![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is membrane potential? |
It is the charge difference between the cell's cytoplasm and the extracellular fluid |
|
|
What is membrane voltage? |
Membrane potential = membrane voltage Voltage is the separation of charge with the potential to do work Greater difference in charge, greater voltage |
|
|
When it comes to membrane potential, what does the plasma membrane act as? |
A barrier to some of the charges |
|
|
At rest, where are most sodium ions? |
Outside of the cell
|
|
|
At rest, where are most potassium ions? |
Inside the cell |
|
|
At rest, where are most chlorine ions? |
Outside the cell |
|
|
At rest, where are most calcium ions? |
Outside the cell |
|
|
At rest, where are most protein molecules? |
Inside the cell
|
|
|
Are neurons polarized at rest? |
Yes |
|
|
What is resting potential? |
Membrane potential when the neuron is not stimulated. In other words, when sodium and potassium reach equilibrium concentrations for inside and outside the cell |
|
|
What is passive diffusion? |
Flow down their concentration gradients |
|
|
What occurs during resting potential? |
Ions moving across membrane |
|
|
What are the two forces at play during resting potential? |
Diffusion (chemical) Electrostatic Pressure (electrical) |
|
|
What is electrochemical equilibrium? |
When diffusion and electrostatic pressure balance each other out |
|
|
What are two integration inputs from the synapses that tell a neuron to depolarize |
Spatial summation and temporal summation |
|
|
What is spatial summation? |
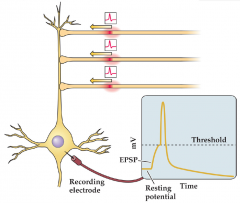
Takes in to account postsynaptic potentials from different location on the neuron |
|
|
What is temporal summation? |
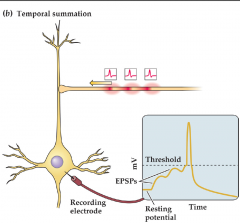
Takes in to account postsynaptic potentials from different times |
|
|
When depolarizing a neuron, what is it called when we observe a characteristic response after reaching a threshold? |
Action potential or "spike" |
|
|
What does a graded response look like? |

|
|
|
What does a all-or-nothing response look like? |

|
|
|
What is the direction of potential propagation and why? |
Along axon away from the cell body because of the refractory period |
|
|
Which has a faster speed of signal conduction: myelinated or unmyelinated axons? |
Myelinated |
|
|
Myelinated axons have what kind of conduction? |
Saltatory conduction |
|
|
Unmyelinated axons have what kind of conduction? |
continuous conduction |
|
|
What are the two types of presynaptic neurons? |
Excitatory and inhibitory |
|
|
What effect does excitatory presynaptic neurons have on postsynaptic potentials? |
Promotes postsynaptic depolarization |
|
|
What effect does inhibitory presynaptic neurons have on postsynaptic potentials? |
Inhibits postsynaptic depolarization |
|
|
The resting potential is A) negative in neurons and positive in glial cells B) partially established by the uneven distribution of ions across the membrane C) a property unique to multipolar neurons D) established partially by the rapid influx of sodium ions |
B) partially established by the uneven distribution of ions across the membrane |
|
|
Upon reaching the threshold for an action potential, the next step in its generation is the opening of _____ channels. |
Sodium |
|
|
A particular spider venom causes potassium channels in motor neurons to constantly leak (stay open). If the spider bit its prey, would the prey be able to move? Why or why not? Be sure to mention molecular components involved. |
Its prey will not be able to move. In order for the prey to move its muscle, information has to be sent via motor neuron. If the motor neuron's potassium channels are constantly open, then the resting potential will be altered. Specifically it would be highly negative inside the cell and an action potential would not occur. The influx of sodium ions would not raise the membrane potential to threshold. |

