![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
define meningitis
encephalitis: |
meningitis:inflammation of the pia-arachnoid membranes
encephalitis: inflammation of the brain |
|
|
pt comes in with a fever, nuchal rigidity, some altered mental status, but says I am having the most severe headache of my life...
* |
Acute Meningitis
|
|
|
please list the 3 most common causes of bacterial meningitis today
affects who mostly? * |
most: strep pneumoniae-adults
N. meningitidis- young adults (college) H. influenzae- elderly and infants (who don't have Hib vaccine) NOTE: you will still likely see s.pneumoniae as the leading cause in elderly, but if you see h. influenzae it will be in an old fart |
|
|
please list the shape, G-/+, catalase -/+, and if Streptococci is able to ferment sugar
|
Gram positive cocci in chains
Catalase negative Ferment sugars → lactic acid → low pH Need enrichment with blood to support growth |
|
|
S. agalactiae is also known as group B strep...what type of Hemolysis does it under go?
what is strep pyogenes known as? what type of hemolysis does it undergo? what type of hemolysis does s. pneumoniae undergo? * |
s. agalactiea: beta hemolysis
s. pyogenes (group A strep): beta hemolysis s. pnuemoniae: alpha |
|
|
what are 3 lab tests that can show s. pneumoniae?
|
Optochin S
Bile solubility pos Quelling test pos |
|
|
this can cause septicemia, meningitis, and pneumonia and Infect neonates during vaginal delivery. What is it? What is the capsule like?
|
Group B Streptococcus (Streptococus agalactiae)
Sialic acid capsule similar to E. coli K1 |
|
|
Gram positive, lancet shaped, diplococci with a polysaccharide capsule
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae
also has pneumolysin and C substance (choline and teichoic acid) C-substance + C-reactive protein → activates |
|
|
Gram negative diplococci, coffee bean shape
Oxidase positive - produce cytrochrome oxidase (aerobic) Describes? |
Neisseria
|
|
|
most common serotypes of neisseria meningitidis in the US
|
B and C
others are: A, Y, W135 |
|
|
major virulence factors of N. meningitidis ?
|
Pili
Capsular polysaccharide (remember, gonorrhea does not) Lipooligosaccharide (LOS) Outer membrane proteins IgA protease |
|
|
Small, Gram-negative, pleomorphic, fastidious rods
|
Haemophilus influenzae
|
|
|
H. influenza requires what to grow in culture?
|
X factor - hemin
V factor - nicotinamide adenine dinucleatide (NAD) Provided by chocolate agar (red blood cells lysed by heating) |
|
|
if a child has immigrated and looks like they have meningitis, what was the likely cause?
|
Haemophilus influenza
didnt get the Hib vaccine |
|
|
Intracellular parasite of macrophages causes meningitis in newborns and elderly
Associated with food poisoning with symptoms of gastroenteritis bug? Gram +/-? Rod/Cocci? |
Listeria monocytogenes
short gram + rod |
|
|
primary virulence of Listeria monocytogenes?
|
Virulence due to listeriolysin O (pore forming cytolysin): allows organism to escape phagocytic vacuole
|
|
|
In pregnant woman this presents as mild genital infection with flu-like symptoms..bug?
|
Listeria monocytogenes
|
|
|
a meat company has to recall a number of cold-cuts because they are causing food-borne illness...cause?
|
Listeria monocytogenes
|
|
|
Distinctive tumbling motility when grown at 25oC
|
Listeria monocytogenes
|
|
|
which meningitis agent is most likely to cause rash?
|
Neisseria meningitidis
can lead to septisemia and gangrene |
|
|
pathogenesis of meningitis?
|
Colonization of the oropharynx
Organism enters blood stream through the mucous membranes Resist killing primarily by capsule formation and other evasive mechanisms and multiply Penetrates blood-brain barrier at the choroid plexus Inflammation on blood side → spillage into CNS Correlated with microbial load in blood (>105 org/ml) |
|
|
how can meningitis survive in the CNS?
|
Reduced host defenses in CSF compared to blood → low levels of complement and antibodies → reduced phagocytosis
Bacteria survive and grow in the cerebral spinal fluid |
|
|
why is pnuemococcus the leading killer of bugs that cause meningitis?
|
in meningitis the CSF becomes thick and causes pressure
pneumococcus is the best at doing this |
|
|
if you suspect meningitis, what should you do first
brain image initiate antimicrobial therapy |
initiate antimicrobial therapy
|
|
|
in bacterial meningitis, what will you see in your CSF obtained from lumbar puncture?
Cell type Glucose Protein Stained Smear Result of Culture |
>50% PMNs
reduced glucose (bacteria eating it up) >100 protein (permeation of BBB, allowing more albumin into spinal fluid) Stained smear usually positive result of culture is usually positive |
|
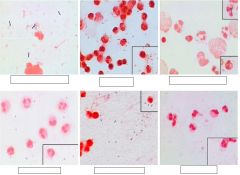
|
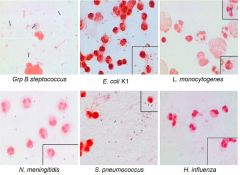
|
|
|
Virulence Factor of Common Meningitis Causing Bacteria?
|
Polysaccharide capsule
(Sialic acid found in N. meningitidis group b, E. coli K1 and Group B Strep) |
|
|
Emperic DOC for Meningitis?
|
vancomycin + cefotaxime or ceftriaxone + dexamethazone
|
|
|
tx for S. pneumoniae (Pen sens)
|
Penicillin G
|
|
|
tx for S. pneumoniae (Pen resist)
|
Vancomycin or linezolid
|
|
|
tx for N. meningitidis
|
Penicillin G
|
|
|
tx for H. influenza betalactamase pos
|
Cefotaxime or ceftazidime
|
|
|
tx for Grp B Streptococcus
|
Penicillin G
|
|
|
Chemoprophylaxis for N. meningitidis?
(intimate contacts) |
DOC: rifampin
|
|
|
Immune response of polysaccharide vaccine versus conjugate vaccine
what is the difference? *** |
polysaccharide: B cell initiated leads to IgM formation (lack memory, T cells, can't do boosting)
conjugate: T and B cells formed, get memory and IgG |
|
|
Due to a rupture of a superficial infective focus in subarachnoid space
Ocular palsies in ~½ of cases Lab Diagnosis: Lymphocytic pleocytosis in CSF Usually 100-200 WBC’s CSF cultures (need 10-20 ml) Conversion on skin test (most often not helpful) |
Tuberculosis Meningitis
REMEMBER: HIV PTs LIKELY TO HAVE TB |
|
|
bug for lyme dz?
|
Borrelia burgdorferi
|
|
|
test that has to be done to confirm treponema pallidum (syphilis) meninigitis?
|
VDRL on CSF,
if pos confirm with FTA: include with aseptic meningitis workup |
|
|
pt has multiple erythema migrans, presents as viral meningitis, have headache > 5 days, and cranial neuritis (cranial nerve palsy or papilledema). What is going on and what is the tx?
|
Lyme Meningitis (Borrelia burgdorferi)
DOC for Lyme meningitis: ceftriaxone |
|
|
what normally causes brain abscesses?
how does this occur? should you draw CSF to diagnose? How will it present? |
anerobic bacteria (staph a)
chronic infections that have spread to the brain (mastoids, sinuses, that spread) lumbar puncture CONTRAINDICATED A focal infection of the brain parenchyma that causes specific focal deficits |

