![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the pattern of multiple sclerosis called? It involves? 3 |
Perivascular pattern Juxtacortical Periventricular Corpus callosum |
|
|
What cutoff size of lesion that are unlikely to be vascular in nature? |
>15 mm |
|
|
What locations make you think less vascular 3 and which are highly vascular in nature 1? |
Juxtacortical, corpus callosum, infratentorial, Basal ganglia |
|
|
2 main points in McDonald's criteria ? |
Dissemination in place more than 1 in at least 2 of these locations ( juxtacortical, periventricular and infratentorial) Dissemination in time ( active and non active lesions) |
|
|
Commonest subtype of MS ? |
Relapsing remitting course 85% |
|
|
Most specific site for MS lesions? |
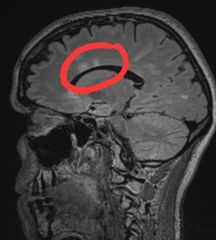
Calloso-septal Interface 98% specific for MS |
|
|
Differences in involvement of MS in adult and pediatric? |
Pediatric more infratentorial Adult supratentorial |
|
|
Most common location of MS in spine ? Cervical, thoracic and lumbar |
Cervical spine 65% |
|
|
MS spinal cord lesions tend to be ------- located. |
Peripherally located |
|
|
Which sequence is most sensitive in detection of MS lesions supra and infratentorial? |
Supra T2FLAIR ( juxta and periventricular) Infra T2 |
|
|
MR spectroscopy finding in MS ? |
Reduced NAA peaks within the plaques |
|
|
Active vs non active MS lesions? |
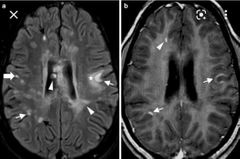
Active incomplete ring enhancement and diffusion restriction |
|
|
Tumor vs MS lesions? |
MS incomplete ring enhancement Tumor complete ring enhancement |
|
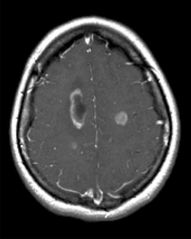
Sign Diagnosis |
Open ring sign ADEM |
|
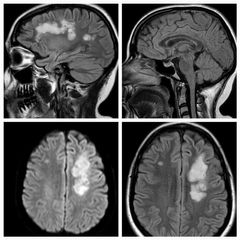
Findings Diagnosis |
Multiple high T2 FLAIR signals in the white matter periventricular and juxtacortical with sparing of callososeptal interface, they show also diffusion restriction ADEM |
|
|
ADEM stands for |
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis |
|
|
Causes of ADEM? 2 |
Viral infection Post vaccination |
|
|
How ADEM lesions enhances ? Course of the disease? |
Nodular open ring enhancement
Disappear after 6 months ( monophasic) |
|
|
What is the fulminant form of ADEM? |
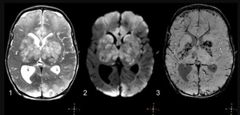
Acute hemorrhagic leukoencephalitis ( massive brain swelling, hemorrhage and death) |
|
|
What is Devics disease? 2 Other name ? |
Transverse myelitis and optic neuritis Neuromyelitis optica |
|
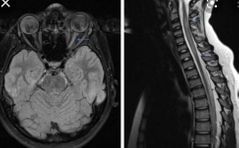
Findings Diagnosis |
High t2 signal of the left optic nerve and high t2 signal of within the cervical spine Neuromyelitis optica ( Devics) |
|
|
Marburg variant of MS? |
Childhood variant that is fulminant leading to death and has febrile prodrome |
|
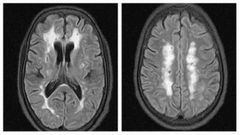
Finding Diagnosis |
Multiple high T2 FLAIR signal in the white matter of centrum semiovale and periventricular areas with sparing of U fibers. Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy |
|
|
What is SAE ? Other name ? |
Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy Multi infarct dementia of white matter only Binswanger disease |
|
|
SAE Age of onset Risk factor 2 radiological features of subcortical artriosclerotic encephalopathy?
|
Involving centrum semiovale Spares U fibres Patient > 50 years HTN |
|
|
If you see features of SAE but in a patient less than 40 years you think of ? |
Genetically transmitted CADASIL |
|
|
Most common hereditary stroke disorder is ? |
CADASIL |
|
|
CADASIL stands for ? 2 clinical presentation? |
Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarction and leukoencephalopathy
Migraine and stroke |
|
|
Which chromosome affected in CADASIL? |
Notch 3 chromosome 19 |
|
|
Typical appearance of CADASIL in MRI? |
Involving U fibres Multiple high t2 white matter disease of different vascular territories. |
|
|
Commonly and less commonly involved lobes in CADASIL? |
Common temporal lobe and frontal Spares occipital lobe |
|
|
Top 3 primary tribes for dementia? |
1- Alzheimer disease 2- Multi infarcts dementia 3- Lewi body dementia |
|
|
Main three descriptors in Alzheimer disease ? |
Tauopathy Amyloid cascade Neurofibrillary tangles |
|
|
Two main risk factors for Alzheimer disease? |
Age Down syndrome |
|
|
Two main MRI finding in Alzheimer disease? |
Hippocampal atrophy Temporal horn atrophy > 3mm in 65% of cases |
|
|
FDG pattern in Alzheimer disease ? |
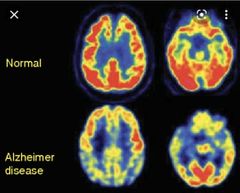
Low posterior temporo- parietal FDG uptake |
|
|
What other tracer can be use in Alzheimer disease? Why? |
Pittsburgh compound B ( 11C PiB) It is amyloid binding tracer |
|
|
Other term for multi infarcts dementia? |
Vascular dementia |
|
|
Risk factors for vascular dementia ? 4 |
Fatty food HTN Smoking CADASIL |
|
|
MRI features of vascular dementia 2 FDG feature 2 |
Brain atrophy disproportionate to age Multiple cortical and lacunar infarcts Variable reduced uptake and it can involve motor strip unlike AD and Lewi body dementia |
|
|
Dementia with Lewi bodies, Pathophysiology terms ? 2 |
Synuclein and alpha synuclein |
|
|
Clinical triad of lewi body dementia? |
1- visual hallucinations 2- spontaneous parkinsonism 3- fluctuating concentration and alertness |
|
|
How lewi body dementia is different than parkinsons? |
Parkinsonism comes after dementia |
|
|
MRI features of lewi bodies dementia?2 |
Mild Generalised brain atrophy Hippocampus normal |
|
|
FDG pattern in Lewi bodies dementia? |
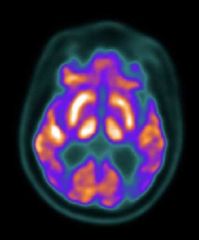
Decreased uptake of the lateral Occipital cortex with sparing of mid posterior cingulate gyrus ( cingulate Island sign) |
|
|
MRI finding in frontotemporal dementia? Other term for it? |
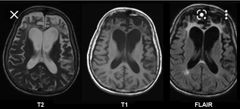
Severe symmetrical Atrophy of the frontal lobes Picks disease |
|
|
FDG uptake in frontotemporal dementia? |
Low uptake in frontotemporal region |
|
|
Picks disease Age of onset and clinical symptoms? |
40-50s Abnormal behaviour |
|
|
First area to be affected by Alzheimer disease ? |
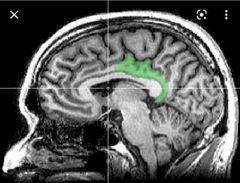
Posterior cingulate gyrus |

