![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which brain structures are involved in emotional memory processing? |
- Hypothalamus
- Frontal Cortex - Prefrontal Cortex - Amygdala - Hippocampus |
|
|
What is the role of the hypothalamus in emotional memory processing?
|
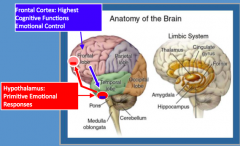
- Regulates primitive emotional responses (Fighting, Feeding, Fleeing, Mating)
- Reciprocal feedback loop with frontal lobe |
|
|
What is the role of the frontal cortex in emotional memory processing?
|
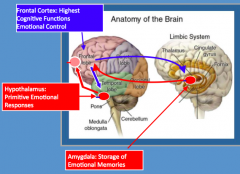
- Highest cognitive functions - control over emotions
- Judgment, decision-making, morality, compassion, responsibility - Reciprocal feedback loop with Hypothalamus and Amygdala |
|
|
How long does it take for full development of the frontal cortex?
|
>20 years
|
|
|
What is the role of the prefrontal cortex in emotional memory processing?
|
Production and appreciation of art (beauty) as an emotion
|
|
|
What is the role of the amygdala in emotional memory processing?
|
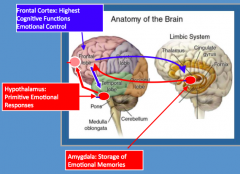
- Storage of emotional memories
- Feedback loop with frontal cortex |
|
|
What is the role of the Hippocampus in emotional memory processing?
|
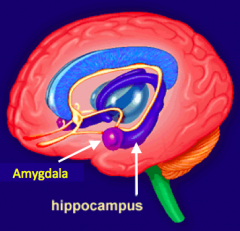
Storgage of Emotional Memories (EPISODIC MEMORY) - activated and inhibited by emotionality
|
|
|
What is hippocampal functioning necessary for? How can it be disrupted?
|
- Explicit, episodic or declarative memory
- Highly susceptible to disruption by stress |
|
|
What is synaptic plasticity?
|
Ability of synapses to change their strength in response to experience and a cellular model of learning and memory
|
|
|
What are the types of Glutamatergic receptors?
|
- AMPA Receptors - basal synaptic transmission
- NMDA Receptors - blocked by Mg2+; activated when cells are depolarized; important for synaptic plasticity |
|
|
How does Calcium affect AMPA receptors?
|
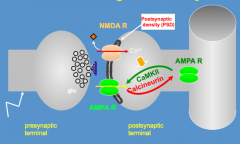
- Ca2+ enters post-synaptic terminal via NMDA receptors
- Activates CamKII (CaM kinase II) - Moves AMPA R to postsynaptic density - Calcineurin (phosphatase) action acts to remove AMPA R from postsynaptic density |
|
|
How does the action of NMDA and AMPA receptors mediate synaptic plasticity?
|
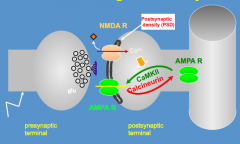
- Synaptic Plasticity = ability of synapses to change their strength in response to experience and a cellular model of learning and memory
- NMDA R activated --> leads to AMPA R joining post-synaptic density (both are glutamatergic receptors) |
|
|
What kind of receptors are blocked by Mg2+?
|
NMDA Glutamatergic Receptors (activated by depolarization)
|
|
|
How is CaM-Kinase II related to synaptic plasticity?
|
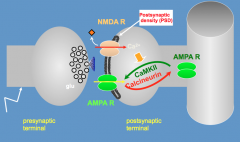
- When Ca2+ enters through an NMDA-R it activates CaM-Kinase II
- CaMKII phosphorylates AMPA-R and brings it to the postsynaptic density (PSD) - Increases conductance of post-synaptic neuron * Long-Term Potentiation * |
|
|
How is Calcineurin related to synaptic plasticity?
|
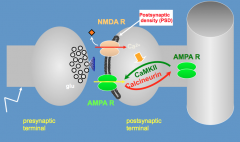
- Calcineurin is a phosphatase that removes the phosphate from AMPA-R
- This leads to the AMPA-R being removed from the post-synaptic density (PSD), decreasing conductance *Long-Term Depression* |
|
|
What are the two phases of Long Term Potentiation (LTP)?
|
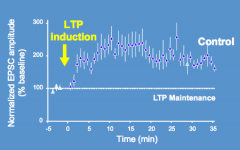
- LTP induction
- LTP maintenance |
|
|
How does Long Term Potentiation (LTP) represent a cellular model for learning and memory?
|
- Generated through changes in synaptic function
- Operates in a network of neurons - Pathway specific - Different forms with varying durations |
|
|
What types of evidence is there that Long Term Potentiation (LTP) represents a cellular model for learning and memory?
|
- Electrophysiological
- Pharmacological - Genetic - Structural - Disease States - LTP and Place cells |
|
|
What tests can be used to study learning and memory on the behavioral level?
|
- Morris Water Maze
- Fear Conditioning |
|
|
What happens in the Morris Water Maze? What are you testing?
|
- Put mouse in pool, there is one quadrant that has a raised platform; if they're capable of learning they will return to the platform quickly when returned; if you remove the platform, they will keep checking that same location
- Behavioral learning and memory - Tests spatial memory (hippocampal-dependent task) |
|
|
What happens in Fear Conditioning? What are you testing?
|
- Expose mouse to tone and shock in light environment (30 min. - 1 day)
- Later expose mouse to same context w/o cue, or new context w/ cue - Should get fear response - Behavioral learning and memory - Context --> hippocampus and amygdala - Cue --> Amygdala |
|
|
A cued-dependent (e.g., tone) fear conditioning response relies on what part of the brain to get the fear response?
|
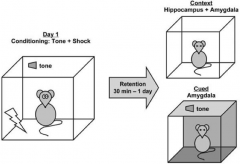
Amygdala-dependent task
|
|
|
A context-dependent (e.g., same cage) fear conditioning response relies on what part of the brain to get the fear response?
|
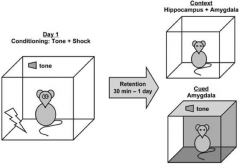
Hippocampus and Amygdala
|
|
|
How does Long Term Potentiation (LTP) affect synapses?
|
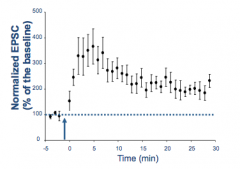
Strengthens / enhances synaptic strength
|
|
|
How does Long Term Depression (LTD) affect synapses?
|
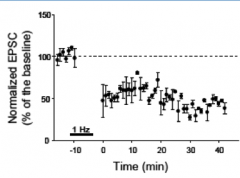
Depresses synaptic strength
|
|
|
Which enzymes are important for LTP and LTD?
|
- LTP - CaMKII
- LTD - Calcineurin |
|
|
What molecule controls the synaptic plasticity balance? How?
|
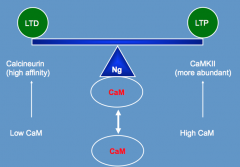
- Neurogranin
- Regulates CaM availability (CaM necessary for LTP) |
|
|
What deficits occur to learning and memory with age?
|
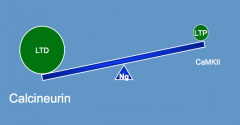
- Synaptic plasticity imbalance
- Changes in levels of important molecules (e.g., CaMKII and Calcineurin) |
|
|
How do older mice perform on the Water Maze Test?
|
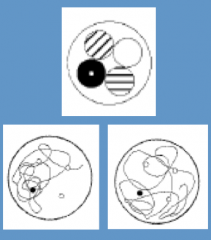
- May not remember to go directly back to same platform (bottom right)
- This is a hippocampal dependent task |

