![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What two systems control and adjust the activities of other organ systems? |
Nervous and endocrine |
|
|
What are the 2 anatomical subdivisions of the nervous system? |
1. Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) |
|
|
The CNS consists of the ________ and the _____________. |
brain, spinal cord |
|
|
The PNS can be further subdivided into: |
1. Afferent Division 2. Efferent Division |
|
|
This division of the PNS is associated with receptors of various kinds that provide sensory input to the CNS. |
Afferent Division |
|
|
This division of the PNS carries motor commands effectors that include muscle cells and gland cells. |
Efferent Division |
|
|
What two systems can the efferent division be divided into? |
1. Somatic Nervous System (SNS) 2. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) |
|
|
This system of the efferent division controls skeletal muscle contractions |
Somatic Nervous System (SNS) |
|
|
This system of the efferent division regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glandular activity. |
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) |
|
|
Neural tissue contains two cell types: |
1. Neurons 2. Neuroglia |
|
|
These cells transfer and process information |
neurons |
|
|
These cells serve various supportive roles for neurons. These cells comprises about half the volume of nervous tissue but there are about 5 times as many of these as neurons. |
Neuroglia |
|
|
4 types of glial cells are found in the CNS : "As Oli Mimics Epen" |
1. Astrocytes (Astro=star) 2. Oligodendrocytes (oligo-few + dendron- branch) 3. Microglia 4. Ependymal Cells |
|
|
This glial cell is the most numerous and the largest. They have numerous processes that contact the surfaces of neurons and capillaries. |
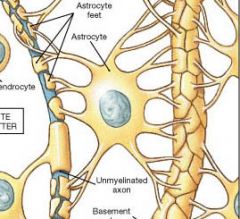
Astrocytes |
|
|
These types of glial cells physically isolate and support the neurons. |
Astrocytes |
|
|
What are the functions of Astrocytes? |
a. maintain the blood-brain barrier b. create a three-dimensional framework for the CNS c. performs repairs in damaged neural tissue d. guide neuron development e. controls the interstitial environment |
|
|
the glial cells have fewer cell processes than astrocytes. They tie clusters of axons together, regulate extracellular ion concentration, and provide MYELINATION for CNS axons. |
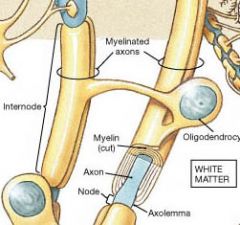
Oligodendrocytes |
|
|
______________ consists of multiple layers of the cell membrane of either oligodendrocytes or Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes) wrapped around the axons of neurons. |
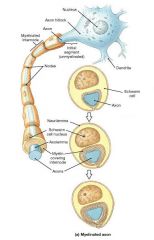
Myelination |
|
|
The cell membrane wrapping is called ___________. |
myelin |
|
|
The myelination contributed by each glial cell is called an _____________. |
internode |
|
|
The small gaps between internodes are _________ or _______________. |
nodes, nodes of Ranvier |
|
|
White and gray matters refer to _________________. |
two regions of the CNS |
|
|
Regions dominated by myelinated axons appear glossy _________________. |
white |
|
|
Regions dominated by neuron cell bodies, dendrites and unmyelinated axons appear dusky ___________. |
gray
|
|
|
These are the smallest glial cells and have slender cytoplasmic processes with many fine branches. |
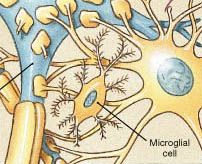
Microglial |
|
|
These glial cells are phagocytic cells that engulf cellular debris, waste products and pathogens. They makeup only 5% of glial cells but increase dramatically during injury or infection. |
Microglial |
|
|
The fluid-filled space within the CNS are lined by ________________. |
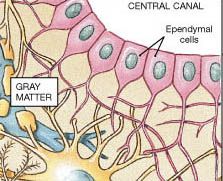
ependymal cells |
|
|
These are epithelial cells that monitor the composition of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) When specialized, these cells also participate in the secretion of CSF. |
Ependymal cells |
|
|
Two types of neuroglial cells are found in the PNS: |
1. Satellite cells 2. Schwann cells ( neurolemmocytes) |
|
|
These cells surround and support neuron cell bodies in ganglia. These calls regulate the exchange of materials between the cell and the extracellular environment. |
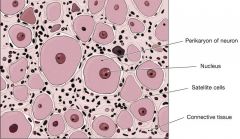
Satellite cells |
|
|
these cells surround and support the axons of the PNS. |
Schwann cells |
|
|
the is the cell membrane of the axon |
Axolemma |
|
|
this refers to the cytoplasmic covering provided by the Schwann cell |
Neurolemma |
|
|
This is the part of the neuron that contains the nucleus |
Cell body (soma, perikaryon) |
|
|
these are processes that receive information primarily at the dendritic spines. |
Dendrite |
|
|
this is the process that carries information away from the cell body. |
Axon |
|
|
this part of the axon is an elevated surface of the cell body that gives rise to the axon. |
Axon hillock (little hill) |
|
|
the proemial part of the axon that is unmyelinated and is designed to trigger an impulse |
Initial segment |
|
|
cytoplasm of the axon |
Axoplasm |
|
|
side branches of the main axon |
Collaterals |
|
|
fine terminal branches of the axon |
Telodendria |
|
|
end of telodendria where the axon makes contact with another neuron or effector. |
Synaptic terminal |
|
|
Where does communication occur between neurons? |
synapse |
|
|
Neurotransmitters are released when an ________________ arrives a the synapse. |
electrical impulse |
|
|
found only in CNS, these neurons are small with processes whose axons cannot be distinguished from dendrites. |
Anaxonic neurons |
|
|
The branches of a dendrite fuse to form a single dendrite and the cell body lies between this dendrite and the axon. Unmyelinated and rare, these cells are associated with the special senses of sight, hearing and smell. |
Bipolar neurons |
|
|
the dendritic and axonal processes are continuous. Impulses are initiated at the base of dendritic branches and the remainder of the fused processes acts essentially as an axon. |
Pseudounipolar neurons |
|
|
Most sensory neurons of the PNS are of this type |
Pseudounipolar neurons |
|
|
these neurons are the most common type in the CNS. These neurons have several dendrites and one axon. All motor neurons that control skeletal muscles are this type: |
Multipolar neurons |
|
|
Sensory neurons deliver information from the peripheral receptors to the CNS along ________ fibers. |
afferent fibers |
|
|
Sensory neurons are subclassified into: Somatic sensory neurons which include: |
1. Exteroceptors 2. Proprioceptors |
|
|
thesis sensory neurons monitor the position of muscles and joints |
proprioceptors |
|
|
these sensory neurons provide information about the external environment including touch, temp, pressure, special senses and pain that affects the limbs and body surfaces. |
Exteroceptors |
|
|
These neurons monitor deep press and pain in various internal organ systems. |
Visceral sensory neurons or interoceptors |
|
|
Chemical concentrations and pressure in the cardiovascular system. Chemicals in the oral cavity and pharynx are detected and perceived as taste: |
Visceral sensory neurons |
|
|
motor neurons stimulate or modify the activity of peripheral tissue, organs or organ systems along __________ fibers. |
efferent |
|
|
Motor neurons are subclassified into: |
Somatic motor neurons Visceral motor neurons |
|
|
these motor neurons innervate skeletal muscles by neurons whose cell bodies are in the CNS and whose axons extend to the muscle fibers they control. Most are consciously controlled |
Somatic motor neurons |
|
|
these motor neurons innervate effectors other than skeletal muscles. There are two types. |
Visceral motor neurons |
|
|
What are the two types of Visceral motor neurons? |
1. preganglioinc fibers 2. Postganglionic fibers |
|
|
the neurons have cell bodies in the CNS and synapse on postganglionic neurons in peripheral ganglia. |
preganglionic fibers |
|
|
these neurons have there cell bodies in peripheral ganglia and synapse onto the peripheral effectors. |
Postganglionic fibers |
|
|
Interneurons are also called _______________ |
association neurons |
|
|
these neurons are located entirely in the CNS and analyze the sensory input and coordinate motor output. |
Interneurons |
|
|
These neurons greatly outnumber motor neurons. |
Interneurons |
|
|
Interneurons may either be ____________ or _____________ depending on their effects on other neurons. |
excitatory, inhibitory |

