![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the conditions for a NON-neoplastic growth disturbance? (reversible)
|
1. Responsive to normal controls for growth
2. Reversible when stimulus is removed 3. May occur separately or in combination 4. Precise point of loss of reversibility (transformation) cannot be accurately determined; only the consequences can be observed |
|
|
What pre-neoplastic growth disturbances contribute to neoplasia?
|
1. Atrophy**
2. Hyperplasia** 3. Prosoplasia** 4. Metaplasia*** 5. Dysplasia**** 6. Combination w/Dysplasia******* |
|
|
What is of shrinkage in the size of a tissue due to a reduction in number of cells (cancers of prostate and stomach)
|
Atrophy
|
|
|
What is a increase in the size of a tissue due to an increase in the number of cells (reaction to irritation or hormones)
|
Hyperplasia
|
|
|
What is an increase in the size of a tissue due to an increase in the size of cells (physical stresses or exercise of muscle)
|
Hypertrophy
|
|
|
What is a substitution of a more highly specialized tissue for a less specialized tissue (GERD-Barrett's esophagus)
|
Prosoplasia
|
|
|
What is a substitution of a less specialized tissue for a more highly specialized tissue (smokers bronchi)?
|
Metaplasia
|
|
|
What is an abnormal pattern of maturation (CIN; oral precancer)?
|
Dysplasia
|
|
|
What does the word neoplasia mean?
|
The emergence of a new form of tissue (altered cells that form a mass or tumor)
|
|
|
What is a main way that neoplastic cells vary from normal cells?
|
Neoplastic cells are not responsive to the normal controls for growth.
|
|
|
T/F
Hypertrophy causes neoplastic disease |
False
Hypertrophy is not know to predispose to neoplastic disease |
|
|
What type of pre-neoplastic condition occurs from ischemia and ischemia reprofusion injury in particular creates the conditions favorable to the production of free radicals that attack DNA and in nutritional deficiencies, there can be a lack of adequate levels of essential components for normal growth and/or maturation of cells?
|
Atrophy
|
|
|
What are the causes of atrophy?
|
1. Damaged DNA due to cell injury
2. Ischemia and reprofusion produce free radicles that attack DNA 3. Nutritional deficiencies 4. Cell Aging |
|
|
What type of preneoplastic condition is evident in Prostate Carcinogenesis and what are the stages?
|

Atrophy
Columnar cells shrink causing proliferative inflammatory atrophy. Then the cells undergo prostatic intraepithelial Neoplasia and become prostate cancer |
|
|
What are the steps for atrophy as a pre-neoplastic condition?
|
Proliferative inflammatory atrophy (PIA)
Low-grade PIN High-grade PIN Invasive carcinoma |
|
|
In the carcinogenesis model of hyperplasia, ______ increase the number of tumors that form, _______ cause the mutations.
|
Promoters
Initiators |
|
|
What are the properties of hyperplasia as a premalignant condition?
|
1. Intrinsic/extrinsic stimulated cell replication
2. Enlarged pool of cells duplicating DNA 3. Increased chance for spontaneous DNA errors or action of deleterious agents on replication DNA (mutation) 4. In the carcinogenesis model, promoters increase the number of tumors that form, whicle initiators cause the mutations e. Association with many types of cancers (including oral SCC) |
|
|
What is the best example of Prosoplasia as a pre-neoplastic condition?
|
Barrett esophagus in longstanding GERD (often referred to as intestinal metaplasia)
|
|
|
What is the progression of barrett's esophagus to adenocarcinoma?
|
Prosoplasia occurs changing the epithelium to gastric-like mucosa.
That is followed by dysplasia then adenocarcinoma |
|
|
What pre-neoplastic condition is a reversible change in which one adult cell type is replaced by another adult cell type?
|
Metaplasia
|
|
|
What type of pre-neoplastic condition represents an adaptive substitution of cells sensitive to stress by cell types better able to withstand the adverse environment?
|
Metaplasia
|
|
|
What is the most common epithelial metaplasia?
|
Pseudostratified Columnar to squamous cells in the respiratory tract in response to chronic irritation as in the habitual cigarette smoker.
|
|
|
What are some factors that can induce metaplasia in the respiratory tract?
|
Vitamin A deficiency
Chronic smoking irritation |
|
|
Which pre-neoplastic condition has microscopic characteristics of the cells are very similar to the cytologic features of malignancy?
|
Dysplasia
|
|

What is this abnormal maturation of the covering epithelium?
|

Epithelial Dysplasia
|
|
|
What are two microscopic features of epithelial dysplasia that do not indicate dysplasia by themselves but may be present in conjunction with other features such as hyperchromatism?
|
Hyperkeratosis (hyperorthokeratosis; hyperparakeratosis) and Acanthosis
|
|
|
What protein plays a pivotal role in maintaining cell proliferation?
|
Ki-67
is used as a labelling index (the % of cells in a tissue staining for Ki-67 indicates the growth fraction) |
|
|
What is used for grading and lebelling index?
|
Ki-67 Protein
|
|
|
A labelling index greater than 20% is seen in high grade ____________
|
Non-hodgkin's lymphomas
|
|
|
Low grade lymphomas with a labelling index in excess of 5% have a ____ prognosis than those with an index of less than 5%.
|
Worse
|
|
|
In soft tissue sarcomas, Ki-67 index is positively correlated with _________, ________, and the histological ________.
|
mitotic count
cellularity histological grade |
|
|
What is a cell cycle inhibitor protein that binds to cyclin D and CDK4 and causes arrest in G1 phase?
|
p27 protein
|
|
|
How is p27 activated?
|
TGF-β (transforming growth factor β)
|
|
|
What might a mutation in p53 lead to?
|
Loss of control over the cell cycle leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation.
|
|
|
What are essential for the initiation of DNA replication and have been found to be releveant markers for prognosis in a variety of tumors?
|
Minichromosome Maintenance (MCM) proteins
|
|
|
What can Mcm2 expression be used to assess?
|
Tumor proliferation and may be useful as an additional prognostic marker to refine the prediction of outcome in a variety of cancers.
|
|
|
T/F
p27 and Ki-67 may be useful in estimating prognosis of the patients who have mucoepidermoid carcinoma of intraoral minor salivary glands. |
False
p27 is useful (NOT Ki-67) |
|
|
What color stain indicates protein Ki-67 presence?
|
Brown
|
|
|
What encodes a DNA-binding transcription factor that is responsible for cell cycle checkpoints that are activated to exposure to DNA damaging agents?
|
p53 gene
|
|
|
What is true about the p53 gene's expression in tumors?
|
it is mutated and expressed at much higher levels
|
|
|
In a normal cell, what inactivates the p53 protein?
|
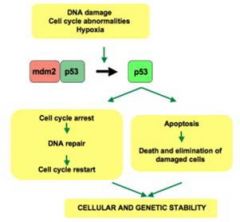
p53 is inactivated by its negative regulator mdm2 (murine double minute 2 protein)
|
|

Upon DNA damage or other stress, various pathways lead to the dissociation of the p53 and mdm2 complex. Once activated, p53 will either_________?
|

Induce a cell cycle arrest to allow repair and survival of the cell OR apoptosis to discard the damaged cell.
|
|
|
What does the p53's activity do to formation of tumors?
|
p53 Stops the formation of tumors
(it is a tumor supressor gene) |
|
|
If only one functional copy of the p53 gene is inherited what happens to the patient?
|
They are predisposed to cancer and develop several independent tumors in a variety of tissues in early adulthood. This condition is rare and is known as LyFraumeni syndrome.
|
|
|
How does p53 protein prevent tumors?
|
1. p53 binds DNA
2. protein p21 is made 3. p21 binds to cdk2 (cell division-stimulating protein) 4. Once the p21 complexes with cdk2 the cell cannot pass through to the next stage of cell division |
|
|
When p53 is mutated, what happens?
|
it can't bind to DNA effectively and does not perform the stop signal for cell division.
|
|
|
What proteins are the key element down regulated in prostate cancer?
|
Pten proteins - repair DNA damage
|
|
|
What is the literal translation of pleomorphsim?
|
"Pleomorphism" literally mean "many shapes" (pleo- = many; -morph = shapes). It is a characteristic of anaplasia
|

