![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Basilar aa location
|
- ventral to pons
|
|
|
Anterior spinal aa
|
Ant 2/3 Spinal Cord
Lower Brainstem; Medulla - pyramids - ML - roots to CN XII |
|
|
Internal Carotid System
- branches |
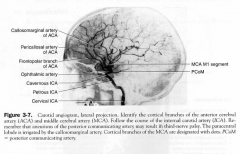
- opthalmic aa.
- Posterior communicating aa. - anterior choroidal aa - anterior cerebral aa. - middle cerebral aa. |
|
|
opthalmic aa
|
- opthalmic aa. (enters orbit with CN II and branches to central aa. of retina)
- causes blindness |
|
|
- Posterior communicating aa.
|
- supplies hypothalamus & ventral thalamus
- 2nd most common site for aneurysm and causes IIIN palsy |
|
|
Anterior Choroidal aa
|
- LGN
- globus pallidus - posteior limb of internal capsule |
|
|
Anterior Cerebral aa
|
- medial surface of hemisphere from frontal pole to parieto-occipital sulcus
1. paracentral lobule (leg-foot motor and sensory) 2. Most common aneurysm of circle of willis causing a bitemporal lower quadrantanopia 3. Medial striate aa. are the penetrating aa and supply anterior putamen and caudate nucleus and anteriorinferior internal capsule |
|
|
Middle cerebral aa.
|
1. lateral convexity of the hemisphere
a. broca's and wernickes areas b. face, arm motor and sensory c. frontal eye field (in prefrontal cortex for attention and movements) 2. Lateral Striate aa. - internal capsule, caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus |
|
|
Territories of the cerebral aa.
|
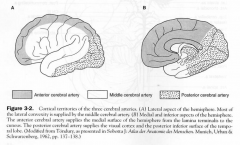
|
|
|
BS to brain
|
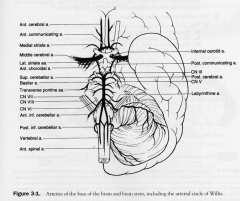
|
|
|
Vertibrobasilar System
|
- vertebral aa
- basilar aa |
|
|
Vertebral aa.
|
- branch of subclavian
- branches to anterior spinal aa and PICA, dorsolateral quadrant of the medulla (NA, CN IX, X, XI) and inferior surface of cerebellum |
|
|
Basilar aa.
|
- formed by 2 vertebral aa.
1. paramedian branches of the pontine aa, base of the pons (corticospinal and VI fibres) 2. Labyrinthine aa 15% from basillar 85% of people from the AICA 3. AICA: supplies caudal lateral potine tegmentunm, CN VII, spinal trigeminal tract and inferior curface of cerebellum 4. Superior cerebellar aa; dorsolateral tegmentum of rostral pons, superior cerebellar peduncle, superior surface of the cerebellum and cerebellar nuclei and the cochlear nuclei 5. Posterior cerebral artery connected to carotid via posterior communicating aa. Major BS to midbrain, thalamus, lateral and medial geniculate bodies and occipital lobe - occlusion of PCA = contralateral hemianopia with macular sparing |
|
|
BS of the internal Capsule
|
- mainly lateral striate aa of MCA and anterior choroidal aa
|
|
|
Veins of the Brain
|
1. superior cerebral (bridging) veins; drain the superior sagittal sinus.
2. Great Cerebral Vein of Galen drains deep cerebral veins into the straight sinus |
|
|
Venous Dural Sinuses
|
1. superior sagittal sinus recieves from bridging veins and arachnoid villi
2. Cavernous sinus |
|
|
Venous Sinuses
|
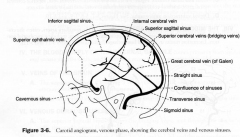
- confluence of the sinuses
- transverse sinus - straight sinus |
|
|
Middle Meningeal aa
|
branch off maxillary aa
- enters through foramen spinosum - supplies most of the dura |
|
|
Carotid and vertebral Angiograms
|
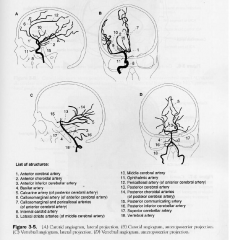
|

