![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
121 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Forebrain (prosencephalon) |
Telencephalon: cerebrum, hippocampus, basal ganglia, amygdala Diencephalon: thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, epithalamus |
|
|
|
Midbrain (mesebcephalon) |
Tectum: superior and inferior colliculi Tegmentum: cerebral aqueduct, periaqueductal gray, reticular formation, substantial nigra, red nucleus |
|
|
|
Hindbrain (rhombencephalon) |
Metencephalon: cerebellum, pons Myelencephalon: medulla oblongota |
|
|
|
Brainstem |
Midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata |
|
|
|
Sympathetic nervous system |
Fight or flight Norepinephrine neurotransmitter |
|
|
|
Parasympathetic nervous system |
Rest and digest AcH transmitter |
|
|
|
Limbic system |
Corpus callosum, olfactory tract, mammillary bodies, fornix, thalamus nuclei, amygdala, hippocampus, parahippocampal gyrus, Cingulate gyrus, hypothalamic nuclei Control and expression of mood and emotion, recent memory, smell, appetite |
|
|
|
Frontal lobe |
Voluntary movements Broca’s area Personality Reasoning Behavior Executive functions |
|
|
|
Parietal lobe |
Sensation, vibration, temp Receives info from other areas Interpret language Spatial and visual perception |
|
|
|
Temporal lobe |
Primary auditory processing and olfaction Wernickes area Interpret emotions |
|
|
|
Occipital lobe |
Main processing center for visual info Processes visual info Judgment of distance |
|
|
|
Hippocampus |
Forming and storing new memories Declarative memory Learning language Sends memory for long term storage |
|
|
|
Basal ganglia |
Gray matter deep within white matter of cerebrum Caudate, putamen, globus pallidus, substantia nigra, subthalamic nuclei Voluntary movement,autonomic movement, posture, muscle tone |
|
|
|
Anygdala |
Emotional and social processing Fear and pleasure responses Arousal Processing of memory |
|
|
|
Thalamus |
Processes info that goes to cerebral cortex Coordinates sensory perception and movement Relays info appropriately to other areas of cortex |
|
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Receives and integrates info from ANS and regulates hormones Controls hunger, thirst, sexual behavior, sleeping Regulates temp, adrenal glands, pituitary gland |
|
|
|
Subthalamus |
Regulates movements produced by muscles Associated with basal ganglia and sunstantia nigra |
|
|
|
Epithalamus |
Represented by pineal gland Secretes melatonin and involved in circadian rhythms Associated with limbic system and basal ganglia |
|
|
|
Cerebellum |
Anterior, posterior, and flocculonodular Damage to one side produces ipsilateral impairments to body Lessons produce ataxia, nystagmus, tremor, poor coordination |
|
|
|
Pons |
Regulation of respiratory rate Associated with orientation of head in relation to visual and auditory stimuli CN5-8 originate here |
|
|
|
Medulla oblongata |
Autonomic nervous activity and regulation of respiration and heart rate Relays somatic sensory info from internal organs Arousal and sleep CN 9-12 originate here |
|
|
|
Brainstem |
Midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata Relay station sending messages between various parts of body and cerebral cortex |
|
|
|
Anterior cerebral artery and stroke |
Anterior frontal lobe Medial surface of frontal and parietal Contralateral LE motor and sensory involvement Neglect, aphasia, behavior |
|
|
|
Middle cerebral artery and stroke |
Flat affect Wernickes or brocas Homonymous hemianopsia Apraxia UE > LE |
|
|
|
Posterior cerebral artery and atroke |
Contralateral pain and temp sensory loss Contralateral hemiplegia Ataxia |
|
|
|
Vertebral basilar artery and atroke |
Pons, midbrain, cerebellum, medulla, midbrain Consciousness, hemi or tetra, lot of bad stuff |
|
|
|
Meninges - dura mater |
Outermost layer, four folds, lines periosteum of skull, subdural space separates this and arachnoid |
|
|
|
Meninges - dura mater |
Outermost layer, four folds, lines periosteum of skull, subdural space separates this and arachnoid |
|
|
|
Meninges - arachnoid |
Middle layer, impermeable, subarachnoid space separates this and pia |
|
|
|
Meninges - pia mater |
Innermost layer, covers contours of brain, forms choroid plexus in ventricular system |
|
|
|
Meningitis |
Fever, headache, stiff neck, lumbar pain, budzinskis sign, kernigs sign Lumbar puncture gold standard |
|
|
|
Epidural space |
Area between skull and outermost layer |
|
|
|
Subdural space |
Dura and arachnoid space |
|
|
|
Subarachnoid space |
Between arachnoid and pia mater, contains CSF and circulatory system of cerebral cortex |
|
|
|
Blood brain barrier |
Meninges, glial cells, capillary beds of brain Exchange of nutrients between CND and vascular system Protects CNS by restricting certain molecules to pass |
|
|
|
Fasciciulus cuneatus |
Sensory- trunk, neck, UE Proprioception, vibration, 2 point |
|
|
|
Fasciculus gracilis |
Sensory- trunk, LE Proprioception, vibration, 2 point |
|
|
|
Fasciculus gracilis |
Sensory- trunk, LE Proprioception, vibration, 2 point |
|
|
|
Spinocerebellar tract dorsal |
Ipsilateral subconscious proprioception, tension, joint sense, posture of trunk and LE |
|
|
|
Fasciculus gracilis |
Sensory- trunk, LE Proprioception, vibration, 2 point |
|
|
|
Spinocerebellar tract dorsal |
Ipsilateral subconscious proprioception, tension, joint sense, posture of trunk and LE |
|
|
|
Spinocerebellar tract ventral |
Some fibers cross and recross at level of pons, ipsilateral subconscious proprioception, tension, joint sense, posture of trunk, UE and LE |
|
|
|
Spino olivary tract |
Ascend to cerebellum Relays info from cutaneous and proprioceptive organs |
|
|
|
Spino reticular tract |
Afferent pathway for reticular info to influence consciousness |
|
|
|
Spino tectal tract |
Spinovisual reflexes and assists with movement of eyes and head toward stimulus |
|
|
|
Anterior spinothalamic tract |
Light touch and pressure |
|
|
|
Lateral spino thalamic tract |
Pain and temp |
|
|
|
Anterior corticospinal tract |
Pyramidal motor for ipsilateral voluntary, discrete, and skilled movements Positive babinskis |
|
|
|
Lateral corticospinal tract |
Pyramidal motor contralateral voluntary fine movement Positive babinskis |
|
|
|
Reticulospinal tract |
Extrapyramidal motor for facilitation and inhibition of voluntary and reflex activity through alpha and gamma motor neurons |
|
|
|
Brachial plexus |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Rubrospinal tract |
Extrapyramidal motor input of gross postural tone, facilitating activity of flexors and inhibiting of extensors |
|
|
|
Tectospinal tract |
Extrapyramidal motor for contralateral postural muscle tone associated with auditory/visual stimuli |
|
|
|
PNS terminology |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
PNS terminology |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
PNS Alpha fibers |
Muscle spindle, GTO, tocuh |
|
|
|
PNS beta fibers |
Touch, kinesthesia, muscle spindle |
|
|
|
PNS gamma fibers |
Touch, pressure, gamma motor neurons |
|
|
|
Cranial nerves |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Brachial plexus |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
LE innervation |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
DTRs |
Biceps - C5-6 Brachioradialis - C5-6 Triceps - C6-7 Patellar - L3-4 Achilles - S1-2 Hamstring -L4-5 |
|
|
|
UMN vs LMN |
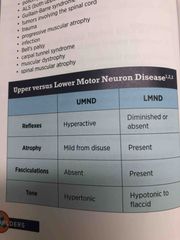
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Modified ashworth scale |
Assesses spasticity |
0 - no increase 1 - slight muscle tone increase, catch and release 1+ - slight increase, catch followed by minimal resistance 2 - more increase but still easily move through ROM 3 - considerable increase, PROM difficult 4 - rigid in flexion or extension |
|
|
Classification of acute nerve injuries |
Neurapraxia - mild Aconotmesis - mod severe Neurotmesis - most severe |
|
|
|
Vestibuloocular reflex |
Head/eye movement coordination Supports gaze stabilization |
|
|
|
Vestibuloocular reflex |
Head/eye movement coordination Supports gaze stabilization |
|
|
|
Vestibulospinal reflex |
Stabilize body and control movement Assists with stability while head is moving and coordination of trunk |
|
|
|
Postural strategies |
Ankle - first to elicit with small perturbation Hip - greater force to elicit Stepping - big perturbation |
|
|
|
BPPV |
Vertigo with changes in head position Most often posterior semicircular canal Usually otoconia loosens and goes into canal Dix-hallpike used to assess and treat |
|
|
|
Spontaneous nystagmus |
Imbalance of vestibular signals Fast and slow phase Acute vestibular lesion |
|
|
|
Peripheral nystagmus |
Peripheral vestibular lesion Inhibited with gaze fixation |
|
|
|
Central nystagmus |
Central lesion Not inhibited by visual fixation |
|
|
|
Positional nystagmus |
Induced by change in head position Semicircular canals stimulate nystagmus |
|
|
|
Gaze-evoked nystagmus |
When eyes shift from primary position to alternate position Caused by inability to maintain stable gaze position Indicative of CNS pathology |
|
|
|
Central vs peripheral nystagmus |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Fluent aphasia |
Temporal, wernickes, or parietal Word output is fine Jibberish |
|
|
|
Fluent aphasia |
Temporal, wernickes, or parietal Word output is fine Jibberish |
|
|
|
Non fluent aphasia |
Frontal lobe of dominant hemisphere usually Poor word output Content is present |
|
|
|
Wernickes aphasia |
Posterior region of superior temporal gyrus “Receptive aphasia” Comprehension impaired |
|
|
|
Conduction aphasia |
Actuate fasciculus Comprehension fine Impairment with repetition Word finding difficulties |
|
|
|
Brocas aphasia |
“Expressive” aphasia Comprehension is good Word output is bad |
|
|
|
Global aphasia |
Frontal, temporal, parietal Comprehension is bad Impaired writing, naming Involuntarily verbalize |
|
|
|
Dysarthria |
Motor disorder of speech UMN lesion |
|
|
|
Alzheimer’s disease |
Progressive neurodegenerative Irreversible damage within cortex and subcritical areas Less AcH Amyloid plaques develop and neurofibrillary tangles |
|
|
|
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
Chronic degenerative disease UMN and LMN impairments Loss of anterior horn cells in spinal cord Loss of motor cranial nerve nuclei Weakness and muscle atrophy |
|
|
|
Guillain barre syndrome |
Acute polyneuropathy Inflammation and demyelination of peripheral myelin sheaths |
|
|
|
Multiple sclerosis |
Demyelination of myelin sheaths surrounding nerves in brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
Myasthenia gravis |
Autoimmune disease Neuromuscular junction pathology Block and destroy AcH receptors for muscle contraction |
|
|
|
Parkinson’s disease |
Primary degenerative disorder Decreased dopamine production in substantia nigra of basal ganglia |
|
|
|
Transient ischemic attack |
Atherosclerotic thrombosis causing temporary blockage to brain Usually resolve in 24-48 hours Carotid and vertebrobasilar artery most common |
|
|
|
Ischemic stroke |
Loss of perfusion to part of brain |
|
|
|
Hemorrhagic stroke |
Abnormal bleeding in brain from rupture of blood supply |
|
|
|
Motor learning cognitive atage |
Initial stage Concentration on conscious processing of info |
|
|
|
Motor learning associative stage |
More independent to distinguish correct vs incorrect Linking feedback to performance Avoid excessive external feedback |
|
|
|
Motor learning autonomous stage |
Final stage of learning Improving efficiency of activity Automatic |
|
|
|
Motor learning - non associative |
Single repeated stimulus |
|
|
|
Motor learning - associative |
Understanding relationship between two stimuli Classical and operant conditioning |
|
|
|
Motor learning - procedural |
Learning tasks performed without attention or concentration |
|
|
|
Motor learning - procedural |
Learning tasks performed without attention or concentration |
|
|
|
Motor learning - declarative |
Requires attention, awareness, reflection, to obtain knowledge |
|
|
|
Open vs closed loop |
Closed - constant feedback and adjustment Open - single transfer of info with no feedback |
|
|
|
Brunnstrom stages |
1 - no volitional movement 2 - basic limb synergy, beginning of spasticity 3 - synergies performed voluntarily, spasticity increases 4 - spasticity decreases, movement patterns not dictated solely by limb synergies 5 - more decrease, independence from limb synergies 6 - isolated joint movements performed with coordination 7 - normal |
|
|
|
ASIA scale |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
SCI anterior cord |
Incomplete lesion Loss of motor function and pain and temp below lesion |
|
|
|
SCI Brown sequard |
Incomplete, hemisection lesion Paralysis and vibration and position sense loss on same side Loss of pain and temp on opposite side |
|
|
|
Cauda equina stndrome |
Injury below L1 spinal level Duh |
|
|
|
Cauda equina stndrome |
Injury below L1 spinal level Duh |
|
|
|
Central cord syndrome |
UE > LE Motor affected more than sensory |
|
|
|
Posterior cord syndrome |
Loss of proprioception, two point, and stereognosis Motor function preserved |
|
|
|
Neurogenic bladder |
Flaccid bladder with cauda equina or conus medullaris lesion Reflexive bladder for injury above T12 |
|
|
|
Neurogenic bladder |
Flaccid bladder with cauda equina or conus medullaris lesion Reflexive bladder for injury above T12 |
|
|
|
TBI primary injury |
Initial injury from impact Coup- direct lesion at point of impact Contrecoup- opposite side of impact |
|
|
|
TBI secondary injury |
Damage as a response to initial injury Epidural vs subdural hematoma |
|
|
|
Epidural vs subdural hematoma |
Epidural - hemorrhage between skull and dura Subdural- hemorrhage due to venous rupture between dura and arachnoid |
|
|
|
Ranchos los amigos |
1- no response 2- generalized response 3- localized response 4- confused agitated 5- confused inappropriate 6- confused appropriate 7- automatic appropriate 8- purposeful appropriate |
|
|
|
Glasgow coma scale |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Duchennes muscular dystrophy |
Progressive neuromuscular degenerative disorder Fat and connective tissue replace muscle |
|
|
|
Erbs palsy |
Upper brachial plexus injury C5-6 Affects rotator cuff, deltoid, brachialis, coraco, bicep |
|
|
|
Erbs palsy |
Upper brachial plexus injury C5-6 Affects rotator cuff, deltoid, brachialis, coraco, bicep |
|
|
|
Klumpkes palsy |
Lower brachial plexus injury C7-T1 Flexion and supination of elbow Claw hand posture |
|

