![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Describe neonatal resuscitation approach |
Equipment check: NeoPuff, Sat O2, stethoscope, mask, radiant heat Airway - neutral position, can perform suction but ventilation is priority. Breathing - cry, increase WOB. If not breathing or increased WOB, start ventilation Circulation - measure HR. HR 60 -100, only ventilation. If HB <60 after 30sec, chest compression. |
Equipment, A, B, C Need suction? When to ventilated, when to chest compression |
|
|
Setting of NeoPuff and ventilation rate - Breathing Term baby n pre-term baby - PIP, PEEP, flow rate, oxygen settingEquipment check |
Term - PIP 30, PEEP 5, 40-60 per mins (more 40 side), start oxygen 21-30%
More mature --- less ventilation rate Can increase PIP by 5cm H2O if ventilation is not effective Preterm - PIP 25, PEEP 5, 40-60 per mins (more 60), oxygen 21-30% More mature --- less ventilation rate Equipment : check max PIP n PEEP : hold mask to check PEEP. Hold air flow part to check PIP. Check max Protective PIP by dialling pressure |
|
|
|
When to perform Neonate chest compression and how? |
HR remains less than 60 despite of ventilation for 30sec or not breathing. Rate- 3 compression to 1 ventilation. 90compression per mins Set oxygen 100% |
|
|
|
Describe haem metabolism - Bilirubin |
RES 1. RBC breakdown in Reticuloendothelial system (RES - spleen) into Hb, Fe, Globin + myoglobin, haem precursor 2. Hb --- haem oxygenase ---> biliverdin 3. Biliverdin --- biliverdin reductase --> unconjugated bilirubin
Blood vessel 1. Bilirubin + Albumin ---> transport to liver
Liver 1. Dissociate from albumin complex 2. Bilirubin --- glucuronly reductase --> conjugated bilirubin --> bile duct --> small intestine
Small intestine : conjugated bilirubin 1. Enterohepathic circle : transport back to liver 2. Colon bacteria metabolise into urobilinogen and stercoblin 3. Urobilinogen into kidney -- urine urobilinogen 4. Stercoblin into faeces
|
|
|
|
What's stool and urine colour in conjugated bilirubinaemia?? |
Stool - pale as not much stercoblin (Brown colour) Urine - dark amber due to high conjugated bilirubin in urine, not much urobilinogem |
|
|
|
Describe the approaching in neonate jaundice |
1. Baby - full term vs preterm - when to notice jaundice- getting worse or better - feeding, weight gain, active, urine/faeces frequency, colour change- baby blood group 2. Mother - complication during pregnancy n delivery 3. FHx n ethnicity |
|
|
|
The criteria of hyperbilirubinaemia |
Unconjugated - term > 205, preterm > 255 Conjugated - > 40 |
|
|
|
Describe physiological jaundice - pathophysiology, features n treatment |
1. Pathophysiology Usually unconjugated bilirubin due to high RBC concentration, shorter life span of RBC, immature of liver enzyme, increased enterohepatic circulation due to immature GI movement/metabolism 2. Features Appear > 24hr, peak day 3-5, usually increase less than 88mmol, rarely go over 260. Completely recovery within 1 week (term), 2 week (preterm) 3. Treatment Goal of TX is to prevent kernicterus (bilirubin > 360, affecting brain tissue) UV 450-460nm light therapy. Cease when SBR fall 25-50 below threshold Need to monitor temp, dehydration, eye damage, diarrhoea, rashes |
|
|
|
Ddx of neonatal unconjugated bilirubinaemia |
Non- serious one 1. Physiological jaundice 2. Breast feeding jaundice
Serious one 1. Haemolytic jaundice - FBE, combs test, other genetic tests - Rh, ABO, G6PD, thalasaemia, spherocytosis 2 Cephalohaematoma - clinical exam 3. Metabolic - galactosemia, hypothyroidism (TFT, urine metabolites) 4. Infection- TORCH infection - dehydration makes jaundice worse 5. Decreased GI movement (due to increase enterohepatic circulation) : meconium ileum, hirschprung disease, intestinal atresia: ask parent passing poo? 6. Liver issues- cannot perform conjugation - genetic issues : Gilbert's syndrome, Crigler - Najjar syndrome (glucuronyl transferase) |
|
|
|
Ddx of conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia |
Largely hepatobiliary disease 1. Hepatitis 2. Biliary arterisia 3. Compressing region into biliary tree 4. Alpha 1 anti- trypsin deficiency 5. TPN cholestasis - bile duct degeneration, portal inflammation, and fibrosis with total parental nutrition. Therefore, early enters feeding is important. |
|
|
|
Ddx of Prolong jaundice |
1. Obstructive jaundice 2. Metabolic cause - hypothyroidism 3. Breast feeding jaundice - ddx of exclusion |
|
|
|
Investigation n Treatment of neonatal jaundice |
Investigation 1. SBR ( fraction) 2. Harmolysis screen 3. Infection screen 4. Metabolic screen Treatment 1. Phototherapy - use nomogram 2. IV immunoglobulin in I so immune haemolytic jaundice - RTC showed reduced maximum serum bilirubin and the need for exchange transfusion. 3. Exchange transfusion - blood group incompatibility, preterm or term with DM mother with SBR > bilirubin 340 |
|
|
|
Exchange transfusion - what does it remove and provide? |
Remove - unconjugated bilirubin - Antibody coated RBC - Antibodies against RBC antigen Provide - more durable RBC - free albumin binging sites Do not remove tissue bilirubin |
|
|
|
Kernicterus risk factors |
Complications of neonatal jaundice. Risk increased by - early gestation (35-38weeks, - low albumin - rapid rise - hypoxia, acidosis, hypoglycaemia, sepsis |
|
|
|
Premature and NICU admission - what gestational age for NICU |
Usually NICU admission over 26weeks - 25weeks borderline may admit based on the discussion. Survival rate is around 75% at 26weeks n 90% 27weeks. However, the mod to severe disability rate is higher in preterm ( 20% in 26weeks, 10% in 28weeks, around 40% in 23weeks) |
|
|
|
Describe complications among NICU graduates |
1. Parental psychological issues - mother n father 2. Growth issues - gross n fine motor 3. Sensory - vision n hearing - 1 -2% before 30weeks blind due to POR - 2-3% before 30weeks need hearing aids 4. Language n speech n social behaviour - learning difficulties - tends easily distracted. Need early parental intervention n encouragement. 5. Medical issues - chronic lung diseases - GORD - anaemia n osteopenia - hernia (inguinal) and hydrocele 6. Cerebral palsy - caring severity. 1 in 10 27-29wks , 1in 5 <27 wks |
|
|
|
Immunisation in preterm bany |
Use chronological age - do not adjust Prematurity does not need to be adjusted beyond 2yrs. We do think of post menstrual age when assessing development upto 12 months of age Consider influenza n RSV vaccine during RSV season |
|
|
|
Neonate urine. Pinkish-red stain urine normal? when to void urine? |
93% void in 24hr, 98% in 48hr Pinkidh-red stain urine on nappy --> normal (Urate) |
|
|
|
Neonate faeces. ?when to void? |
96% in 24hrs, 98% in 48hrs Great variaton in colours, consistenecy, frequency Transitional stoll about day 3-4 |
|
|
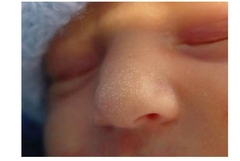
Name? what is it? Normal? |
Milia Milia are keratin-filled cysts that form just under the skin and can look very similar to whiteheads. Normal, usually disappear within days to week |
|
|
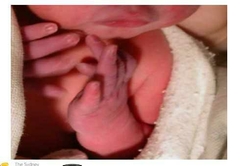
Name? normal? |
Acrocyanosis Peripheral cyanosis. Not concerning features. However, central cyanosis needs to be investigated |
|
|

name? how to tell apart from bruise? |
Mongolian spot
can be found anywhere in the body; usually buttock
How to know not bruise --> mongolian spot is flat and does not change colour over time |
|
|
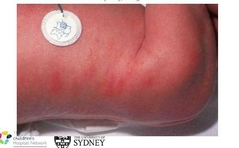
Name? DDx? |
Erythema toxicum
Erythema toxicum is characterized by blotchy red spots on the skin with overlying white or yellow papules or pustules. It is thought to be immune response and usually disappear in about 2 weeks.
Other DDx infective lesions, including HSV, Impetigo, other staphy infection.
Erythema toxicum baby is well and no signs of infection. However, if in doubt, skin swap and scraping of region is required. |
|
|
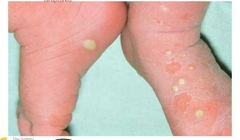
name? |
Neonatal pustular melanosis A benign idiopathic skin condition mainly seen in newborns with skin of color, has distinctive features characterized by vesicles, superficial pustules, and pigmented macules. The lesions of transient neonatal pustular melanosis are present at birth. They occur on the chin, neck, forehead, chest, buttocks, back, and, less often, on the palms and soles. The vesicles and pustules rupture easily and resolve within 48 hours. After being ruptured, it leaves hyperpigment area, the brown macules may persist for several months |
|
|
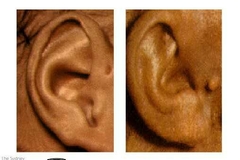
Name? Any investigation?? |
Preauricular pits or fissures are located near the front of the ear and mark the entrance to a sinus tract that may travel under the skin near the ear cartilage. These tracts are lined with squamous epithelium and may sequester to produce epithelial-lined subcutaneous cysts or may become infected, leading to cellulitis or abscess. Simple preauricular cysts should not be confused with first branchial cleft cyst. Imaging is not indicated for routine preauricular cysts and sinuses. However, it is indicated in patients who present with pits or fistulas located in atypical regions, those with cartilage duplication around the external auditory canal that extends into the parotid, and those with recurrent parotid swelling. Patients who have preauricular cysts or pits and a branchial cleft cyst should undergo renal ultrasonography to rule out branchio-oto-renal syndrome. |
|
|
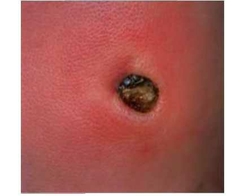
Name? Management |
Omphalitis Need hospital admission for IV Abx. It presents as a superficial cellulitis that can spread to involve the entire abdominal wall and may progress to necrotizing fasciitis, myonecrosis, or systemic disease. Bacteria --> Staphy aureus, Group A Strep, Klesiellar pneumonia, E.Coli, Proteus mirabilis |
|
|
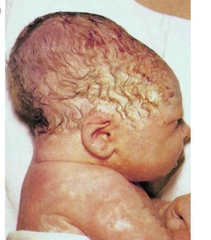
Name? |
Caput Succedaneum swelling of brain, which across multiple suture lines. It is asscoiated with instrumental birth develivery. Usually no treatment is required and self resolved within a few days. |
|
|
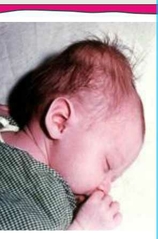
Name |
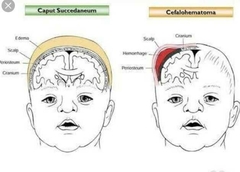
Cephalohematoma Swelling usually confined in one suture line. Need to closely monitor for neonatal jaundice. |
|
|
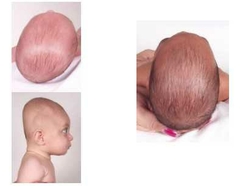
Skull shape defects. Why ?? |
Due to early fusion of suture line Left-Top: early fusion of lambdoid suture Left-bottom: early fusio of saggital suture Right: Positional plagicephaly (baby not turning its head) |
|
|
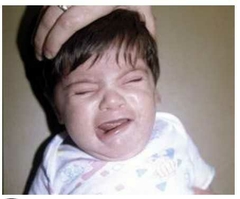
Name? DDx? |
Asymetrical Crying faces DDx is Facial falsy. Baby with facial palsy is not able to close eye on the affected side. Facial nerve is peripheral nerve. It can have incomplete facial nerve palsy but it is rare. Need to think of upper motor lesion in case of Forehead sparing feature |
|
|

Name? Cause? |
Macroglossia The most common causes of tongue enlargement are vascular malformations (e.g. lymphangioma or hemangioma) and muscular hypertrophy (e.g. Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome or hemihyperplasia) |
|
|

Name? |
Sucking blister No treatment is required |
|
|
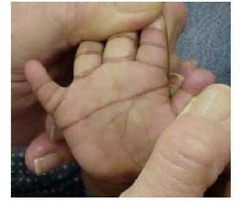
Name? |
Single Simian Crease Down syndrome |
|
|
|
Posssible injury from baby with shoulder dystocia? |
Fracture of clavicle
Brachial plexus palsy - Erb's palsy Torticollis - due to clavicular fracture and fibrosis/shortening of SCM (sternoclaviculomastoid) muscle.
|
|
|
|
What's Erb's palsy? what birth condition is associated with? |
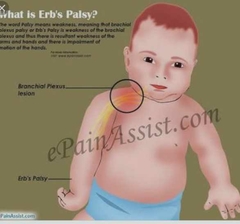
Brachial plexus injury, usually C5-C6. Often associated with traumatic birth, especially shoulder dystocia. Weakness of arm and forearm and hand. Waiter's tip hand position. Baby does not use the affected arm on Moro reflex. |
|
|
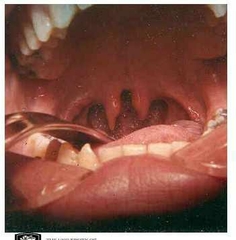
name? associated feature? Lx? |
Bifid uvula can associated with submucosa cleft, which can cause speech and swallowing difficulty Submucosa palate - A submucous cleft palate is a congenital defect of the palate, which forms the roof of the mouth. Lx by Nasopharyngoscopy |
|

