![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Neural tube defects
|
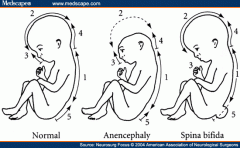
-if neuropores fail to fuse (fourth week), there will be persistent connection between amniotic cavity and spinal canal
-associated with LOW FOLIC ACID intake – before conception and during pregnancy -elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in amniotic fluid and maternal serum -elevated acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in amniotic fluid is a helpful confirmatory test --fetal AChE in CSF transudates across defect, into amniotic fluid |
|
|
-spina bifida occulta
|
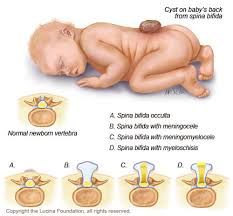
-failure of bony spinal canal to close, but NO STRUCTURAL HERNIATION
-usually seen at lower vertebral levels -dura is intact -associated with tuft of hair of skin dimple at level of bony defect |
|
|
-meningocele
|
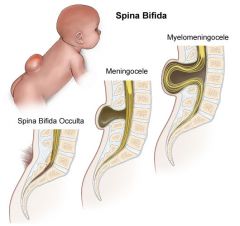
-meninges (but not spinal cord) are herniated through the spinal canal defect.
-AFP normal |
|
|
-meningomyelocele
|
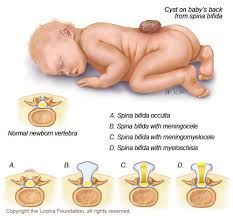
-most severe
-meninges AND spinal cord herniate through spinal canal defect |
|
|
Forebrain anomalies
-anencephaly |

-anencephaly is malformation of anterior neural tube, resulting in NO FOREBRAIN, with open calvarium ("frog-like appearance")
-elevated AFP -polyhydraminioos (no swallowing center in brain) -associated with maternal diabetes (type I) -maternal folate supplementation DECREASES RISK |
|
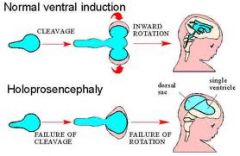
Forebrain anomalies
-holoprosencephaly |
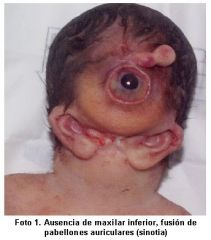
-holoprosencephaly is failure of left and right hemispheres to separate
-usually occurs in weeks 5-6 -complex multi-factorial etiology possibly related to mutations in sonic hedgehog signaling pathway -moderate for has cleft lip/palate -most severe form results in cyclopia (one eye) |
|
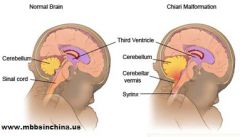
Posterior fossa malformations
-Chiari II (Arnold-Chiari malformation) |
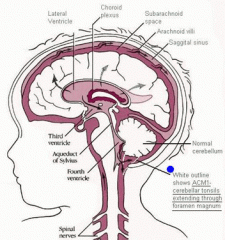
-Chiari II (Arnold-Chiari malformation) = significant herniation of CEREBELLAR TONSILS AND VERMIS through foramen magnum
-with aqueductal stenosis and hydrocephalus -often presents with limbo-sacral myelomeningocele and paralysis below the defect |
|
|
Posterior fossa malformations
-Dandy-Walker |
-agenesis of cerebellar vermis, with cystic enlargement of fourth ventricle (fills the enlarged posterior fossa)
-associated with hydrocephalus and spin bifida |
|
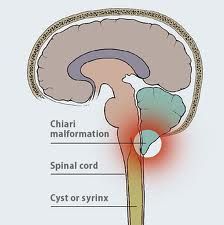
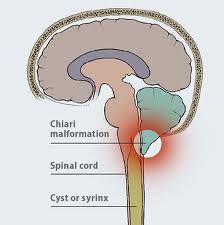
Syringomyelia
|
-cystic cavity (syrinx) within spinal cord
--if central canal, called hydromyelia -crossing anterior spinal commissural fibers are typically damaged first -results in "cape-like" bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation in upper extremities --fine touch sensation is preserved |
|
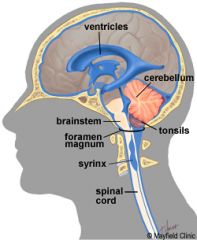
Syringomyelia (part 2)
|
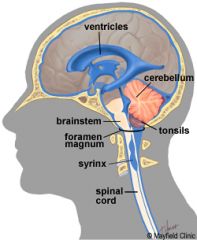
-Syrinx = tube (syringe)
-most common at C8 to T1 -syringomyelia associated with Chiari I malformation --over 3-5 mm cerebellar tonsillar ectopia --congenital, usually asymptomatic in childhood, then manifests with headaches and cerebellar symptoms |
|
Tongue development and innervation
|
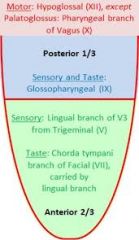
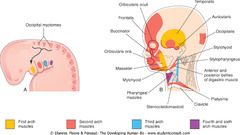
-first and second branchialarches form anterior 2/3 --> sensation via CN V3, taste via CN 7
-third and fourth branchial arches form posterior 1/3 --> sensation and taste mainly via CN 9, extreme posterior via CN 10 -motor innervation of tongue is via CN 12 -muscles of tongue are derived from occipital myotomes |

