![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
113 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
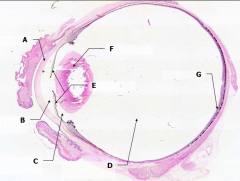
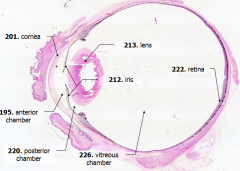
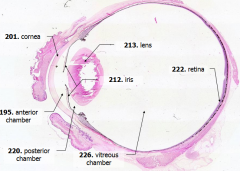
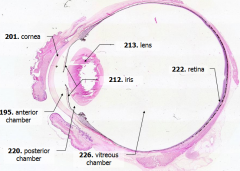
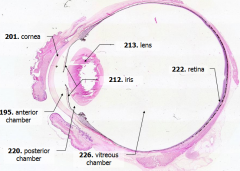
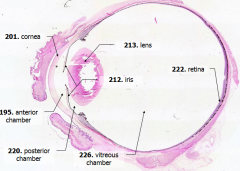
What is Structure A? |
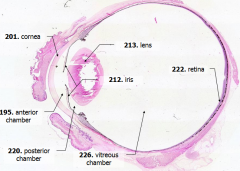
Cornea - bulging from front of eye
|
|
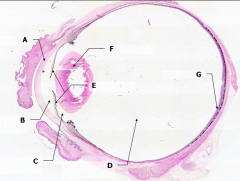
What is Structure B?
|
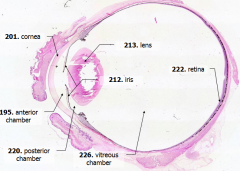
Anterior Chamber - between cornea and iris
|
|
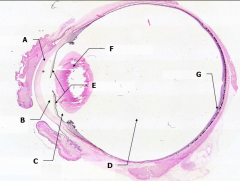
What is Structure C?
|
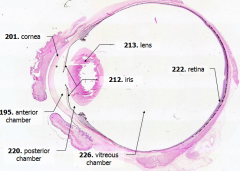
Posterior Chamber - between iris and lens
|
|
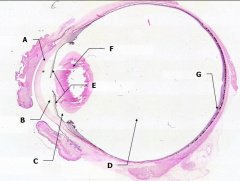
What is Structure D?
|
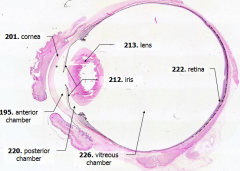
Vitreous Chamber - posterior to the lens
|
|
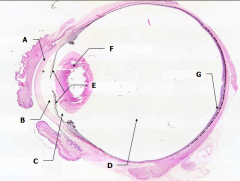
What is Structure E?
|
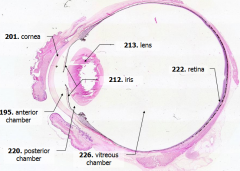
Iris - pigmented material anterior to the lens
|
|
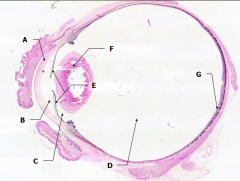
What is Structure F?
|
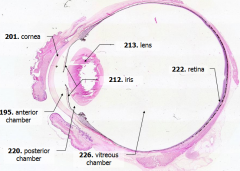
Lens - pink-stained disk
|
|
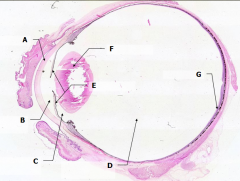
What is Structure G?
|
Retina - purple-stained layer at posterior of the eye
|
|
|
What are the three tunics which enclose the contents of the eye?
|
- Corneoscleral layer - fibrous layer composed of cornea and sclera
- Uveal layer - vascular and pigmented layer composed of iris, ciliary body, and choroid - Neural layer - retina |
|
|
What are the components of the corneoscleral layer?
|
Cornea and Sclera
|
|
|
What are the components of the uveal layer?
|
Iris
Ciliary body Choroid |
|
|
What are the components of the neural layer?
|
Retina
|
|
|
What is the major refractive structure of the eye?
|
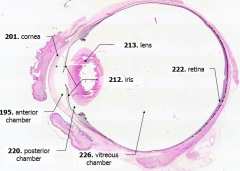
Cornea
|
|
|
How much of the corneoscleral layer is from the cornea?
|
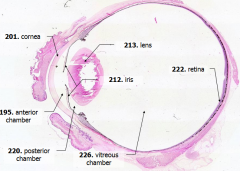
Anterior 1/6
|
|
|
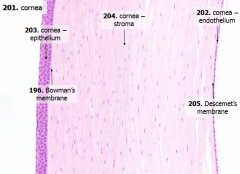
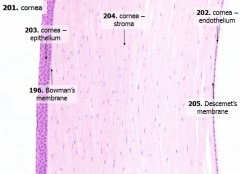
What are the 5 layers of the cornea?
|
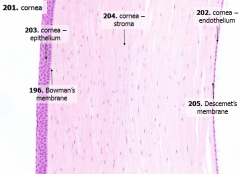
- Corneal epithelium
- Bowman's membrane - Stroma (substantia propria) - Descemet's membrane - Corneal endothelium |
|
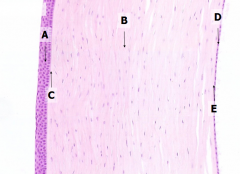
What is Structure A?
|
Corneal Epithelium
|
|
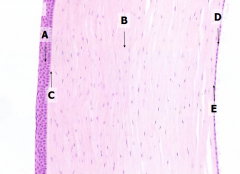
What is Structure B?
|
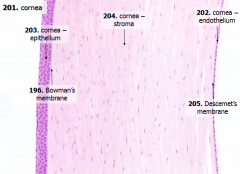
Stroma (substantia propria)
|
|
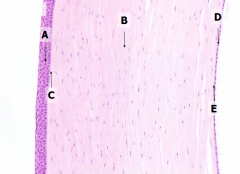
What is Structure C?
|
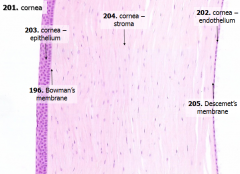
Bowman's Membrane
|
|
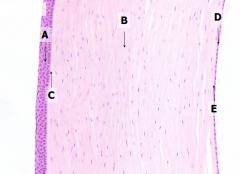
What is Structure D?
|
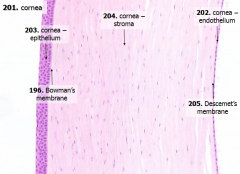
Corneal Endothelium
|
|
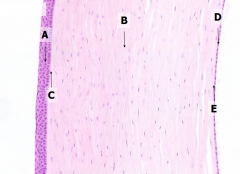
What is Structure E?
|
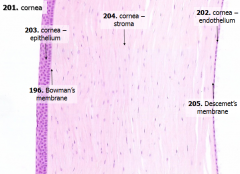
Descemet's Membrane
|
|
|
What are the contents of the corneal epithelium? How thick?
|
- Stratified, squamous, non-keratinized epithelium
- 5 cells thick - Many free nerve endings |
|
|
What is Bowman's membrane?
|
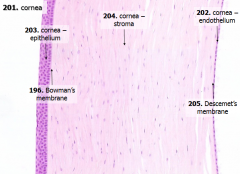
- Thick basement membrane of anterior epithelium
- Pale pink - Amorphous layer deep to basal cells of anterior epithelium |
|
|
What does the bulk of the cornea consist of?
|
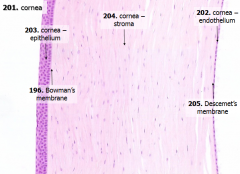
- Stroma (substantia propria) ~80%
- ~200-250 lamellae of dense collagenous tissue (Type I collagen fibrils) - Interspersed w/ glycosaminoglycans, glycoproteins, and cells (fibroblasts, macrophages, neutrophils, and lymphocytes) |
|
|
What type of collagen fibers are in the lamellae of the stroma (in the cornea)? How are they arranged?
|
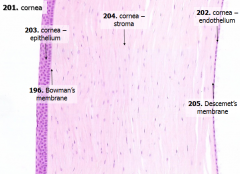
- Type I Collagen Fibers
- Within a single lamella they are parallel - Collagen fibers in adjacent lamellae are perpindicular |
|
|
What is Descemet's membrane?
|
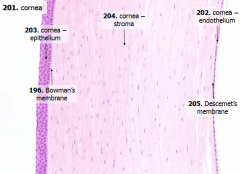
Basement membrane underlying the corneal endothelium
|
|
|
What are the contents of the corneal endothelium?
|
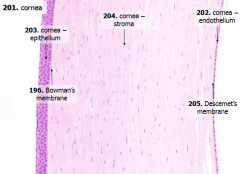
Flattened cells that line the inner surface of the cornea
|
|
|
How are corneal abrasions detected?
|
- Place a drop of fluorescein in eye
- Observe eye w/ a slit lamp using a cobalt-blue light - Damage is revealed by yellow fluorescence of exposed basement membrane |
|
|
What does LASIK surgery involve?
|
- LAser in SItu Keratomileusis
- Remove a superficial flap of cornea - Reshape underlying cornea w/ a laser - Replace flap so that it conforms to underlying surface |
|
|
What layer is scraped away during a LASIK procedure?
|
Stroma
|
|
|
What does the iris control?
|
Amount of light entering the eye through its central aperture (pupil)
|
|
|
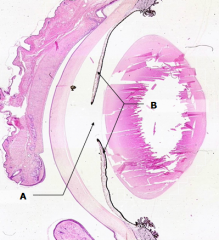
What is the anterior compartment of the uveal layer?
|
Iris
|
|
What is Structure A?
|
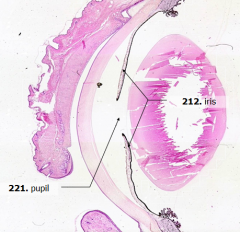
Pupil
|
|
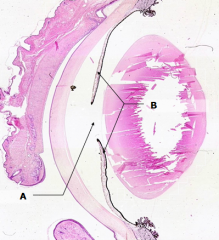
What is Structure B?
|
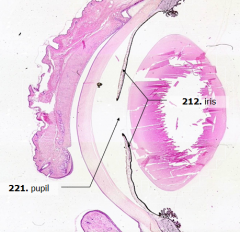
Iris
|
|
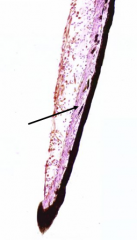
What is the arrow pointing to?
|
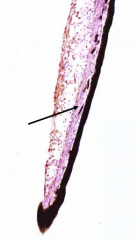
Sphincter pupillae muscle
|
|
|
The sphincter pupillae muscle receives what type of innervation?
|
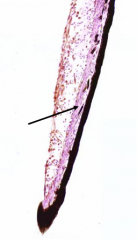
Parasympathetic
|
|
|
The dilator pupillae muscle receives what type of innervation?
|
Sympathetic
|
|
|
What does the iris divide?
|
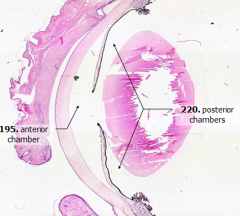
Anterior compartment into anterior and posterior chambers
|
|
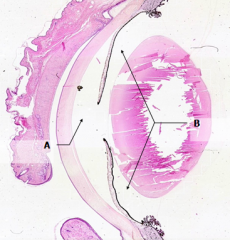
What is Structure A?
|
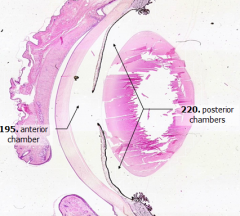
Anterior Chamber
|
|
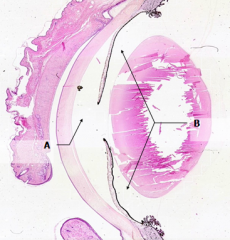
What is Structure B?
|
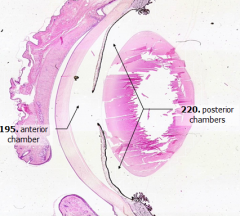
Posterior Chamber
|
|
|
What are the components of the lens?
|
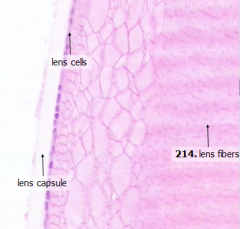
- Anterior lens cells
- Lens fibers |
|
|
What kind of cells are the anterior lens cells?
|
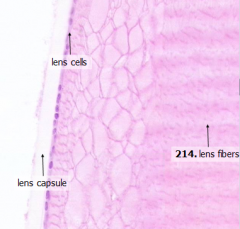
Simple cuboidal epithelial cells
|
|
|
What is the structure of the lens fibers?
|
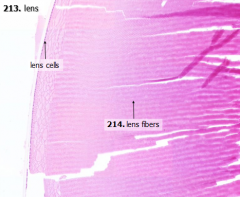
- Extremely elongated
- Tightly packed cells - Do not contain nuclei, except where they are forming at the periphery |
|
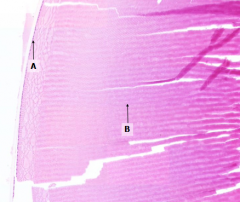
What is structure A?
What is structure B? |
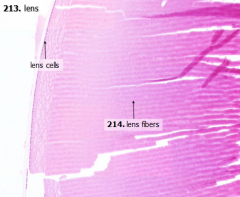
A = Lens cells
B = Lens fibers |
|
|
What is the lens surrounded by?
|
Lens capsule = thick epithelial basement membrane
|
|
|
What structure extends from the lens?
|
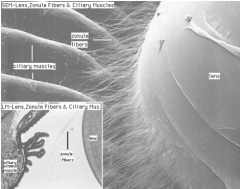
Zonule fibers - insert into the lens capsule
|
|
What is Structure A?
|
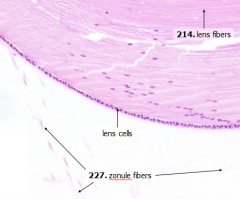
Zonule Fibers
|
|
|
What is a cataract?
|
Loss of transparency from the lens
|
|
|
What is the space between the lens and the iris?
|
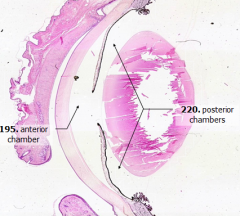
Posterior Chamber
|
|
|
What is the space between the cornea and iris?
|
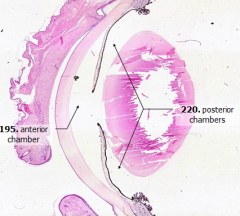
Anterior Chamber
|
|
|
What is the space posterior to the lens?
|
Vitreous Chamber
|
|
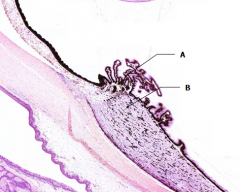
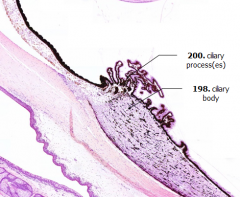
What is Structure A?
|
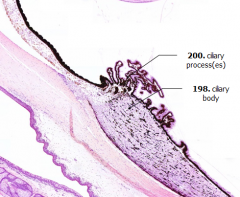
Ciliary Processes
|
|
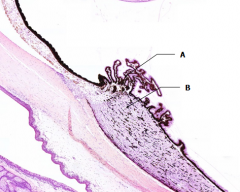
What is Structure B?
|
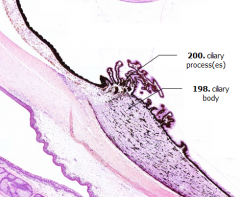
Ciliary Body
|
|
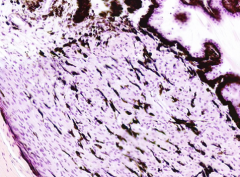
What is the bulk of this structure?
|
Ciliary Muscle (bulk of the ciliary body)
|
|
|
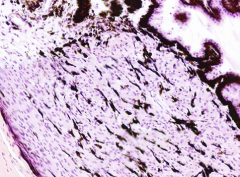
What is the shape of the ciliary body?
|
- In cross-section it looks triangular
- In 3D it is a ring-like structure |
|
|
What does the ciliary body continue as anteriorly? Posteriorly?
|
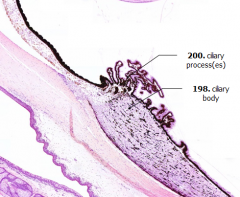
- Anteriorly - iris
- Posteriorly - choroid |
|
|
What happens when the ciliary muscles contract?
|
- Zonule fibers become slack
- Reduces tension in lens - Lens thickens |
|
|
Ciliary muscles receive what type of innervation?
|
Parasympathetic
|
|
|
What covers the ciliary processes?
|
Double layer of epithelium which continues anteriorly to cover the posterior surface of the iris (double layer because of the invagination of the optic bulb to form the optic cup)
|
|
|
Which cells secrete aqueous humor?
|
Cells of the outer epithelium covering the ciliary processes
|
|
|
What is aqueous humor?
|
Clear, watery fluid, similar in composition to CSF
|
|
|
What does the aqueous humor supply nutrition to?
|
Avascular cornea and lens
|
|
|
Aqueous humor is released into what space?
|
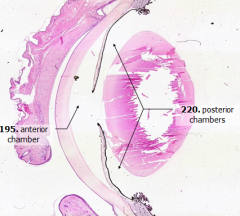
Posterior chamber
|
|
|
How does aqueous humor get from posterior chamber to anterior chamber?
|
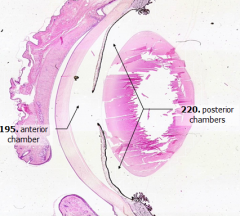
Through the pupil
|
|
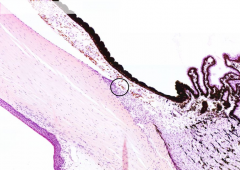
What is the circled structure?
|
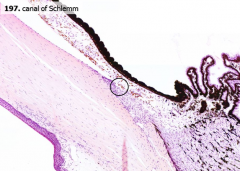
Canal of Schlemm
|
|
|
From the anterior chamber, where does the aqueous humor drain?
|
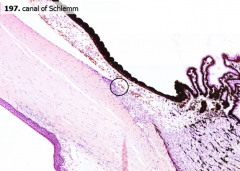
Through the Canal of Schlemm into the venous sinuses of the sclera
|
|
|
Where is the Canal of Schlemm located?
|
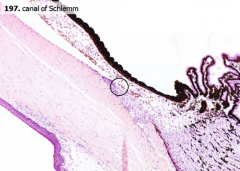
Near the junction of the cornea and iris (iridiocorneal angle) - angle of the eye
|
|
|
Posteriorly, the cornea is continuous with what?
|
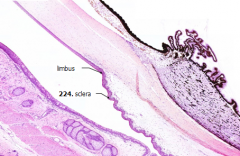
Sclera - the white, opaque connective tissue that covers the posterior 5/6 of the eye
|
|
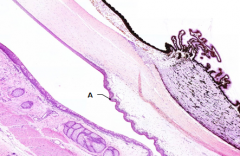
What is Structure A?
|
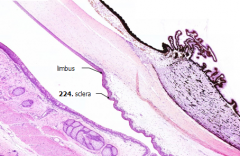
Sclera
|
|
|
What is the junction between the cornea and the sclera?
|
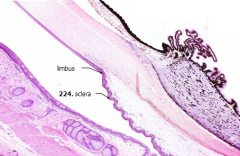
Limbus
|
|
|
Where do the extraocular muscles insert?
|
Sclera
|
|
|
What is the posterior part of the uveal layer?
|
Choroid - highly vascular, heavily pigmented layer that stains dark brown
|
|
|
What is the function of the pigment in the choroid?
|
May absorb stray light
|
|
|
The junction between the anterior and posterior parts of the neural layer is called what? What is the difference between the anterior and posterior parts?
|
Ora Serrata
- Anterior - non-photosensitive - Posterior - photosensitive |
|
|
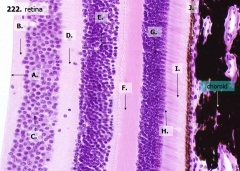
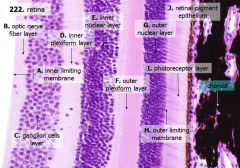
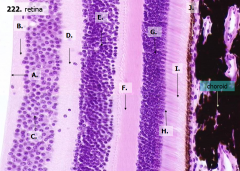
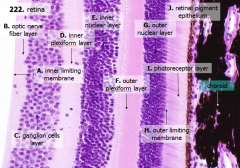
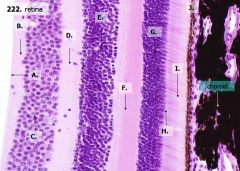
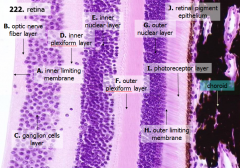
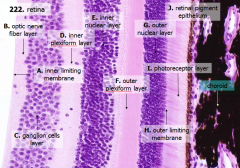
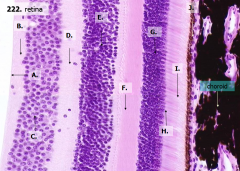
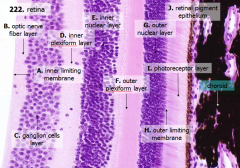
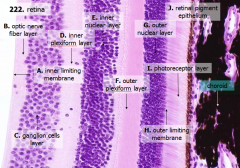
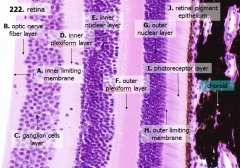
How many layers are there in the retina?
|
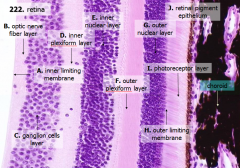
10
|
|
|
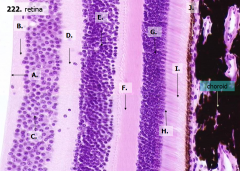
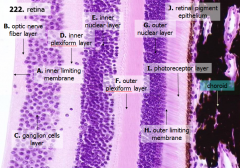
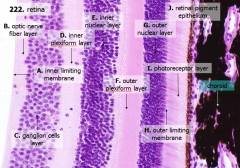
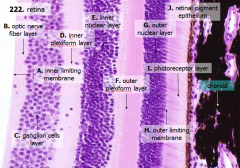
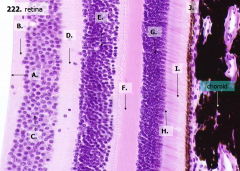
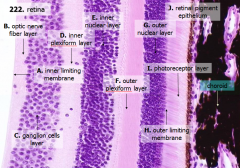
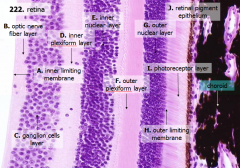
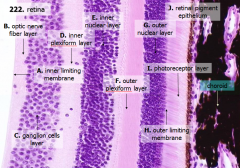
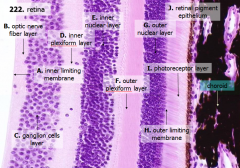
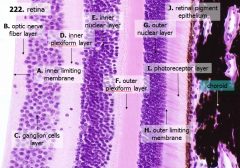
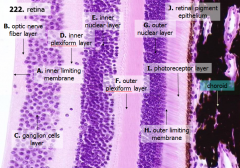
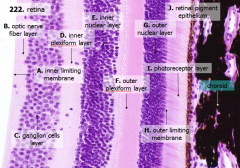
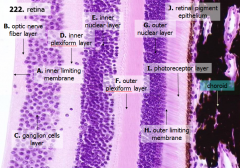
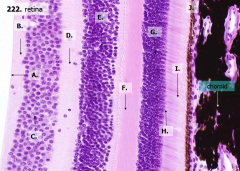
What are the layers of the retina from exterior to interior?
|
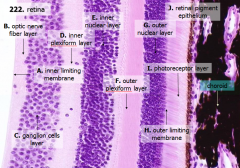
J - Retinal pigment epithelium
I - Photoreceptor layer H - Outer limiting membrane G - Outer nuclear layer F - Outer plexiform layer E - Inner nuclear layer D - Inner plexiform layer C - Ganglion cell layer B - Optic nerve fiber layer A - Inner limiting membrane |
|
|
The most external layers of the retina are adjacent to what? The most internal layers of the retina are adjacent to what?
|
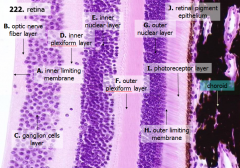
- External - choroid
- Internal - vitreous humor |
|
|
What layer is between the choroid and the first layer of the retina?
|
Bruch's membrane - thin basement membrane
|
|
What is Structure J?
|
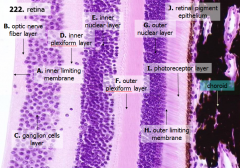
Retinal Pigment Epithelium - first layer of the retina, closest to the choroid
|
|
|
What kind of cells are in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (1)?
|
Simple cuboidal epithelium
|
|
|
What structure is on the cells of the retinal pigment epithelium (1)?
|
- Microvilli
- Extend to surround outer segments of photoreceptor cells |
|
|
What is the function of the cells of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (1)?
|
- Phagocytose the vesicles shed by the outer segments of the photoreceptors
- Pigment absorbs stray light that passes through the retina |
|
What layers of the retina include the photoreceptors (rods and cones)?
|
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (1/J)
- Photoreceptor Layer (2/I) - Outer Limiting Membrane (3/H) - Outer Nuclear Layer (4/G) - Outer Plexiform Layer (5/F) |
|
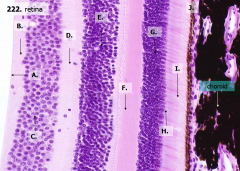
What is structure I?
|
Photoreceptor Layer (2)
|
|
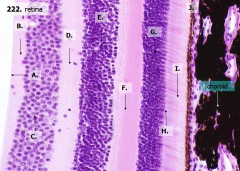
What is structure H?
|
Outer Limiting Membrane (3)
|
|
What is structure G?
|
Outer Nuclear Layer (4)
|
|
What is structure F?
|
Outer Plexiform Layer (5)
|
|
|
Where are the outer segments of the rods and cones?
|
Embedded in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (1)
|
|
|
What structures are in the outer segments of the rods and cones?
|
Light sensitive pigment
|
|
|
What structures are in the inner segments of the rods and cones?
|
Organelles for protein synthesis and energy production
|
|
|
What does the Outer Limiting Membrane separate?
|
- Separates the inner segments of the rods and cones (photoreceptor layer) from the
- Nuclei of the photoreceptors (Not actually a membrane, but simply a visible junction between two parts of the photoreceptor cells) |
|
|
Where are the inner segments of the rods/cones located?
|
Photoreceptor Layer (2)
|
|
|
Where are the nuclei of the rods/cones located?
|
Outer Nuclear Layer (4)
|
|
|
Where do the axons of the photoreceptors synapse? Onto what?
|
- Outer Plexiform Layer (5)
- Onto Interneurons |
|
What is structure E?
|
Inner Nuclear Layer (6)
|
|
|
What kind of structures are in the inner nuclear layer (6)?
|
Nuclei of the integrating neurons (bipolar cells, amacrine cells, and horizontal cells)
|
|
What is structure D?
|
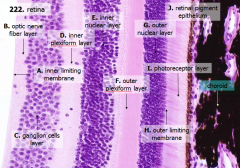
Inner Plexiform Layer (7)
|
|
|
What is in the Inner Plexiform Layer (7)?
|
Axons of bipolar cells and amacrine cells synapsing on ganglion cells
|
|
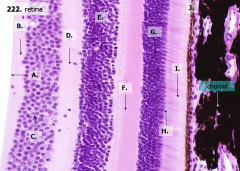
What is structure C?
|
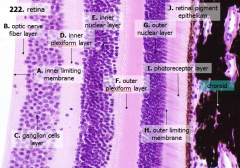
Ganglion Cell Layer (8)
|
|
|
What is in the ganglion cell layer (8)?
|
Cell bodies of ganglion cells
|
|
|
Are the axons of ganglion cells myelinated or not?
|
Unmyelinated
|
|
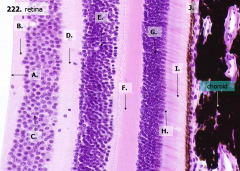
What is structure B?
|
Optic Nerve Fiber Layer (2)
|
|
|
What is found in the optic nerve fiber layer?
|
Unmyelinated axons of ganglion cells
|
|
|
Where do the axons of the ganglion cells go after leaving the optic nerve fiber layer?
|
Toward the optic disc where they exit the eyeball as the optic nerve
|
|
What is structure A?
|
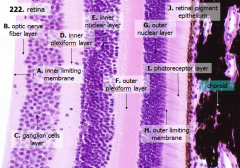
Inner Limiting Membrane
|
|
|
What separates the vitreous humor from the retina?
|
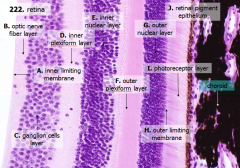
Inner limiting membrane - glial boundary
|
|
|
Light travels through the optic nerve fiber layer and nuclear and plexiform layers before reaching the photoreceptors, true or false?
|
True
|
|
|
Why are the axons of the proximal neurons in the retina unmyelinated?
|
In order to be relatively transparent
|
|
|
What happens to the cell bodies of the proximal neurons in the region of the fovea?
|
The cell bodies are shifted out of the path of light to achieve high visual acuity
|
|
|
Retinal detachment usually begins with a tear where?
|
Peripheral retina
|
|
|
What causes an increase in retinal detachment once it begins as a tear in the peripheral retina?
|
Vitreous humor insinuates between the retina and underlying retinal pigment epithelium
|
|
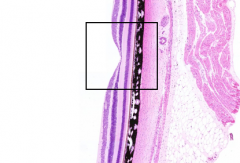
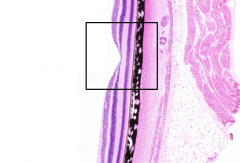
What is the structure in the box?
|
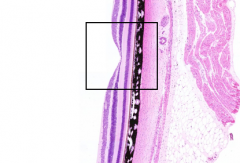
Fovea
|
|
|
What makes the fovea the area of highest visual acuity?
|
Photoreceptors are almost exclusively cones
|
|
|
Which layers are nearly absent in the fovea?
|
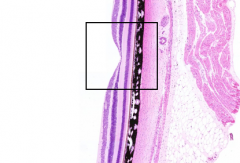
- Ganglion cell layer
- Inner nuclear layer |
|
|
The fovea is in the center of what?
|
A small yellow disk called the macula lutea
|

