![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the IPv4 and private addresses? |
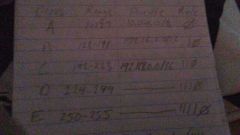
|
|
|
How many bits in MAC, IPv4, IPv6 addresses? |
MAC: 48 bits IPv4: 32bits IPv6: 128 bits |
|
|
What is a router? |
A device with multiple interfaces that route traffic to different subnets |
|
|
What does checksum do? |
Checks packets for corrupted data |
|
|
Number of collision and broadcast domains |
Routers split up broadcast domains and switches split up collision domains |
|
|
OSI Layers |
(All People Seem To Need Data Processing) Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical |
|
|
What is a network diagram? |
Graphical representation of how a network is set up |
|
|
Twisted pair cables prevent ________ |
Crosstalk |
|
|
Contingency planning |
Planning for things happening |
|
|
POE |
Power over Ethernet, devices that get power from their Ethernet cable |
|
|
Five types of network topologies |
Star, bus, mesh, ring, hybrid |
|
|
UPS provides _____ |
Clean power, free from noise |
|
|
What layer do common network devices operate at? |
Router: 3 Hub: 1 Switch: 2 Bridge: 2 |
|
|
What protocol is responsible for providing MAC addresses to IPs? |
ARP |
|
|
Data Link sublayers |
LLC - data flow control MAC - checks if wire is free |
|
|
Wiring that interconnects circuits with other circuits |
Cross Connect Facilities |
|
|
Difference between C/P and P/P |
In P/P has no central authority/no PC more important |
|
|
Telecommunications closet v MDF |
Closets extend to close range users and a MDF is the core of a network |

