![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the area of the eye that has high visual acuity, and what is responsible for this? |
Fovea: it has a high concentration of cones. |
|
|
What are saccades of eye movement? |
Rapid eye movement ( >700 deg / sec) Precalculated No feedback used |
|
|
What are intorsion and extortion of the eye?
|
The movement of the top of the eye: Intorsion: top goes toward nose Extortion: top goes away from the nose |
|
|
What movement does the left eye do during a left head tilt? |
Intorsion |
|
|
What is strabismus? |
misalignment of the eye |
|
|
Define the following: Esotropia Exotropia Hypertropia Hypotropia Diplopia |
Medial deviation Lateral deviation Upward deviation Downward deviation Double vision |
|
|
How is the direction of a nystagmus movement defined? |
By the direction of the fast movement |
|
|
What innervates the lateral rectus? |
CN VI (Adducens) |
|
|
What is innervated by CN III? |
Medial rectus Superior rectus Inferior rectus Inferior oblique |
|
|
What are 4 intrinsic causes of CN VI lesions? |
ICA aneurysm Incr. ICP AICA an Stroke of ventral pons |
|
|
Where is the lesion: Right eye abducted during forward gaze, No movement of right eye during left gaze, Both eyes appropriate left gaze Both eyes appropriate for convergence |
Right abducens nerve lesion |
|
|
Where is the lesion: Both eyes deviate left on forward gaze Both eyes midpoint on right gaze Both eyes appropriate for left gaze Convergence appropriate |
Right abducens nucleus lesion |
|
|
Where is the lesion: Left eye outward on forward gaze Left eye no movement of right gaze, nystagmus in right eye Appropriate on left gaze both appropriate on convergence |
Left MLF lesion |
|
|
What innervates the superior oblique muscle? |
CN IV (Trochlear) |
|
|
How will a trochlear nerve lesion present? |
Ipsilateral elevation, adduction, and extorsion Problems with reading and stairs |
|
|
Through what nucleus do the eyes' parasympathetics run? |
Edinger-Westphal Nucleus |
|
|
How will a CN III lesion present? |
ipsilateral ptosis, down and out, blown pupil, consensual of contralateral eye, but not direct pupillary light reflex, no ipsilateral consensual reflex |
|
|
Patient with only a conjugate gaze defect to the right? |
Right conjugate gaze center lesion |
|
|
What is the function of the cerebellum in eye sight? |
Cancel the vestibule-ocular reflex |
|
|
What is the function of the superior colliculus? |
Relay from frontal eye field and posterior parietal area for reflexive saccades. |
|
|
How will a Frontal eye field lesion present? |
preferential gaze toward side of lesion |
|
|
What eye transducer is responsible for low light vision, what is there color modality and their distribution in the retina? |
Rods, Black and white, peripherally |
|
|
Why is there a blind spot in front of the optic disk?
|
Absence of rods and cones. |
|
|
What are two of the reasons rods have high sensitivity to light? |
More visual pigment and convergent wiring. |
|
|
Are rods or cones used in high light and why? |
Cones: The rods are hyperpolarized due to cGMP gates opening and Na+ current increase |
|
|
How is an image sharpened? |
Cell inhibits neighboring by hyper polarization ones via horizontal cells. |
|
|
What is a protanope? |
Person lacking red cones |
|
|
What is a deuteranope? |
Person lacking green cones. |
|
|
What causes bending of light? |
one side of the beam hits another medium first and slows down before the other side |
|
|
What type of sense is said to be converging and what will be the resultant focal distance? |
Convex, get closer to the lens the more round the lens gets. |
|
|
What is another word for a divergent lens and the result of the focal point of light? |
Concave, will never converge, the focal point will be in front of the lens. |
|
|
What type of lens will treat astygmatism? |
Cylindical |
|
|
What type of optic power does a converging lens have? A divergent lens? |
+, - |
|
|
What part of the eye allows for accommodation? |
The lens: It will get fatter by contraction of the ciliary muscles. |
|
|
Is accommodation parasympathetic or sympathetic? |
Parasympathetic |
|
|
Why do we need reading glasses as we get older? |
Ciliary muscle weaken / lens stiffens --> loss of accommodation --> unable to focus close objects |
|
|
What does presbyopia mean? |
Loss of accommodation due to aging. |
|
|
How is presbyopia corrected? |
+ (converging) lens |
|
|
Why do we get cross eyed as an object moves closer? |
To keep the image on the fovea |
|
|
Why is it beneficial to move the eye around in order to see in low light? |
We tend to point the fovea on the area of concentration. This results in the image hitting cones, which have less sensitivity. By moving the eye we allow for the image to hit cones (more sensitive). |
|
|
How do the pupils react during accommodation? |
Constriction (parasympathetic) |
|
|
What is myopia? |
Near sightedness |
|
|
What is the most common cause of myopia? |
Eye ball too long, image doesn't hit the retina when at a distance |
|
|
What type of lens is needed for myopia?
|
- (divergent) lens, lengthens the focal point. |
|
|
What is hyperopia? |
Farsightedness, can't focus on close objects |
|
|
What is the most common cause of hyperopia? |
Eye ball too short |
|
|
How is hyperopia corrected? |
+ (convergent) lens shortens the focal point on an image |
|
|
|
|
|
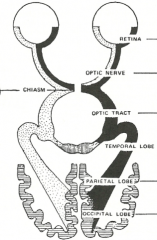
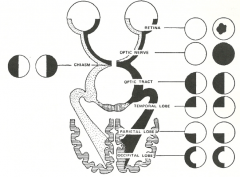
What is the function of the parietal cortex (Dorsal / M-path) in vision? |
Motion detection, depth perception, visual attention |
|
|
What is the function of the temporal lobe (Ventral / P-path) in vision? |
Recognition, memory, color processing |
|
|
What is simultanagnosia? |
Not able to identify the whole picture, only one part at a time |
|
|
What is akinetopsia? |
Look like a strobe light - skipping motions |
|
|
What is prosopagnosia? |
Not recognizing faces |
|
|
What is achromatopsia? |
Loss of color vision |

