![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How can you evaluate the CNS post mortem?
|
-it can be sometimes hard to access
-spine should be removed in all cases of CNS disease -in small animals the spinal cord can be exposed by performing a dorsal laminectomy with bone rongeurs -removed by holding the dura matter with forceps and sectioning the spinal roots as close to the intervertebral foramina as possible |
|
|
T/F
Clinical signs increase with time with neoplastic and degenerative disease. |
True
infections and trauma show CNS signs sooner |
|
|
What are cells that make up the nervous system?
|
neurons
glia Ependyma Endothelial cells Pericytes of blood vessels Meninges |
|
|
What are neurons?
|
the functional cells of the nervous system in which two protpplasmic properties are highly developed
- generate impulse and can transmit pulse to a different location neurons can be located entirely withing the CNS or entirely or partially in the PNS |
|
|
What is a neuroglia?
|
macroglia - astrocytes and oligodendrocytes
microglial cells glial cells play a significant role in the maintenance (support, protection and clean up) of neuronal microenvironment |
|
|
What are the functions of oligodendrocytes?
|
provide support and the myelin sheath to axons within the CNS
unlike Schwann cells in the PNS, oligodendrocytes form myelin sheaths for several axons at once (octopus shape) |
|
|
What are the functions of microglia?
|
function as immunosurveillance, immunoregulation and are phagocytic
gitter cells are microglial cells that are globular and swollen after having phagocytized debris from injured cells |
|
|
What are gitter cells?
|
microglial cells that are globular and swollen after having phagocytized debris from injured cells
|
|
|
What is chromatolysis?
|
breakdown of cytoplasmic nissi bodies (aggregate of RER and polyribosomes) indicates neuronal cell injury
other neuronal changes include satelitosis and neuronophagia |
|
|
What do we see with ischemic cell change when dealing with neurons?
|
affects neurons are shrunken and exhibit cytoplasmic eosinophilia, nuclear pykrnosis or karyolysis
energy-deprivation change should be more suitable since it may be the result of ischemia and hypoglycemia |
|
|
When do we see status spongiosus (spongiform change)?
|
in areas of loss of myelin
seen in animals with hepatic encephalopathy and canine distemper virus (see perivascular cuffing) |
|
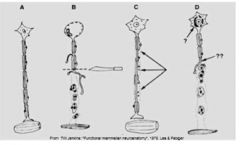
Label Letters A through D: What is the problem with the neuron?
|
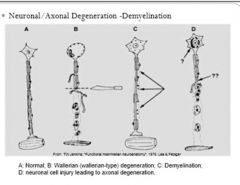
A normal Neuron
B Wallerian Degeneration C Demyelination D neuronal cell injury leading to axonal degeneration |
|
|
What is microencephaly?
|
small brain
in some cases as a result of prosencephalic hypoplasia in calves can be due to BVD in piglets due to in utero infection of classical swine fever |
|
|
What is hydrocephalus?
|
increased CSF volume
can be internal (most common) - fluid accumulates in the ventricles and arachnoid space can be compensatory -increased CSF to take up the space where the parenchyma has been destroyed or failed to develop, or both can be obstructive -aquaductal atresia or stenosis (mesencephalic aquaduct) can be congenital or secondary to inflammation |
|
|
What is the cause of cerebellar hypoplasia in kittens? Calves?
|
panleukopenia virus acquired in utero
BVD virus |
|
|
What is a lysosomal storage disease?
|
diseases that affect animals of various cell types where they are unable to eliminate normal by-products of their metabolism because of some biochemical defect
diseases are progressive, lethal, genetically determined or by neurotoxic substances that inhibit specific lysosomal activities -alpha-mannosidosis - consumption or locoweeds in sheep, cattle and horses |
|
|
What are examples of lysosomal storage diseases?
|
Gangliosidosis
Globoid cell leukodystrophy Alpha and beta mannosidosis Mucopolysaccharidosis Ceroid-lipofuscinosis Niemann-pick disease |
|
|
Why is it easy to get increased intrcranial pressure, cerebral swelling and edema?
|
there is only an narrow space separating the brain and the dura matter.
the dura matter and the skull are unyeilding structure that only allow a small increased in volume of the intracranial contents without increasing intracranial pressure can see cerebellar coning |
|
|
What are coup and countercoup lesions?
|
initial inpact (coup) causes a counter coup when the brain strikes inside the skill
Shaking disrupts the brains normal chemical balance The brain swell in severe cases and puts pressure on the brain stem, which controls breathing and other basic functions causing chronic traumatic encephalopathy |
|
|
What are causes, signs and results of spinal injury?
|
can result from external or internal causes
internal injuries associalted with intervertebral disk disease, vertebral abcesses or cervical stenotic myelopathy (wobbler disease) external can be due to trauma |
|
|
What is polioencephalomalacia?
|
degenerative disease of the CNS due to thiamine deficiency, sulfur toxicity, lead toxicity, salt poisoning/water deprivation
animals can present with opisthotonus (thiamine def) on gross appearance there are areas of pallor within grey matter of the cortex (yellowish color) In salt poisoning/water deprivation in pigs you might see perivascular and menigeal Eosinophilic infiltration on histology in addition to the polioencephalomalacia |
|
|
Diets containing fish as the primary ingredient causes what in dogs, cats and wild carnivores?
|
Chastek paralysis
thiamine deficiency fish contains high levels of thiaminase seen in diets based entirely in cooked meat in carnivores - lesions in brain stem and hippocampus |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy?
|
congenital or acquired liver disease causing neurologic signs due to the escape of ammonia, short chain fatty acids and mercaptans in the blood
|
|
|
What can cause degenerative conditions in the brain?
|
ammonia
clostridium perfingens type D (episilon toxin) moldy corn toxicity Nigropallidal Encephalomalacia |
|
|
What does Clostriduim perfringens type D cause?
|
multifocal, bilaterally symmetric encephalomalacia
|
|
|
What is moldy corn toxicity?
|
seen in horses
caused by ingestion of moldyfeed, specially corn and corn byproducts contaminated by the fungus Fusarium vertilliodes causes leukoencephalomalacia |
|
|
What is Nigropallidal Encephalomalacia?
|
chewing disease of horses
causes dysfunction of muscles of motor fibers of cranial nerves V, VII XII. repin is the toxic principle causing glutathion depletion and results in oxidative damage, mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal cell death. caused by centraurea solstitialis (yellow star thistle) or Centraurea repens (russian knapweed) |
|
|
What does bacterial cause in the CNS?
|
suppurative meningitis (strep)
meningo-encephalitis, ependymitis and ventriculitis (e.coli in pigs) |
|
|
What is the most important cause of disease in feedlot cattle?
|
Histophilus somni
can cause thrombotic menigoencephalitis fibrino suppurative hemorrhagic and necrotizing meningoencephalitis can be seen in sheep |
|
|
What does listeria monocytogenes causes?
|
abcesses
can be seen in the medulla oblongata |
|
|
What are examples viral induced inflammatory disease?
|
Equine encephalomyelitis
eastern, western, venezuelan from the togaviridae family of alphavirus can induce polioencephalomyelitis west nile virus encephalitis herpesvirus myeloencephalitis - causing ataxia, paresis and parlysis vasculitis Bovine herpesvirus encephalitis -causes necrotixing mengoencephalitis BHV-5 meningoencephalomyelitis BHV-1 canine herpesvirus encephalitis causes acute highly fatal disease of neonates rabies canine distemper - affected oligodendrocytes causes demyelination and intracytoplasmic and intranuclearinclusion in astrocytes feline infectious peritonitis - causes pyogranulomatous inflammation causing vasculitis CAE in sheep - demyelinating encephalomyelitis |
|
|
What is equine protozoa myeloencephalitis?
|
most common disease in horses with multifocal or asymmetric neurologic deficits
sudden or gradual onset of pelvic limb paresis and ataxia caused by sarcocystus neurona which is identical to sarcosytus falcatula which is a protozoal parasite in oppossums |
|
|
What is halicephalobus gingivalis and strongulus vulgaris cause when there is larval migration
|
Most common cause of verminous encephalomyelitis in horses
|
|
|
What can toxoplasma gondii cause in cats?
|
See cyst containing bradyzoites on histo
Causes a non-suppurative encephalitis |
|
|
What is transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy
|
Believed to be cause by a prion, an abnormal protein with chonformational changes that renders it resistant to protease degradation and accumulates withing neurons
Causes progressive and fatal neurological disease of humans and animals TSE in humans are Creutzfeldts-Jakod-Disease, Familial Fatal Insomnia, Kuru and Gertsmann-Straussler-Scheinker Disease |
|
|
What transmissible spongiform encephalopathies has the longest incubation period?
|
BSE 2-8 years
Clinical signs include aggression, incoordination, abnormal posture, hypermetria, progressive weakness and decrease milk production and emaciation |
|
|
What do you seen clincally with sheep that have Scrapie?
|
Fleece self-inflicted damage caused by pruritus
|
|
|
What is rocky mountain spotted fever?
|
A rickettsial disease clinically seen in the dog
Caused by rickettsia ricketsi and the disease is characterized by vasculitis |
|
|
What is canine Ehrlichiosis?
|
Caused by Ehrlichia canis and transmitted by ticks
Causes a non suppurative meningitis/meningo-encephalitis |
|
|
What can cryptococcus neoformans cause?
|
Crpytococcal meningo-encephalitis
Viscous mucoi exudcate - mucopolysaccharide capsule of the yeast seen often in cats |
|
|
What are primary neoplasms of the brain?
|
Menigiomas
Astrcytomas Olingodengrogliomas Choroid plexus papillomas Ependymomas Medulloblastomas Neuroblastomas |
|
|
What are causes of secondary metastatic neoplasms?
|
Hemangiosarcoma
Mammary adenocarcinoma Pulmonary carcinomas Lymphosarcoma Melanoma |

