![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Sensory input |
To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body |
Functions of nervous system |
|
|
Integration |
To process and interpret sensory input and decide if action is needed |
Functions of the nervous system |
|
|
Motor input |
1- a response to integrated stimuli 2- the response activates muscles or glands |
Functions of the nervous system |
|
|
Central nervous system |
1- brain 2- spinal cord |
Structural classification of the nervous system |
|
|
Peripheral nervous system |
Nerve outside the brain and spinal cord |
Structural classification of the nervous system |
|
|
Sensory (afferent) division |
Nerve fibres that carry information to the central nervous system |
Functional classification of the peripheral nervous system |
|
|
Motor (efferent) division |
Nerve fibres that carry impulses away from the central nervous system |
Functional classification of the peripheral nervous system |
|
|
Motor (efferent) division |
Somatic nervous system= voluntary Autonomic nervous system= involuntary |
Subdivisions |
|
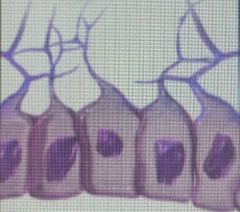
Front (Term) |
Ependymal cells |
CNS Neuroglia |
|
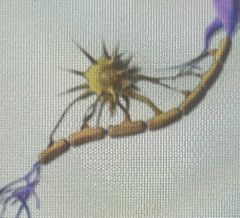
Front (Term) |
Oligodendrocytes |
CNS neuroglia |
|
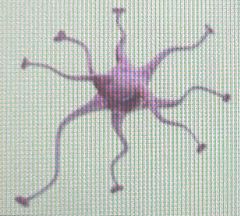
Front (Term) |
Astrocytes |
CNS neuroglia |
|

Front (Term) |
Microglia |
CNS neuroglia |
|
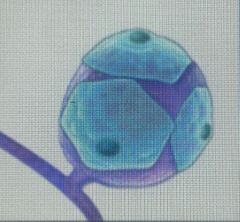
Front (Term) |
Satellite cells |
PNS neuroglia |
|

Front (Term) |
Schwan cells |
PNS neuroglia |
|
|
Astrocytes |
Brace neurons Form barrier between capillaries and neurons Control the chemical environment of the brain |
Functions |
|
|
Microglia |
Spider-like phagocytes Dispose of debris |
Functions |
|
|
Ependymal cells |
Line cavities of the brain and spinal cord Circulate cerebrospinal fluid |
Functions |
|
|
Oligodendrocytes |
Produce myelin sheath around nerve fibres in the CNS |
functions |
|
|
Satellite cells |
Protect neuron cell bodies |
Functions |
|
|
Schwann cells |
Form myelin sheath in the PNS |
Functions |
|
|
Cell body |
Nucleus and metabolic centre of the cell |
Major regions of neurons |
|
|
Processes |
Fibres that extend from the cell body (dendrites and actions) |
Major regions of neurons |
|
|
Dendrites |
Conduct impulses toward the body (many) |
Extensions outside the cell body |
|
|
Axons |
Conduct impulses away from the cell body (only 1) |
Extensions outside the cell body |
|
|
Gray matter |
Cell bodies and unmylenated fibres |
Neuron cell body location CNS |
|
|
White matter |
Cell axons (generally mylenated) |
Neuron cell body location CNS |
|
|
Ganglia |
Collections of cell bodies outside the CNS |
|
|
|
Reflex arc |
Direct route from a sensory neuron, to an interneuron, to an effector |
The reflex arc |
|
|
Autonomic reflexes |
Smooth muscle regulation Heart and blood pressure regulation Regulation of glands Digestive system regulation |
Types of reflexes and regulations |
|
|
Grey matter |
Outer layer of cerebrum Composed mostly of neuron cell bodies |
|
|
|
White matter |
Inner layer of cerebrum Fiver tracts (bundles of axon in the brain) |
|
|
|
Diencephalon |
Sits on top of the brain stem and is made of three parts Thalamus Hypothalamus Epithalamus |
Made of three parts |
|
|
Thalamus |
Surrounds the third ventricle The relay station for sensory impulses Transfers impulses to the correct part of the cortex for localisation and interpretation |
It’s functions |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Under the thalamus Important autonomic nervous system centre Helps regulate metabolism, water balance, body temperature |
|
|
|
Epithalamus |
Forms the roof of the third ventricle Houses the pineal body (an endocrine gland) Includes the choroid plexus- forms cerebrospinal fluid |
|
|
|
Brain stem |
Attaches spinal cord Parts of the brain: Midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata |
|
|
|
Midbrain |
Mostly composed of tracts of nerve fibres Reflex centres for vision and hearing Cerebral aqueduct |
|
|
|
Medulla oblongata |
Lowest part of brain stem Merges into the spinal cord Contains important control centres: Heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, swallowing, vomiting |
|
|
|
Somatic reflexes |
Activation of skeletal muscles |
Types of reflexes and regulation |
|
|
Regions of the brain |
Cerebral hemispheres Diencephalon Brain stem Cerebellum |
CDBC |
|
|
Surface lobes of the cerebrum |
Frontal Parietal Occipital Temporal |
FPOT |
|
|
What are fissures? |
Deep grooves that decide the cerebrum into lobes |
Cerebrum |
|
|
Frontal lobe |
Thinking, memory, behaviour and movement, fine motor control |
Can’t believe you don’t remember |
|
|
Parietal lobe |
Language and touch |
|
|
|
Occipital lobe |
Sight, vision |
|
|
|
Temporal lobe |
Hearing, learning and feeling |
|
|
|
Layers of the cerebrum |
Grey matter White matter |
|
|
|
Traumatic brain injuries |
Concussions Alzheimer |
|

