![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
93 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
fluid contained by membranous labyrinth?
|
K rich endolymph
|
|
|
fluid contained by bony labyrinth?
|
Na rich perilymph
|
|
|
2 components of the membranous labryinth?
|
cochlea
vestibule |
|
|
what is the cochlea?
|
fluid filled coil of hose
sensory organ invoved in hearing -cochelar nerve exit |
|
|
what is the vestibule
|
sensory organ involved in balance
-vestibular nerve exist from it |
|
|
Which CN is involved in hearing/balance?
|
vestibulochlear nerve (CNIII)
|
|
|
Pinna
|
"ear" that directs sound waves into the external auditory meatus
|
|
|
tympanic membrane:
-location -function |
-at the end of the external auditory meatus
-moves back and forth as sound waves strike it, transferring movement to middle ear osicles |
|
|
name middle ear ossicles
|
maleus
incus stapes |
|
|
what is the oval window
|
stapes moves in and out of this window= waves in fluid filled cochela
|
|
|
round window
|
fluid waves in cochlea terminate here, exciting sensory cells
|
|
|
saccule
|
part of vestible
linear acceleration in vertical direction |
|
|
utricle
|
part of vestibule
linear acceleration in horizontal directio |
|
|
semicircular canalas
|
part of vestibular
detect rotation acceleration w/ crista, sensory organ |
|
|
What are the primary sensory cells in the middle ear? what are they made of?
|
hair cells
stereocilia |
|
|
Tallest stereocilia?
|
kinocilium
|
|
|
What happens when hairs are displaced toward kinocilium
|
hair cell excites
tip links= open cation channels= K from endolymph into cell more nt |
|
|
What happens when hairs are displaced away from kinocilium
|
Inhibited
cation channel springs shut less nt |
|
|
What happens when hairs are displaced orthoganoly from kinocilium
|
there is no change
|
|
|
where are the cell bodies of cells for the vestibule?
|
scarpa's ganglion
|
|
|
Where are the cell bodies of cells for the cochlea?
|
spiral ganglion
|
|
|
How does the semicircular canal work
|
Crista bulges into canal
hairs on crista are embeded in gelatinous cupula Head rotates, acnal rotates in same direction endolymph doesn't move= pushes cupula in opposite direction |
|
|
How do utricle and saccule work?
|
They have hairs embedded in a gelatonous otolith membrane
otoconia (calcium carbonate crystals) sit on otolith membranes Body accelerates, otoconia don't move= hair is forcesd in oposite direction |
|
|
Orientation of kinocilia:
utricle saccule semicircular canal |
utricle- different
saccule-different semicircular- all same direction |
|
|
maintaining the head in a tilted position produces the same effects as __?
|
linear acceleration
|
|
|
Pathway of signals from vestinular sensory organs
|
1. vestibulocochlear nerve (CN8)
2. synapse on vestibular nuclei in pons 3. project to spinal cord, CN nuclei that control eye movement, and the cortex via the thalamus |
|
|
Vestibulospinal system allow?
|
maintaining balanced, upright posture
|
|
|
Vestibulospinal system?
|
1. lateral vestibulospinal tract= project ipsilaterally to motor nuerons in all levels of the spinal cord= move body to maintain posture
2.medial vestibulospinal tract= project bilaterally to motor neurons in cervical spinal cord= adjust head and neck posture |
|
|
Vestibulo-ocullar system allows?
|
maintaining steady gave even when head is moving
|
|
|
Vestibulo-ocular revlex if head rotates to left
|
1. head rotates left
2. left horizontal semicircular canal 3. activation of left vestibular nucleus 4. left vestibular nucleus projects to contralateral abducens nucleus (VI) 5. abduces sends fibers to activate latera rectus muscle 6. abducens sends fibers (medial longitudinal fasiculus) to cross the midline and go to the occulomotor nucleus (CNIII) which activates the medial rectus muscle) 7. eye moves right |
|
|
goal of thalamocortico vestibular system
|
give concious spatial orientation and self motion
|
|
|
pathway of thalamocortico vestibular system
|
1. vestibular nuclei to VPL
2. VPL to 3b of S1 and to Area 2 of parietal cortex |
|
|
nystagmus
|
slow VOR-mediate eyemovement followed by quick resetting eyemovements
|
|
|
normal response to constant rotation is nystagmus that beats in the same/opposite direction of motion?
|
same
|
|
|
Caloric stimulation test: warm water into left ear
|
1. warm= activates left semicircular cnal
2. should have left beating nystagmus |
|
|
caloric stimulation test: cold water into left hear
|
1. cold= inhibits left semicircular canal
2. right beating nystagmus |
|
|
Patient comes into office with constant, right-beating nystagmus: what does this indicate?
|
lesion to left semicircular canal
|
|
|
fxns of the middle ear ossicles?
|
1. amplify sound pressure waves
2. impedance matching- transfer sound energy into fluid wave energy |
|
|
____ is the spance between the eardrum and the labrinth
|
middle ear
|
|
|
___ connect the middle ear to pharynx
|
eustachain tube
|
|
|
ostoclerosis
|
disease of middle ear
overgrowth of bone/tissue= ossicles movement restrictited |
|
|
otitis media
|
middle ear infection= inflammation that often blocks the eustachian tube
|
|
|
scala vestibuli
|
part of coclea that contains perilymph
|
|
|
scala tympani
|
part of cochlea that contains perilymph
|
|
|
scala media
|
part of cochlea that contains endolymp
|
|
|
helicotrema
|
at apex of cochlea where scala vestibuli and scala tympani connect
|
|
|
What happens when stabes is forced into motion
|
pushed into oval window
periymph waves thru scala vestibuli, helooctrema and into scala tympani buldge in round window this fluid also displaces basilar membrane, disturbing scala media hair cells embeded in ogan of corti get shoved into tectorial membranes channels open K flows in from endolyph spiral ganglion activates cochlear nerve |
|
|
Inner hair cells
|
in cochlea
mediate hearing, signals to brain stem |
|
|
outer hair cells
|
in cochlea
moderate firing of inner hair cells by altering their own shape/location in tectorial membrane |
|
|
otoacoustic emission
|
sound made when outer hair cells change shape
|
|
|
basilar membrane of cochlea responds to ____ at apex?
|
low frequency sound (floppy)
|
|
|
basilar membrane of cochlea responds to ____ at base?
|
high frequency sound (stiff)
|
|
|
place code?
|
place in cochlear membrane /type of hair cell determines preffered frequency (high or low)
|
|
|
rate code?
|
cochlear nerve fibers an action potential at a frequency equal to the sound that stimulates them
|
|
|
Auditory pathway
|
1. signal from cochlea
2. vestibulocochlear nerve 3. brainstem- synapse on cochlear nuclei 4. sends info bilateraly via the trapezoid body to the superior olivary complex 5. projects as lateral leniscus to inferior colliculus 6. projects to medial geniculate nucleus 7. projects to A1 (primary auditory cortex/ heschl's gyrus) on superior back of temporal lobe |
|
|
fxn of medial superior olive
which type of frequency? |
localizes sound by detectint interaural time difference= knows if sound if from left or right
best for low frequencies |
|
|
fxn of lateral superior olive?
|
localizes sound by detecting teraural intensity difference= intensity shows if sound is from left or right
best for high frequencies |
|
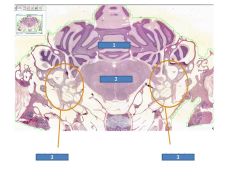
fxn
|
1= cerebellum
2= brain stem 3= labryinth |
|
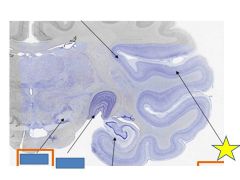
fxn
|
Primary auditory cortex- recieves info from MGN, on superior bank of temporal lobe
|
|
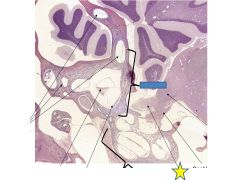
fxn
|
Vestibular nerve- carries balance info from the sensory structures of the vestibule to the brainstem
|
|
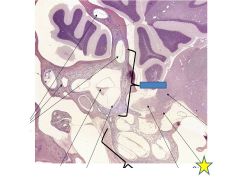
fxn
|
cochlear nerve- carries auditory info from the cochlea to the brainstem
|
|
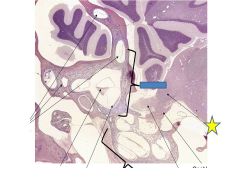
Fxn?
|
Vestibulochoclear nerve (CN 8)- carries jxn of vestibular nerve and cochear nerve
|
|
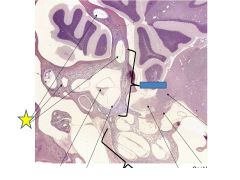
fxn
|
Semicircular canal- detec rotational acceleration
|
|
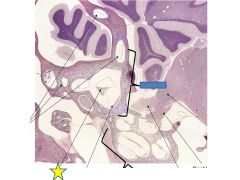
fxv
|
Utricle- detects linear acceleration in the horizontal direction
|
|
|
Fxn?
|
saccule=-detects linear acceleration in the verticle direction
|
|
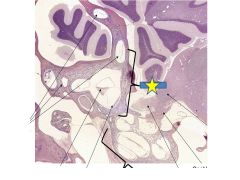
|
Vestibule
|
|
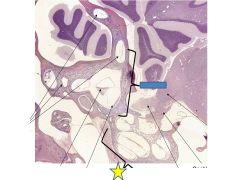
|
cochlea
|
|
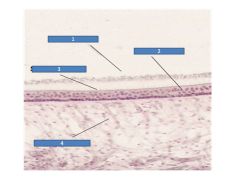
|
Utricle
1= otoconia 2= hair cells 3= sterocilia 4= afferent processes of CNVIII |
|
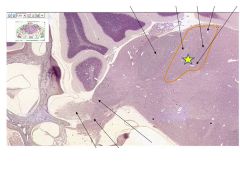
Fxn
|
Vestibular nuclei- synapse site of signals from vestibular sensory organs
|
|
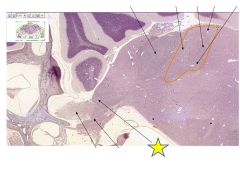
|
Vestibuloar occular nerve
|
|
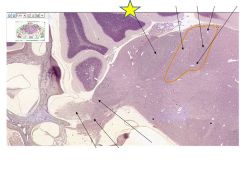
|
Inferior cerebral peduncle
|
|
|
fxn
|
Abducens nerve- VOR (sends fibers to rectus muscles of the eye)
|
|
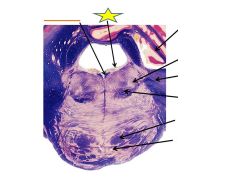
fxn
|
Abducens nerve- VOR (sends fibers to rectus muscles of the eye)
|
|
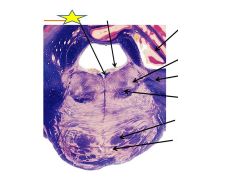
Fxn
|
Medial longitudinal fasiculus- receives fibers from abducens nerves and activates the CNIII (medial rectus) and CN IV
|
|
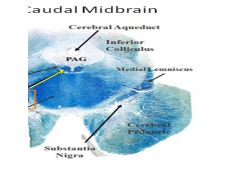
Fxn
|
Medial longitudinal fasiculus- receives fibers from abducens nerves and activates the CNIII (medial rectus) and CN IV
|
|
|
Fxn
|
Trochlear nerve- recieves fibers from Medial longitudinal fasiculus
|
|
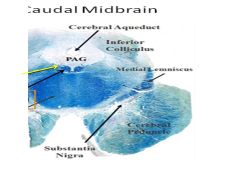
Fxn
|
Trochlear nerve- recieves fibers from Medial longitudinal fasiculus
|
|
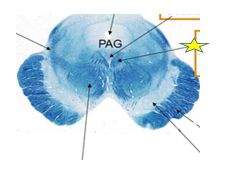
Fxn
|
Medial longitudinal fasiculus- receives fibers from abducens nerves and activates the CNIII (medial rectus) and CN IV
|
|
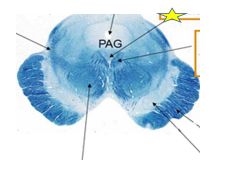
fxn
|
Occulomotor nucleus- recieves fibers from medial longitudinal fasiculus and activates the medial rectus
|
|
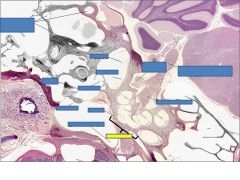
|
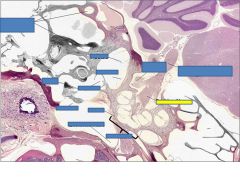
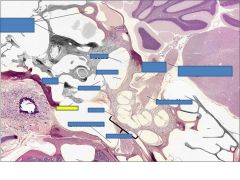
cochlea
|
|
|
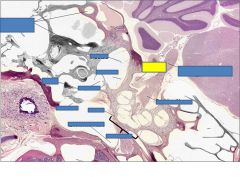
Cochlear nerve
|
|
|
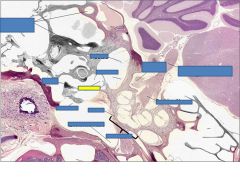
vestibular nerve
|
|
|
malleus
|
|
|
stapes
|
|
|
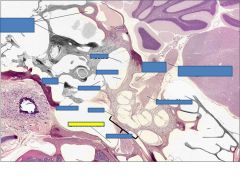
Eustachian tube
|
|
|
Scala vestibuli
|
|
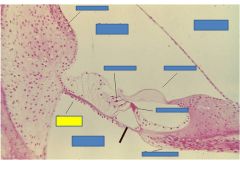
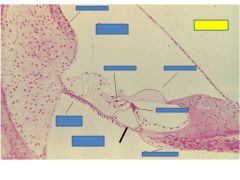
fxn
|
Basilar membrane- displaced sterocilia of hair cells to shear into the tectorial membrane
|
|
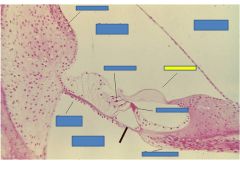
fxn
|
Tectorial membrane- when hair cells enter channels open and K from endolymph flows in causing excitation
|
|
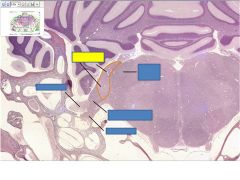
fxn
|
Cochlear nuclei- synapse site of vestibulochlear nerve
|
|
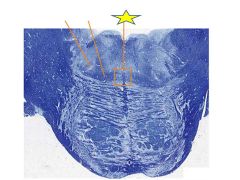
fxn
|
Trapezoid body-Projection from cochlear nuclei to superior olivary nucleus
|
|
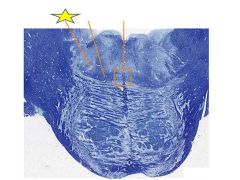
fxn
|
Superior olivary nucleus- receives from trapezoid body, projects as lateral lemniscus to inferior colliculus
|
|
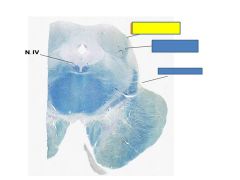
fxn
|
Inferior colliculus- receives info from lateral leminiscusand projects ot medial geniculate nucleueus of the thymus
|
|
fxn
|
Medial geniculate nucleus of the thalamus -Receives input from inferior colliculus and sends it to A1
|

