![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Discuss Bilirubin Metabolism |
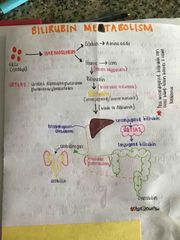
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Pathological vs Physiological Jaundice |
Pathological: With 24hrs TSB>275mmol/l Increases by 85mmol/l daily Direct serum bilirubin >34 mol/l Persists >1/52 term,>2/52 preterm Physiological: Dx of exclusion TSB doesn’t exceed upper normal range Peaks @150mmol/L in term on D3 Peaks @170-200 mol/L in preterm on D5-7 |
|
|
Prolonged Jaundice |
Jaundice>14/7 in term,>21/7 in preterm DDx: breast milk jaundice UTI Bile duct atresia Hypothyroidism Undx congenital syphilis Hepatitis Mx: feeding Urine MCS & reducing substances LFT and TSB Thyroid function Syphilis |
|
|
Mix of Jaundice |
Within 24hrs: Mother blood group,if group O test for ABO incompatibility: direct Coombs, mother&infant blood group, Hb,peripheral blood smear+/- Red cell enzyme &Hb electrophoresis 3hrly TSB and start phototherapy
After 24hrs: Blood groups+PCV Check feeding Exclude haemorrhage/Haematoma/infection
|
|
|
Rx for Jaundice |
*assess jaundice severity, age and gestation, well or unwell,risk factors and rx needed 1.Anti-D globulin to Rh neg. mothers within 72hrs post deliver 2. Phototherapy:eyes, hydration and temp checks 3. IV gamma globulin 4. Exchange transfusion |
|
|
Causes of Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinaemia |
Excessive haemolysis: Rhesus disease ABO incompatibility Haemorrhage or haematoma Polycythemia G6PD deficiency Speherocytosis
Defective Conjugation: Prematurity Infection Infant of diabetic mother Hypoglycaemia Hypothyroidism Hypoxaemia |
|
|
Causes of Conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia |
Congenital syphilis/other infections Galactosaemia/other inborn errors of metabolism Hepatocellular injury(normal bile duct) Bile duct atresia Choledochol cyst Cystic fibrosis TPN Bile flow obstruction +/- hepatocellular injury |
|
|
Complications: Hyperbilirubinaemia Exchange transfusion |
Hyperbilirubinaemia: Bilirubin encephalopathy Severe anaemia Prolonged jaundice
Exchange transfusion: Blood: transfusion rxn, metabolic instability, infection Catheter: vessel perforation,haemorrhage Procedure: NEC, hypotension |
|
|
Bilirubin encephalopathy |
Unconjugated bilirubin crosses BBB Kernicterus: yellow stain on basal ganglia+hippocampus @autopsy Clinically: Lethargic Poor sucking Pyrexia Convulsions Hypertonia Opisthotonus High pitch cry Setting sun eyes Pulmonary hge Long term: learning abilities, MR, deafness, cerebral palsy |

