateral to lesion
|
|
|
Ventral anterior and ventral lateral nuclei of thalamus ("motor nucleus) receive input from 2 places…
|
basal ganglia and cerebellum
|
|
|
2 areas that regulate circadian rhythmns
|
pineal gland
suprachiasmatic nucleus of hypothalamus |
|
|
_ is involved in pupillary light reflex, some types of eye movement
|
pretectal nucleus
|
|
|
_ is a magnocellular hypothalamic nucleus involved c/ oxytocin and vasopressin secretion
|
supraoptic nucleus
Every (or nearly every) neuron in the nucleus has one long axon that projects to the posterior pituitary gland, where it gives rise to about 10,000 neurosecretory nerve terminals |
|
|
Korsakoff's syndrome:
hemorrhagic lesions in what 3 places? |
Mamillary bodies
Dorsomedial nucleus of thalamus Periventricular regions of 3rd, 4th ventricles |
|
|
Caudate nucleus is a component of the _, which does _
|
Component of the neostriatum
Initiation of voluntary mvmts |
|
|
Locus ceruleus has _-secreting neurons that project to several areas of brain
involved in _, _ |
Locus ceruleus has noradrenergic neurons that project to many brain areas
Attention, arousal |
|
|
2 muscles that control pupil diameter
|
1. Radial dilator: alpha adrenergic stim => mydriasis (contraction)
2. Pupillary sphincter: muscarinic stim => constriction |
|
|
Pain + temperature information is carried in _ tract.
cell bodies reside in _ Fibers enter _ side of spinal cord, synapse in _ Secondary neurons cross in _, ascend as the _ tract in _ region of cord, ascend to brainstem as the _, and synapse in _ of thalamus |
Spinothalamic tract.
Pain + temp sensation from contralateral body Fibers enter dorsal spinal cord, synapse in dorsal horn Cell bodies reside in dorsal root ganglia Secondary neurons cross in anterior white commissure, ascens as the spinothalamic tract in ventrolateral cord, ascend to brainstem as the spinal lemniscus, and synapse in VPL nucleus of thalamus |
|
|
lesion to _ lemniscus would cause L-sided loss of proprioception and discriminative touch
|
medial lemniscus
|
|
|
Pt can't adduct R eye during conjugate gaze
Able to adduct R eye during visual convergence Lesion is in_ |
Internuclear opthalmoplegia = lesion in MLF (medial longitudinal fasiculus)
MLF coordinates the 3 brainstem nuclei that supply the extraocular muscles (oculomotor, trochlear, abducens nuclei) |
|
|
Locus ceruleus is implicated in drug withdrawal.
Has _-secreting neurons that project to several areas of brain |
Noraderenergic cell bodies
|
|
|
Nerve fibers:
Efferent: skel muscle Afferent: from muscle spindle _ diameter _ velocity |
Aα nerve fibers
Large diameter High velocity Motor unit = all skeletal muscle fibers innervated by one α motoneuron |
|
|
Nerve fibers:
Efferent: to muscle spindle _ diameter _ velocity |
Aγ nerve fibres
Medium diameter Medium velocity |
|
|
Nerve fibers:
Afferent: touch, fast sharp pain _ diameter _ velocity |
Aβ, Aδ nerve fibers
Medium diameter Medium velocity |
|
|
Nerve fibers:
Afferent: slow dull pain Efferent: Autonomic nerves _ diameter _ velocity |
C nerve fibres
B nerve fibers (autonomic only) Small diameter Low velocity |
|
|
Muscle spindle
_ efferent measures _ _ afferent activates _ when stretched |
γ efferent measures muscle length
1A afferent activates α motoneuron when stretched |
|
|
Golgi tendon organ
_ afferent measures _ Inhibits _ |
1B afferent measures muscle tension
Inhibits α motorneuron |
|
|
Knee jerk reflex:
_ fibers run parallel to skeletal muscle fibers Stretching --> firing of _ afferent --> excites _ = monosynaptic reflex _ inhibits the _ of the antagonistic muscle |
Intrafusal/muscle spindle fibers run parallel to skeletal muscle fibers
Stretching --> firing of 1A afferent --> excites α motoneuron = monosynaptic reflex Interneuron inhibits the α motoneuron of the antagonistic muscle |
|
|
Sensory fibers:
Pressure, slow-adapting In _ of spinal cord |
Merkel disks
Dorsal Column |
|
|
Sensory fibers:
Pressure, fast-adapting Hair follicle sensors In _ of spinal cord |
Meissner's corpuscles
Dorsal Column |
|
|
Sensory fibers:
Vibration _-adapting In _ of spinal cord |
Pacinian corpuscles
|
|
|
Increased muscle tone:
Activation of _ fibers _ motor neuron lesions Temperature _ |
Activation of γ fibers
UMN lesions (hemiplegia) Parkinson's Cold Anxiety |
|
|
Decreased muscle tone:
_ motor neuron lesion Temperature _ |
LMN lesion
Spinal shock = early phase of hemiplegia Warmth |
|
|
4 mechanisms to decrease BP via neurotransmitter signaling
|
1. Nicotinic ganglionic R block
2. Βeta R block 3. Alpha-1 R block 4. Alpha-2 R block |
|
|
Norepinephrine: effect on BP, HR
|
Alpha R stimulation (and Βeta 1) --> vasoconstriction increases systolic + diastolic BP, baroreceptor reflex decreases HR
|
|
|
Epinephrine: effect on BP, HR
|
Alpha and Βeta stimulation --> Βeta predominates --> vasodilation decreases diastolic BP, increase in HR raises systolic BP
|
|
|
Signaling pathway: Nicotinic receptors
|
Adrenal medulla, Sympathetic + Parasympathetic ganglia, NM junction
Ligand-gated non-selective cation channel |
|
|
Signaling pathway:
Βeta 1 adrenergic Actions of isoproterenol, epi, NE |
Gs --> adenylyl cyclase --> cAMP --> protein kinase A
Postsynaptic sympathetic cardiac: chronotropy, inotropy Isoproterenol > Epi = NE |
|
|
Signaling pathway:
Βeta 2 adrenergic actions of isoproterenol, epi, NE |
Gs --> adenylyl cyclase --> cAMP --> protein kinase A
Postsynaptic sympathetic (all others but cardiac): vasodilation, bronchodilation Isoproterenol > Epi >> NE |
|
|
Signaling pathway:
H2 receptors |
Gs --> adenylyl cyclase --> cAMP --> protein kinase A
|
|
|
Signaling pathway:
ACTH |
Gs --> adenylyl cyclase --> cAMP --> protein kinase A
|
|
|
Signaling pathway:
alpha 2 adrenergic receptors |
Gi --> inhibits adenylyl cyclase --> decreases cAMP
Presynaptic sympathetic: decreases catecholamines CNS: decreases sympathetic tone Isoproterenol ≥ Epi >>NE |
|
|
Signaling pathway:
M2, M4 receptors |
Gi --> inhibits adenylyl cyclase --> decreases cAMP
Post-synaptic parasympathetic, Sweat gland sympathetic |
|
|
Signaling pathway:
NO |
NO --> guanylyl cyclase --> cGMP --> protein kinase G
|
|
|
Signaling pathway:
Atrial Natiuretic Peptide |
NO --> guanylyl cyclase --> cGMP --> protein kinase G
increases GFR, Na+ secretion |
|
|
Signaling pathway:
Sildenafil |
Inhibits type V cGMP phosphodiesterase
NO --> guanylyl cyclase --> cGMP --> protein kinase G |
|
|
Signaling pathway:
alpha 1 adrenergic receptors |
Gq --> phospholipase c --> IP3, DAG --> Protein Kinase C
Post-synaptic sympathetic Excitatory Inhibitory in GI Isoproterenol ≥ Epi >>NE |
|
|
Signaling pathway:
H1 receptors |
Gq --> phospholipase c --> IP3, DAG --> Protein Kinase C
|
|
|
Signaling pathway:
M1, M3 receptors |
Post-synaptic parasympathetic, Sweat gland sympathetic
Gq --> phospholipase c --> IP3, DAG --> Protein Kinase C |
|
|
Signaling pathway:
Tachykinins |
Gq --> phospholipase c --> IP3, DAG --> Protein Kinase C
|
|
|
Signaling pathway:
Endothelin |
Gq --> phospholipase c --> IP3, DAG --> Protein Kinase C
vasoconstrictor produced by endothelium - opposite effect to prostacyclin on vessels |
|
|
Signaling pathway:
Insulin |
Tyrosine kinase:
1. Phosphorylates proteins 2. Activates ras --> raf --> MAP kinase cascade to modulate gene expression |
|
|
Signaling pathway:
Growth factors |
Tyrosine kinase:
1. Phosphorylates proteins 2. Activates ras --> raf --> MAP kinase cascade to modulate gene expression |
|
|
Signaling pathway:
Steroid hormones |
Gene expression
|
|
|
Signaling pathway:
Thyroid hormones |
Gene expression
|
|
|
Signaling pathway:
Retinoic acid |
Gene expression
|
|
|
Dense collection of neuromelanin-containing cells - blue/black in unstained tissue
In rostral pons, near lateral edhe of the floor of 4th ventricle Most of NORADRENERGIC innervation to forbrain, including cortex |
Locus ceruleus
Attention, arousal |
|
|
Part of substantia inniminata = a major collection of forebrain CHOLINERGIC neurons
Innervate: neocortex, hippocampus, amygdala (c/ neurons of septal nuclei) What structure? Affected in what disease? |
Meynert (Basal nucleus of Meynert)
Degenerates in Alzheimers |
|
|
Part of basal ganglia, immediately lateral to lateral venticules
GABA-ERGIC projection neurons innervate globus pallidus, substantia nigra pars reticulata. Degnerate in _ CHOLINERGIC interneurons provide most ACETYLCHOLINE to striatum = caudate + putamen |
Caudate nucleus
GABAergic neurons degenerate in Huntington's => enlarged lateral ventricles on MRI Extrapyramidal sx affected by balance b/w striatal ACh and dopamine (Parkinson's dz, parkinsonianism due to anti-psychotics) |
|
|
Located @ midline of brainstem
Serotinergic nerve bodies ennervate virtually every part of CNS |
Raphe nuclei = medial portion of reticular formation
Reticular formation important for hypothalamus/autonomic |
|
|
Located @ midbrain
_ component: nigrostriatal neurons provide striatal dopamine; degenerates in _ or c/ toxicity from _ _component: mostly make _, innervate _ |
Substantia nigra = pars
Pars compacta + pars reticulata Compacta: nigrostrial neurons = source of stiatal dopamine Degenerates in Parkinsons or due to MPTP toxicity Reticulata = mostly GABAergic neurons that innervate the thalamus |
|
|
Located @ midbrain
_ + _ neurons provide dopamine to limbic + cortical areas. Overactivity possibly connected to disease _ |
Ventral tegmentum
Mesolimbic, mesocortical neurons = source of dopamine to limbic + cortical areas Possible etiology of schizophrenia |
|
|
Rigidity (hypertonia that is uniform throughout passive mvmt) is caused by …
|
Basal ganglia lesion, esp. nigrostiatal dopaminergic pathway
|
|
|
Ataxia is caused by 2 things..
|
Cerebellym lesion or dentatirubrrothalamic tract
|
|
|
Interhemispheric fissure of precentral gyrus
|
Precentral gyrus = primary motor cortex. ^Control of legs in interhemispheric fissure
|
|
|
L homonymous hemianopsia can be caused by 3 lesions
|
1. R optic tract
2. R optic radiations 3. R visual cortex |
|
|
Orbicularis oculi has job of _
Innervated by _ |
Forceful eye closure
Innervated by zygomatic branch of CN7 |
|
|
Bell's palsy relates to the path of facial nerve through _ = the longest interosseous course of the nerve
Swells during HSV-1 infection => impingement |
Labrythine canal
|
|
|
What's the difference b/w upper + lower divisions of facial nerve?
|
Upper (temporal, zygomatic, buccal): from both sides of brain
Lower (buccal, marginal mandibular, cervical): unilateral lesion => unilateral paralysis |
|
|
Uvula deviates in _ direction of lesion to nerve _
|
Vagus nerve lesion: uvula deviates AWAY FROM AFFECTED SIDE
|
|
|
Gag reflex: sensory + motor components
|
Sensory: CN9
Motor: CN10 |
|
|
Blink reflex: sensory + motor components
|
Sensory: CN5
Motor: CN7 |
|
|
Tongue deviated in _ direction of lesion to nerve _
|
CN12 lesion; ongue deviates TOWARDS lesion
|
|
|
Palatoglossus = only tongue muscle innervated by _. All others by CN12
|
CN10
|
|
|
Anterior 2/3 of tongue: taste supplied by nerve _, general sensation by nerve _
|
Taste: CN7 chorda tympani
Gen sensation: lingual nerve of V3 |
|
|
Posterior 2/3 of tongue: taste supplied by nerve _, general sensation by nerve _
|
Taste: CN9
Gen sensation: CN7 |
|
|
Contents of superior orbital fissure:
|
Everything but optic nerve that innervates orbital structures:
CN3, CN4, CN6, V1 |
|
|
_ passes through the internal auditory meatus
|
CN7
|
|
|
Mandibular nerve exits the skull via _
|
foramen ovale
|
|
|
Maxillary nerve exits the skull via _
|
foramen rotundum
|
|
|
Middle meningeal artery passes though the skull @ _
|
foramen spinosum
|
|
|
opthalmic artery exits the skull @ the _
|
optic canal
|
|
|
optic nerve + opthalmic artery exit the skull @ the _
|
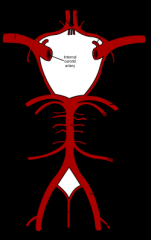
optic canal
(in sphenoid) |
|
|
_ artery crosses the floor of the anatomical snuffbox,
passes through 1st web space then forms the deep palmar arch |
radial artery
|
|
|
_ nerve is responsible for most of elevation of the pharynx
|
Vagus
|
|
|
Taste fibers from anterior 2/3 of tongue are carried via _ to _
|
Chorda tympani to CN7
|

