![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
142 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Functions of the Cerebral Cortex
What does the frontal lobe do? |
*Primary motor area
*Conscious control of skeletal muscles *Broca's area: motor speech area (problem: expressive aphasia - loss of ability to produce language) |
|
|
Functions of the Cerebral Cortex
What does the parietal lobe do? |
*Primary sensory area
*Interpretation of touch, pain and temperature |
|
|
Functions of the Cerebral Cortex
What does the temporal lobe do? |
*Auditory and olfactory areas
*Wernicke's area: speech comprehension (problem: receptive aphasia - person can hear/see print, but cannot make sense of what it means) |
|
|
Functions of the Cerebral Cortex
What does the occipital lobe do? |
*Visual receiving and visual association area
|
|
|
What is the function of the thalamus?
|
*The thalamus is the relay station for sensory impulses
*The thalamus sorts out impulses, and directs them to other areas of the cerebral cortex |
|
|
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
|
*Helps maintain homeostasis
*Regulates body temperature, water balance, sleep, appetite, fear and pleasure |
|
|
The Brain Stem
What is the function of the medulla oblongata? |
*Located between the pons and the spinal cord
*Respiratory center: controls the muscles of respiration *Cardiac center: regulates the rate and force of heart beat *Vasomotor: regulates contraction of smooth muscle in the blood vessel walls |
|
|
The Brain Stem
What is the function of the cerebellum? |
*Made up of 3 parts
*Coordinates voluntary muscles *Maintains balance *Maintains muscle tone |
|
|
What is the function of Broca's area of the brain?
|
*Broca's area is located in the frontal lobe
*Controls speech muscles of the tongue, soft palate and the larynx *When damaged, will result in expressive aphasia, which is the loss of ability to produce language |
|
|
What is the function of Wernicke's area of the brain?
|
*Wernicke's area is located in the temporal lobe
*Speech comprehension area *When damaged, person will be able to see print/hear, but will not understand |
|
|
What is the Myelin Sheath?
|
*The myelin sheath is a fatty material that insulates and protects the axon nerve fiber
*Disorder: multiple sclerosis - development of plaque in the white matter of the CNS, this plaque then damages the myelin sheath and interferes with the impulse transmission between the CNS and the body |
|
|
Cranial Nerves
What are all 12 of the cranial nerves? |
O: olfactory
O: optic O: oculomotor T: trochlear T: trigeminal A: abducens F: facial V: vestibulocochlear G: glossopharyngeal V: vagus A: accessory H: hypoglossal |
|
|
What is cranial nerve I (olfactory), responsible for?
|
*Sensory nerve responsible for smell
*Have client close eyes and identify a scent (coffee, vanilla, peppermint) |
|
|
What is cranial nerve II (optic), responsible for?
|
*Responsible for vision
*Use a Snellen or Rosenbaum chart to check visual acuity |
|
|
What is cranial nerve III (oculomotor), responsible for?
|
*Responsible for pupil constriction, lid elevation, cardinal fields of gaze
*Test client's 6 cardinal fields, assess pupil size by using a flashlight |
|
|
What is cranial nerve IV (trochlear), responsible for?
|
*Responsible for all eye movement
*Assess 6 cardinal fields of gaze for eye movement up, down, and inwards (convergence) |
|
|
What is cranial nerve V (trigeminal), responsible for?
|
*Responsible for jaw movement
*Test face, scalp, and teeth sensation |
|
|
What is cranial nerve VI (abducens), responsible for?
|
*Responsible for lateral eye movement
*Check 6 cardinal gazes for eye movement laterally and and outward |
|
|
What is cranial nerve VII (facial), responsible for?
|
*Responsible for facial movements
*Ask client to smile, frown, show teeth, puff cheeks, ask client to taste something sweet |
|
|
What is cranial nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear), responsible for?
|
*Responsible for hearing and equilibrium
*Test hearing with audiometry *Weber's or Rhinne's test *Assess balance with Romberg test |
|
|
What is cranial nerve IX (glossopharyngeal), responsible for?
|
*Tongue and throat
*Ask client to swallow |
|
|
What is cranial nerve X (vagus), responsible for?
|
*Responsible for gag reflex
*Test gag reflex by touching side of tongue with a tongue blade, ask client to swallow and say "ah" |
|
|
What is cranial nerve XI (accessory), responsible for?
|
*Responsible for movement of head and shoulders up and down
*Have client turn head left to right, and to "shrug" the shoulders |
|
|
What is cranial nerve XII (hypoglossal), responsible for?
|
*Responsible for tongue movement
*Ask the client to stick out their tongue |
|
|
What is the function of the Limbic System?
|
*It is involved in emotional states and behavior
|
|
|
Pain Management & Assessment
What are 2 ways to elicit a response in a client who has a decreased level of consciousness? |
*Observe client's facial expressions, such as facial grimacing, wrinkled forehead and body movements
*Observe if client is moaning and crying, and if they have a decreased attention span |
|
|
Pain Management & Assessment
What kind of questions should the nurse ask about the client's complaint of pain? |
*Where is your pain?
*Does your pain radiate to anywhere else? *What does the pain feel like? Throbbing, burning or stabbing? *When did the pain start? *How would you rate your pain on a scale 0-10, 10 being the worst, 0 being the least? *Is your pain constant or intermittent? *What were you doing when the pain started? *What other symptoms do you experience when you are feeling pain? (check for presence of associated symptoms, such as fatigue, depression, nausea and anxiety |
|
|
Pain Management & Assessment
What are some symptoms that may be associated with severe pain? |
*Tachycardia
*Increased BP *Anxiety *Diaphoresis *Muscle tension |
|
|
Neuro Diagnostic Procedures
What is a Cerebral Angiogram? |
*Cerebral angiogram provides visualization of the cerebral blood vessels, with the use of contrast dye
*It is used to assess the blood flow to and within the brain, identify aneurysms ect. *Blockages in the arteries or veins in the head and neck could indicate impaired blood flow |
|
|
Neuro Diagnostic Procedures
What are some nursing considerations prior to the procedure and post procedure? |
*Pre-procedure: determine if client's are pregnant, assess for allergies to shellfish and iodine (contrast dye), assess if client is on any kind of blood thinner medications such as coumadin, check BUN and creatinine levels (for kidney function to excrete dye)
*Post-procedure: closely monitor the site to assure that clotting occurs, restrict movements for 8-12 hours to prevent rebleeding at the catheter site, check insertion site frequently, push fluids 1500-2000 |
|
|
Neuro Diagnostic Procedures
What is an EEG? |
*An EEG stands for electroencephalogram
*Assesses electrical activity of the brain and is used to determine if there are abnormalities in brain wave patterns *Small electrodes will be placed on the scalp and connected to a brain wave machine or computer *Most commonly used to identify and determine seizure activity, and can also be used to diagnose sleep disorders and behavioral changes *Location of abnormal wave patterns may indicate site of brain that is stimulating seizure activity *Can also be used to indicate brain death |
|
|
Neuro Diagnostic Procedures
What are some nursing considerations prior to the procedure? |
*Pre-procedure: instruct clients to refrain from drinking fluids containing caffeine on day of the test, instruct client to wash hair before (no oils or sprays) and after (to remove electrode glue), if indicated instruct clients to induce "sleep deprivation" the night before the procedure, instruct client to withhold CNS stimulants or depressants and antiepileptic medications, inform clients they will need to take deep breaths and/or will be exposed to bright flashes of light during the procedure
|
|
|
Neuro Diagnostic Procedures
What is the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) used for? |
*Rapid neurological assessment used when a client is admitted to a health care facility on an emergent basis
*Establishes baseline data in 3 areas: eye opening, motor response and verbal response *A score of 15 represents normal neurologic functioning *A score of 8, you must intubate *The lower the score, the lower the client's LOC *GCS scores are helpful in determining changes in the LOC for clients with head injuries |
|
|
Neuro Diagnostic Procedures
How is the GCS score calculated? |
Eye opening (E) - ranging from 4-1
4 = spontaneously 3 = to speech 2 = to pain 1 = none Verbal response (V) - ranging from 5-1 5 = oriented 4 = confused 3 = inappropriate 2 = incomprehensible 1 = none Motor response (M) 6 = obeys commands 5 = localized to pain 4 = withdraws from pain 3 = flexion to pain 2 = extension to pain 1 = none |
|
|
Neuro Diagnostic Procedures
What is an MRI? |
*Produces images that are better than a CT scan
*Does not use ionizing radiation, but relies on magnetic fields; assess for metal (pacemaker!!) *May use a non-iodine based contrast medium *Can be used to evaluate blood flow and vessel abnormalities *Client needs to lie still during procedure, Ativan may be given as a sedative |
|
|
Neuro Diagnostic Procedures
What is a brain scan used for? |
*Used to evaluate vascular lesions
*Assess BUN and creatinine before test, assess allergies, push fluids post procedure *Explain to the client to remain still, contrast medium dye may be used |
|
|
Neuro Diagnostic Procedures
What is a lumbar puncture? |
*Insertion of a spinal needle in the subarachnoid space
*Used to obtain CSF readings *Because of the sudden release of CSF pressure, a lumbar puncture is not done for clients with symptoms indicating ICP *After specimen collection, needle is withdrawn, slight pressure is applied, and adhesive bandage placed over site *Position client in a side-lying position with hips, knees, and chest flexed in towards chest in order to open the intralaminar spaces, pillow can be used for support, sitting position may be used if obese |
|
|
Neuro Diagnostic Procedures
What are the nursing considerations post-procedure for a lumbar puncture? |
*After procedure, sterile dressing is applied, and client is placed in supine position (for 8 hours - lie FLAT to prevent bleeding)
*Most common complication is a post-puncture headache |
|
|
CNS Disorders
What is a migraine headache? |
*Chronic disorder with multiple subtypes
*Classified as long duration cephalgia, because it usually lasts longer than 4 hours *Certain triggers: MSG, artificial sweeteners, caffeine, red wine, missing meals |
|
|
CNS Disorders
What are the symptoms of a migraine headache? |
*Commonly preceded by a temporary focal neurologic sign known as an aura
*Unilateral onset, but may be generalized *Begins as a dull ache that progressively worsens and develops into a pulsating, throbbing pain *The classic signs are: nausea, vomiting, photophobia, phonophobia, and aggravated with activity |
|
|
CNS Disorders
What kind of medications can be used to treat migraine headaches? |
*Triptans: sumatriptans (Imitrex), frovatriptan
|
|
|
CNS Disorders
What are some nursing considerations for patients who experience migraine headaches? |
*Teach client to routinely take preventative drugs
*Teach client to avoid triggers (caffeine, artificial sweeteners *Lay down in a dark, quiet room *Placing a cold cloth on head may help to reduce pain *Client should not take vasoconstricting drugs if pregnant, or has a history of heart disease |
|
|
Seizures & Epilepsy
What is a seizure? |
*An abnormal, sudden, excessive, uncontrolled electrical discharge of neurons
*Epilepsy is defined as 2 or more seizures experienced by an individual |
|
|
Types of Generalized Seizures
What is a tonic-clonic seizure? |
*May begin with an aura (alteration in vision, smell or emotional feeling)
*Tonic-phase: a 15-20 second episode of stiffening of muscles, loss of consciousness, cessation of breathing *Clonic-phase: 1-2 minute episode of rhythmic jerking of the extremities, irregular respirations, biting of the cheek and tongue and bladder and bowel incontinence may occur *Posictal: after the seizure, will experience lethargy |
|
|
Types of Generalized Seizures
What is a absence seizure? |
*More common in children, tends to run in families
*Consists of loss of consciousness lasting a few seconds accompanied by blank staring (daydreaming) and associated automatisms (behaviors client is unaware of, picking at clothes ect.) |
|
|
Types of Generalized Seizures
What are the treatments for clients with seizure disorders? |
*Tonic-clonic seizures: PHENYTOIN, GABAPENTIN, phenobarbital
*Absence seizures: valporic acid |
|
|
Types of Generalized Seizures
What are the nursing considerations for clients who have seizure disorders? |
*Protect the client from injury
*Do NOT force anything into the clients mouth *Do NOT attempt to restrain the client *Turn client to the side to keep the airway open and prevent aspiration *AVOID TRIGGERS: extreme fatigue, excessive stress, exposure to flashing lights |
|
|
Types of Generalized Seizures
What is status epilepticus? |
*Prolonged seizure lasting longer than 5 minutes, or repeated seizures over the course of 30 minutes
*Treatment: IV push ativan or lorazepam |
|
|
Meningitis
What is meningitis? |
*Inflammation of the meninges, which are the membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
*Bacterial meningitis has a high mortality rate |
|
|
Meningitis
What are the signs and symptoms of meningitis? |
*Fever and chills
*Nausea and vomiting *Altered LOC *Petechial purpural rash *Positive Kernig's (resistance and pain with extension of the clients leg from a flexed position - hamstring) *Positive Brudzinki's (flexion of extremities occurring with deliberate flexion of the clients neck) *Seizures *Abnormal eye movements *Opisthotonos *Photophobia |
|
|
Meningitis
What are some nursing considerations for patients who have been diagnosed with meningitis? |
*Isolate clients as soon as meningitis is suspected
*Maintain isolation precautions (droplet precautions) *Implement fever reduction measures, cooling blanket if necessary *Decrease environmental stimuli: provide quiet environment, minimize exposure to bright lights *Maintain client safety, such as seizure precautions *Pad bed rails *Follow ABC's (maintain patent airway) *Take VS an do neuro checks every 2-4 hours *Elevate HOB 30 degrees |
|
|
Meningitis
What is a potential complication of meningitis? |
*Increased intracranial pressure (ICP)
*Meningitis can cause ICP to increase *Elevate client's head 30 degrees, to help reduce intracranial pressure *Monitor for signs of ICP such as decreased LOC, pupillary changes and widening pulse pressure *Provide interventions to reduce ICP (positioning, and AVOIDANCE of coughing and straining) |
|
|
Meningitis
What is the treatment for meningitis? |
*Mannitol (osmotic diuretic) for cerebral edema
*Corticosteroids *Anticonvulsant usually IV or sedative |
|
|
Parkinson's Disease
What is Parkinson's disease? |
*A progressively debilitating disease that grossly affects motor function
*Will eventually lead to the client being unable to stand or walk - will be dependent for all care, and may exhibit dementia *Cause is unknown, but risk factors are advanced age, genetics and reduced estrogen levels, exposure to chemicals |
|
|
Parkinson's Disease
What are the 4 cardinal signs of Parkinson's disease? |
1. Tremor
2. Muscle rigidity 3. Bradykinesia (slow movement) 4. Postural instablity *Caused by degeneration of dopamine |
|
|
Parkinson's Disease
What are the signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease? |
*Muscle rigidity
*Stooped posture *Mask-like facial expression *Tremor beginning in the fingers (pill roll) *Drooling *Bradykinesia *Akinesia *Slow, shuffling and propulsive gait *Progressive difficulty with ADL's *THESE PATIENTS ARE FALL RISK, IMPLEMENT SAFETY PRECAUTIONS* |
|
|
Parkinson's Disease
What is the treatment for Parkinson's disease? |
*Levodopa, a dopamine replacement most effective during early stages and given in doses until symptoms are relieved or adverse effects appear
*Mirapex, a dopamine agonist activates the release of dopamine *Cogentin can also help control temors and rigidity *Adjunct drugs: benadryl (diphenhydramine) - for drug induced extrapyramidal syndrome *Monitor for dyskinesias, and hallucinations |
|
|
Parkinson's Disease
What are some nursing considerations for clients who have Parkinson's disease? |
*Monitor swallowing, and maintain adequate nutrition
*Maintain client mobility for as long as possible *Request referral to a speech-language pathologist *Thick soled shoes (shuffling) *Protect the client from injury (fall risk) *Remove throw rugs *Wide-based stance *Encourage daily ambulation *Increase fiber and fluids to prevent constipation |
|
|
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
What is a spinal cord injury? |
*SCI's involve the loss of motor function, sensory function, reflexes and control of elimination
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
What does complete transection mean? |
*Absence of sensory and motor functions below the level of injury
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
What is quadriplegia? |
*Loss of motor and sensory function of all 4 extremities
*Priority is airway |
|
|
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
What are signs and symptoms of a SCI? |
*Muscle spasm and back pain that worsens with movement
*Loss of motor function, muscle flaccidity *Respiratory impairment |
|
|
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
What findings would the nurse expect in a client with a spinal cord transection at the level of T4? |
*Affects the strength of the abdominal muscles, no motor function below the level of injury
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
List a priority nursing diagnosis for a client with a C5 spinal cord injury? |
*Immobility
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
What is a priority of care for clients who have an SCI? |
*Assessing ABC's
*Nursing interventions: maintain respiratory function, assist the client to cough by applying abdominal thrusts when the client is attempting to cough |
|
|
Spinal Shock
What is spinal shock? |
*Occurs immediately after a SCI as a concussion response to the injury
*Lasts 48 hours to several weeks *Client will have flaccid paralysis and loss of reflex activity below the level of injury *Client may present with paralytic ileus, bladder distention, flaccid paralysis, bradycardia and hypotension, loss of autonomic function |
|
|
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
What is multiple sclerosis? |
*An autoimmune disorder characterized by the development of plaques in the white matter of the CNS - this plaque damages the myelin sheath and interferes with impulse transmission between the CNS and the body
*This disease is marked by relapses and remissions that may or may not return clients to their previous baseline level of function - over time, client's may eventually progress to the point of quadriplegia *Life expectance is not adversely affected by this disease |
|
|
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
What are the signs and symptoms of MS? |
*Fatigue (especially in lower extremities)
*Diplopia, decreased visual acuity *Dysphagia *Muscle spasticity *Ataxia (uncontrolled movements) *Fecal incontinence *Nystagmus (often 1st symptom) *Tremor during activity *Gait, balance and coordination problems |
|
|
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
What is the treatment for MS? |
*Baclofen (muscle relaxant) Tizanadine, Lioresal
*Cyclosporine (Sandimmune) - use immunosuppressive agents to reduce frequency of relapses *Valium, to treat muscle spasticity |
|
|
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
What are the nursing considerations for a patient with MS? |
*Encourage rest periods
*Plan activities when the client has most energy *Instruct clients to avoid temperature increases *Read mail, or newspaper to the client (visual problems) *Remove throw rugs, put up safety rails *Teach client to avoid triggers: viruses and infectious agents, living in a cold climate, emotional stress, pregnancy, hot shower/bath, temperature extremes |
|
|
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
What is ALS? |
*A degenerative neurological disorder of the UPPER and LOWER motor neurons that result in deterioration and death of motor neurons - the result is progressive paralysis and muscle wasting that eventually causes respiratory paralysis and death - cognitive function is not usually affected
*Begins in one area of the body, and will spread until the entire body is involved - including the loss of ability to talk, swallow and breathe *Death typically occurs within 3 years of diagnosis due to respiratory failure *Commonly called Lou Gehrig's disease |
|
|
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
What are the signs and symptoms of ALS? |
*Muscle weakness - usually begins in one part of the body
*Muscle atrophy *Dysphagia *Dysarthria *Difficulty breathing |
|
|
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
What is the treatment of ALS? |
*Riluzole (Rilutek) slows the progression of ALS
*Baclofen or diazepam (Valium) for spasticity |
|
|
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
What are the nursing considerations for patients who have ALS? |
*Focus is maintaining optimum functioning of end of life care
*Assess respiratory status; suction as needed *Refer to hospice, review advanced directives |
|
|
Huntington's Disease
What is Huntington's disease? |
*Hereditary disease (genetic) transmitted as an autosomal dominant (only need to get 1 defective gene from 1 parent to get the disease) at time of conception
|
|
|
Huntington's Disease
What are the signs and symptoms of Huntington's disease? |
*Impaired cognition
*Sudden, jerky involuntary movements (chorea) *Dementia *Slurred speech |
|
|
Huntington's Disease
What is the treatment for Huntington's disease? |
*NO treatment is available to stop or reverse Huntington's
*Tetrabenazine (Xenazine) is the 1st drug approved by the FDA to decrease chorea by increasing dopamine |
|
|
Huntington's Disease
What are some nursing considerations for patients who have Huntington's disease? |
*Genetic counseling is important for the children of clients with the disease
|
|
|
Neuro Pharm
What does Phenytoin (Dilantin) treat? |
*Most commonly prescribed anticonvulsant
*Administered orally with meals *IV Dilantin is diluted in NS because dextrose causes medication to crystallize *Rapid IV administration of Dilantin may cause hypotension and dyshyrthmias *Therapeutic level: 10-20, any higher indicates toxicity *Toxicity symptoms: hallucinations, decreased BP and double vision |
|
|
Neuro Pharm
What are adverse effects of Phenytoin? |
*Gingival hyperplasia
*Elevated glucose (monitor glucose levels) *May cause urine to turn a HARMLESS pinkish-reddish *DO NOT take with alcohol *May cause teratogenic effect to the fetus (assess if pregnant) *May decrease effectiveness of oral contraceptives |
|
|
Neuro Pharm
What is Tegretol used for? |
*Carbamazepine (tegretol) is used for epilepsy, bipolar disorder, trigeminal and postherpetic neuralgia
*Monitor liver function tests *Monitor: persistent nausea, clay colored stools, unusual bleeding |
|
|
Neuro Pharm
What is Gabapentin (neurontin) used for? |
*Used for partial seizures (adults) and postherpetic neuralgia
|
|
|
Neuro Pharm
What is Valporic Acid (depakote) used for? |
*Used for epilepsy, migraine headaches
*Used with EXTREME CAUTION with phenobarbital (Luminal), may cause phenobarbital toxicity *May cause headache, sleepiness, blood dyscrasias, hepatotoxicity (monitor CBC and liver enzymes) |
|
|
Neuro Pharm
What is Valium and Ativan used for? |
*Seizure disorders, drug of choice for status epilepticus (given IV push)
*May cause sedation, drowsiness, dizziness, ataxia, blood dyscrasias |
|
|
Neuro Pharm
What are nursing considerations for patients who are on anticonvulsant medications? |
*Avoid alcohol and OTC medications
*Wear medic-alert bracelet (seizure may occur in public places) *Use caution when driving or performing activities that require mental alertness *Client needs to maintain periodic blood studies to determine toxicity |
|
|
Antiparkinson Drugs
What is Levodopa? |
*A drug that affects dopamine content in the blood
*Levodopa is converted into dopamine by the body; dopamine in small amounts is able to cross the blood brain barrier *Levodopa when used alone can cause adverse effects because of TOO MUCH dopamine in the PNS *Combining levodopa with carbidopa allows more levodopa to reach the brain allowing for a better drug effect *Combination makes more levodopa available and enables dosage to be reduced which decreased peripheral effects *Adverse effects: choreiform movements include involuntary muscle twitching of the limbs and facial muscles, muscle spasms *May cause dizziness, dark sweat or urine *Contraindicated in patients with narrow angle glaucoma |
|
|
Antiparkinson Drugs
What is Amantidine (Symmeterel) used for? |
*Used for Parkinson's disease, drug induced extra-pyramidal syndrome
*May cause: lightheadedness, dizziness, orthostatic hypotension |
|
|
Antiparkinson Drugs
Why is Benadryl (diphendydramine) used for Parkinson's? |
*Used for drug induced extra pyramidal syndrome
|
|
|
Antiparkinson Drugs
What are some nursing considerations for clients who are on antiparkinson drugs? |
*Obtain baseline physical assessment and evaluate client's neuromuscular status
*Antiparkinsonism drugs if effective should decrease severity of symptoms, not eliminate them *Monitor for chronic constipation *Offer frequent sips of water, ice chips if allowed to relieve dry mouth *Stress important for diet high in fiber and fluids to prevent constipation *Monitor liver function tests and observe client for signs of liver dysfunction (jaundice, dark urine, clay colored stools) *Avoid use of alcohol *Instruct client taking Levodopa to AVOID vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), this vitamin may interfere with the action of levodopa (found in whole grains, fortified cereals, liver, green vegetables) |
|
|
Intracranial Pressure
What is the expected preference range for ICP? |
*10-15 mm/Hg
*Elevate head to reduce ICP, and promote venous drainage (30 degrees) *Avoid extreme flexion, extension or rotation of the head, and maintain the body in a midline neutral position, with the head of bed elevated to 30 degrees *Discourage coughing and blowing nose frequently *May administer Colace to help soften stools to decrease strain *Report presence of cerebrospinal fluid from nose or ears to the provider |
|
|
Intracranial Pressure
What is Mannitol (Osmitol) used for? |
*Osmotic diuretic used to treat acute cerebral edema
*Insert indwelling urinary catheter to monitor fluid and renal status |
|
|
Head Injury
What is a skull fracture? |
*Skull fractures are often accompanied by brain injury, damage to the brain tissue may be the result of decreased oxygen supply or the direct impact from the skull fracture which caused the trauma
*A cervical spine injury should always be suspected when a head injury occurs, a cervical spine injury must be ruled out prior to removing any devices used to stabilize the cervical spine |
|
|
Head Injury
What are some signs of increased intracranial pressure? |
*Severe headache
*Deteriorating level of consciousness *Restlessness, irritability *Dilated pupils or pinpoint pupils that are slow to react or non-reactive *Alteration in breathing pattern (cheyne-stokes respirations, apnea) *CUSHING'S reflex: a LATE sign characterized by severe hypertension with a widening pulse pressure (systolic-diastolic = pulse pressure) and bradycardia *Cerebrospinal fluid leakage form the nose and ears ("halo" sign - yellow stain surrounded by blood on a paper towel); fluid tests positive for glucose |
|
|
Head Injury
What are some nursing interventions for clients with head injuries? |
*Monitor respiratory status regularly, the brain is dependent on oxygen to maintain function and has little reserve available if oxygen is deprived - brain function begins to diminish after 3 minutes of oxygen deprivation
*Check pupil accomodation *Monitor for signs of infection (nuchal rigidity occurs with meningitis) *Monitor for changes in LOC |
|
|
Head Injury
A client comes to the ER with "raccoon eyes", what do you suspect has occurred? |
*Skull fracture (basal skull fracture)
|
|
|
Hematomas
What is an epidural hematoma? |
*Accumulation of blood, usually from a temporal artery, between the dura and the skull
*Typically caused from a "blow" to the head |
|
|
Hematoma
A client comes to the ER after slipping on a patch of ice and hitting his head, a CT scan was ordered, and results showed an accumulation of blood between dura matter and the skull, what does this indicate? |
*An epidural hematoma
|
|
|
Surgical Interventions
What is a craniotomy? |
*A complete or partial resection of the brain
*Removed nonviable brain tissue that allows for expansion and/or removal of subdural hematomas *Involved drilling a burr hole or creating a bone flap to permit access to the affected area *Preoperative: explain procedure to clients, instruct clients to discontinue Aspirin products 72 hours prior to the procedure *Postoperatively: provide routine postoperative care to prevent complications, keep HOB elevated to 30 degrees and placed in a neutral position, assist client to avoid straining activities (bowel movements, coughing) |
|
|
Surgical Interventions
What preoperative assessments do you document as a basis as a postoperative comparison? |
*Motor strength in all extremities
|
|
|
Complications
Post craniotomy, the client is experiencing disorientation, headache and weight gain, what does the nurse suspect is occurring? |
*Syndrome of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH)
*This is a condition where fluid is retained as a result of overproduction of vasopressin or antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the posterior pituitary gland *This condition occurs when the hypothalamus has been damaged and can no longer regulate the release of ADH *If SIADH is present, client may be disoriented, report a headache and/or vomit *Treatment: fluid restriction, desmopressin, treatment of hyponatremia |
|
|
Brain Tumors
What is a supraentorial brain tumor? |
*A brain tumor that occurs in the cerebral hemispheres above the tentorium cerebelli
|
|
|
Brain Tumors
What are the signs and symptoms of a supraentorial brain tumor? |
*Severe headache, worse upon awakening, but gets better over time
*Visual symptoms (blurring, visual field deficit) *Loss of voluntary movement or the inability to control movement *Nausea with or without vomiting |
|
|
Neuro Pharm
What other medications may help to reduce cerebral edema? |
*Corticosteroids (solu-medrol)
*Corticosteroids quickly reduce cerebral edema, and may be rapidly administered to maximize their effectiveness |
|
|
Monitoring ICP
What are some ways to monitor a clients ICP? |
*Intraventicular catheter
*Subarachnoid screw *Intraparenchymal sensor *Subdural bolt *Possible complications: infection and hemorrhage |
|
|
Neuro Pharm
What is Phenobarbital (Nembutal) used for? |
*Used to induce a barbiturate coma, to decrease cerebral metabolic demands
*This treatment is preformed when ICP is refractory to treatment, and has exceeded to 25 mm/hg for 30 minutes, and 30 mm/hg in 1 minute |
|
|
Trigeminal Neuralgia
What is trigeminal neuralgia? |
*Also called Tic Douloureux
*Root of the trigeminal (5th cranial nerve), becomes very painful *Cause is unknown, but may be due to blood vessel pressing on trigeminal nerve as it exits the brainstem *Compression causes wearing away or damage to the protective coating around the nerve (myelin sheath) |
|
|
Trigeminal Neuralgia
What are the signs and symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia? |
*Excruciating pain in jaw, and parts of the face that comes in spasms, lasting seconds to hours
|
|
|
Trigeminal Neuralgia
What are some pain triggers of trigeminal neuralgia? |
*Slight touch to the face
*A breeze *Change in temperature *Mouth full of food |
|
|
Bell's Palsy
What is Bell's Palsy? |
*Temporary, partial, one-sided facial paralysis and weakness caused by ischemia or inflammation of the 7th cranial nerve (facial)
|
|
|
Bell's Palsy
What are the signs and symptoms of Bell's Palsy? |
*Lop sided facial appearance
*Left eye on affected side does not close *Client cannot control mouth, drooling *Mouth does not turn up when smiling |
|
|
Bell's Palsy
What are some nursing interventions for the client with Bell's Palsy? |
*Special eye care may be necessary
*Heat and massage *Medications: prednisone *Symptoms will subside gradually (may take months) |
|
|
Neuro Pharm
What is Carbemazepine (tegretol) used for? |
*Treats different types of seizures
*Treats nerve pain and bipolar disorders *Adverse effects: constipation, blurred vision, dizziness and drowsiness *MONITOR LIVER FUNCTION *Potential complications: BLEEDING, TARRY STOOLS, DIPLOPIA |
|
|
Antiparkinson Drugs
What is Cogentin (benzatropine) used for? |
*Treats symptoms of Parkinson's disease
*Adverse effects: blurred vision, nausea and vomiting, confusion *Contraindications: glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, myasthenia gravis |
|
|
Neuro Pharm
What is Baclofen used for? |
*Treats muscle spasms caused by multiple sclerosis or damage to the brain or spinal cord, muscle relaxant
*Adverse effects: lightheadedness, confusion, swelling in ankles |
|
|
Antiparkinson Drugs
What is Mirapex used for? |
*Treats Parkinson's disease and Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS)
*Adverse effects: dizziness, somnolence, insomnia, hallucinations, confusion, nausea, dyspepsia and syncope |
|
|
Neuro Pharm
What is Topamax (topirmate) used for? |
*Helps control and prevent certain kinds of seizures
*Also can prevent migraine headaches in adults *Adverse effects: change in appetite, bitter taste, nasuea |
|
|
Bell's Palsy
What should the nurse include in the plan of care for the client with Bell's Palsy? |
*Prevent corneal damage (provide eye patch and lubricant)
|
|
|
Trigeminal Neuralgia
A patient is complaining of excruciating facial pain, especially after drinking cold beverages, what does the nurse suspect as the diagnosis? |
*Trigeminal neuralgia
|
|
|
Migraine Headaches
You are caring for a patient with a diagnosis of a migraine headache, and reports the pain level to be at a 4, what type of medication does the nurse expect to administer? |
*Non opioid analgesic (Motrin, Acetaminophen)
|
|
|
Intracranial Pressure
You are caring for a client who was admitted to the ER for a gunshot wound to the head, which of the following signs indicate ICP? |
*Headache
*Dilated pupils *Decorticate posturing *Decreasing LOC |
|
|
Surgical Interventions
A patient is scheduled for brain surgery, what do you expect to do as a nurse prior the surgery? |
*Monitor strength in all extremities and document
|
|
|
Brain Trauma
A patient has sustained an injury to the Broca area of the brain, how do you expect to compensate? |
*Provide patient with a whiteboard and marker
|
|
|
Cranial Nerves
A nurse is assessing the client's extra ocular eye movements, which cranial nerves does she assess? |
*3, 4 and 6
*Remember! 3, 4, 6 - the eyes do tricks! |
|
|
The Brain
Which part of the brain controls judgement, personality and affect? |
*Frontal lobe
|
|
|
An older client diagnosed with Parkinson's disease is currently living independently with his wife of 50 years, and takes Levodopa with carbidopa (Sinemet) to control his disease, due to a recent episode of aspiration pneumonia, the client has been admitted to the hospital for IV antibiotics and respiratory therapies.
Which of the following findings should the nurse expect to find when collecting data? (select all that apply) A. Decreased vision B. Pill-rolling tremor of the fingers C. Shuffling gait D. High-pitched, squeaky voice E. Lack of facial expressions F. Frequent periods of sleep |
*B, C, E
*Clients with PD will experience pill-rolling tremor of the fingers, shuffling gait, and lack of facial expressions *High-pitched squeaky voice, decreased vision and frequent periods of sleep are NOT a direct effect of PD *Clients will experience LACK OF SLEEP, rather than frequent periods of sleep |
|
|
Which of the following questions should the nurse ask to determine if the medication is being given in appropriate dosages at the appropriate time?
A. "Is your weight staying the same?" B. "Can you see the television from a comfortable distance?" C. "Are you having periods when walking is more difficult?" D. "Are you experiencing any night sweat?" |
*C, "Are you having periods when walking is more difficult?"
*Increased difficulty walking may indicate the client is having periods when the medication is "wearing off" and adjustment of dosage is indicated |
|
|
Which of the following is the priority intervention the nurse should recommend for inclusion on the client's plan of care?
A. Assist the client to the restroom B. Have assistive personal assist the client with dressing C. Have suction equipment at bedside D. Observe IV catheter insertion site for inflammation every 12 hours |
*C, have suction equipment at bedside
*Using airway, breathing, circulation priority-setting framework, suction equipment should be placed at the client's bedside due to continued risk for aspiration *Remember!!! All other answers may be correct, however, they are not the PRIORITY |
|
|
Decorticate & Decerebrate Posturing
What is decorticate and decerebrate posturing? |
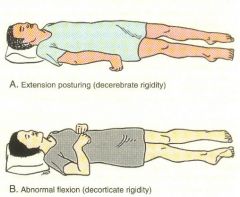
*Decorticate: abnormal flexion (turning inward)
*Decerebrate: abnormal extension (turning outward) |
|
|
A patient comes to the ER suffering from a traumatic brain injury, the nurse is monitoring for signs of intracranial pressure, what signs would you monitor for?
|
*Dilated pupils
*Level of consciousness (early sign) *Breathing patterns |
|
|
A patient is suffering from a head injury. The nurse is watching for signs of intracranial pressure, what are the LATE signs of intracranial pressure?
|
*Cushing's triad: rising BP, bradycardia and widening pulse pressure
|
|
|
A client with ICP is on Osmitol, an osmotic diuretic, how does the nurse assess the effectiveness of the drug?
|
*Assess neuro status
*Assess intake and output |
|
|
A patient is being administered Decadron for an expanding brain tumor, what is the purpose of this drug?
|
*Decadron may help reduce the size of the tumor
*"Decadron may cause you to retain fluids" *You may notice weight gain" *"Decadron is given to reduce swelling in the brain" |
|
|
A client who has been diagnosed with a cerebral aneurysm is complaining of a severe headache, what is the nurse's first action?
|
*Call MD STAT
|
|
|
A client admitted to the ER is complaining of a throbbing, frontal, temporal headache, preceded by visual disturbances, the client fears they will stroke - what does the nurse suspect to be the problem?
|
*Migraine headache
|
|
|
A nurse is developing a teaching plan for a client diagnosed with Guillan Barre to undergo a electromyography, what should the nurse include in preparing the client for the procedure?
|
*Patient may experience a little discomfort, as needles are inserted into the skin
|
|
|
A nurse is caring for a client who just had a CT scan with contrast dye, what important lab level should the nurse evaluate?
|
*Creatinine
|
|
|
What indicates a POSITIVE Romberg test?
|
*Patient unable to keep balance
|
|
|
What nursing interventions should the nurse and AP take to help the client increase mobility and lessen fatigue?
|
*It is important to encourage the client to conserve energy and increase mobility by using assistive devices such as canes, walkers, and wheelchairs
*Client should wear non-slip, flat, tie shoes *The nurse should ensure that the lighting is adequate, and cords and furniture that could trip the client are removed *The nurse should schedule activities that cause fatigue in the morning and then plan rest periods in the afternoon |
|
|
Which of the following client history findings may have triggered this client's MS exacerbation? (select all that apply)
A. Sinusitis B. Broad spectrum antibiotics C. Constipation D. Emotional stress E. Use of a hot tub |
*A, D, E
*Emotional and physical stress and illness, such as sinusitis, can cause an exacerbation of MS *Taking a hot shower or bath, and using a hot tub, can also precipitate an exacerbation |
|
|
A nurse is caring for a client admitted to the hospital with respiratory difficulty after being diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) approximately 1 year ago, the client is also exhibiting difficulty speaking and swallowing.
Which of the following should the nurse anticipate during data collection? (select all that apply) A. Muscle atrophy B. Fluctuations in BP C. Incontinence D. Ineffective cough E. Loss of cognitive function F. Muscle weakness G. Loss of sensation |
*A, C, D, F
*ALS is a degenerative disease of the motor neurons characterized by muscle weakness progressing to muscle atrophy and eventually paralysis and death *Ineffective cough and incontinence may also occur secondary to nerve involvement |
|
|
A nurse is collecting data from a client who was admitted to the medical-surgical unit 12 hours ago after falling off a ladder and hitting his head. The client is drowsy, but responds to verbal commands, and opens his eyes when the nurse calls his name. He is oriented to time, place and person. The nurse should document that the client's Glasgow Coma Scale Score is which of the following?
A. 15 B. 14 C. 13 D. 12 |
*B
*The client's Glasgow Coma Scale Score is 14 *Eye opening response is 3 (secondary to voice) *Verbal response is 5 (coherent and oriented to conversation) *Motor response is 6 (follows commands) *3+5+6 = 14 |
|
|
Which of the following interventions should the nurse expect to implement for a patient with ICP? (select all that apply)
A. Keep head of the bed elevated to 30 degrees B. Ensure SaO2 is greater than or equal to 95% C. Have client cough and deep breathe ever 2 hours D. Ensure PaCO2 is kept at 45 mm Hg or above E. Notify the provider of an ICP of 14 mm Hg F. Encourage the client to assist when being pulled up in bed |
*A, B
*The head of the client's bed should be elevated to 30 degrees at ALL times, with the head in a neutral position *The SaO2 should be kept greater than or equal to 95% to ensure adequate perfusion of the brain *Actions that require coughing, and assisting the nurse when being pulled up in bed should be avoided *A PaCO2 of 45 will cause vasodilation of the cerebral vessels causing increased ICP *An ICP of 14 is within normal range, and does not require notification to the provider |

