![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
UTI ix |
- Only indicated if complicated disease - Urinalysis, MC&S (midstream) - If haematuria present retest post tx, if continuous need haemat workup - USS/CT if evidence of structual problem |
|
|
UTI tx |
- Trimethoprim unless used in the last 3 months (unless preg) - 2nd line (1st in preg): cephlexin - 3rd line: amox+clav - In community-acquired UTIs, approx 20% of E. coli trimethoprim-resistant, <10% are amoxycillin+clavulanate-resistant or cephalexin-resistant - Same drugs for pyelonephritis (severe infection give Gent + amox/ampicillin IV) |
|
|
Nephrotic syndrome ix |
- If there is oedema, dipstick urine to avoid missing renal disease - use spot protein : creatinine ratio or albumin : creatinine ratioon an early morning MSU. |
|
|
Minimal change disease tx |
- Steroid until inflamm abates (self limiting) - cyclophosphamide or ciclosporin/tacrolimus if persistent - ~1%=>ESRF |
|
|
tx Membranous nephropathy (thickened BM + IgG and C3 sub-epithelial deposits) |
- If secondary, treat underlying cause (eg. Hep B) - If idiopathic=> ACE/ARB + diuretics - Spontaneous remission ~30% in 5 years - Trials of immunosuppressants b/c 80% of px have phospholipidase A2 receptor antibodies |
|
|
Mesangio capillary GN tx |
- Treat underlying cause as priority, - ACE/ARB - Immunosuppression if rapid progression of disease + steroids ± cyclophosphamide ifrapid deterioration in renal function. Prognosis: poor where no underlying cause can be found. In patients who reachESRF (usually idiopathic disease) it can recur in transplants and lead to graft loss. |
|
|
FSGS tx and prognosis |
- Responds to corticosteroids in ~30%. - Cyclophosphamide or ciclosporin if steroid-resistant Prognosis: Untreated most progress to ESRF. Spontaenous remission probably <10%. Longer courses of treat-ment lead to response in up to 70%; however, those presenting with abnormalrenal function have much poorer prognosis, 30–50% dec. ESRF. It recurs in approx.20% of transplanted kidneys, and may respond to plasma |
|
|
Lab features nephritic syndrome (PHAROH) |
PHAROH HematuriaAzotemiaRBC castsOliguriaHTN - Proteinuria (but <3.5 g/1.73 m2/d) - Abrupt onset Hematuria (microscopic or macroscopic) - Azotemia (increased Cr and urea) - RBC casts and/or dysmorphic RBCs in urine - Oliguria - HTN(due to salt and water retention) + peripheral edema/puffy eyes, smoky urine |
|
|
Nephrotic syndrome summary table |
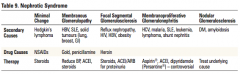
|
|
|
IgA nephropathy tx |
- ACE inhibitors to reduceproteinuria - Early corticosteroids - Only rarely progresses to acute or chronic renalfailure - Reoccurs in transplant |
|
|
IgA nephropath biopsy findings |
§ IgA in the mesangium § Glomeruli may look normalor may show mesangial widening+proliferation, segmental proliferation ofcertain glomeruli § Leukocytes may beoccasionally seen § Immunfluorescence– mesangial deposition of IgA often with C3 |
|
|
Polycystic kidneys mgmt |
- Monitor urea/creat/electrolyte - BP aggresive tx aim <130/80 (ACE-i) - Treat infection - Dialysis or transplant for ESRF - Genetic counselling - Pain helped by laproscopic cyst removal or nephrectomy - Inc H2O intake, decrease Na, avoid caffeine |
|
|
Screening for PKD |
- Genetic testing for PKD1 is difficult as the gene is large and there are hundreds ofdescribed mutations. - USS good sensitivity and specificity dependingon age. - Age 18–39yrs >3 unilateral or bilateral cysts, 40–59yrs >2 cysts in each kidney,>60yrs >4 cysts in each kidney have good sensitivity and specificity and a positivepredictive value close to 100%. - Genetic screening for some PKD2 mutations is available in specialist centres. - Also screen for aneurysms with MR angiography |
|
|
Goodpastures ix |
Anti GBM antibods |
|
|
Pyelonephritis mgmt |
- Gent + ampicillin (or ciprofloxacin) for 2wks - If stones or scarring treat for 6 wks |

