![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
ECG finding of acute pericarditis
|
Diffuse ST elevation and PR segment depression initially. With T wave depression later
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Brugada syndrome
|
Sudden cardiac death in Asian young man with RBBB and ST elevation in V1-V3
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
ECG finding of cocaine use
|
ST elevation with early repolarization.
Use of cocaine may lead to coronary thrombosis, vasospasm, arrhythmia, aortic dissection and accelerated atherosclerosis |
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
ECG finding of major pulmonary embolism
|
sinus tachycardia, RBBB, S wave in lead I, Q wave in lead III, or T wave inversion in lead III
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Skin changes of amyloidosis
|
Purpura & ecchymoses. Factor X binding by amyloid fibrils may be partly responsible
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Common finding of antiphosholipid syndrome
|
Stroke, recurrent pregnancy loss, livedo recitularis, purpura, thrombocytopenia, pulmonary embolism
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Common finding of cryoglobulinemia
|
Palpable purpura, Raynaud phenomenon, digital ischemia. Type I is associated with hyperviscosity and thrombosis
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Common finding of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
|
Mucosal and pulmonary AV malformation lead to epistaxis and GI bleeding, paradoxical embolism with stroke and brain abscess
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Common finding of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
|
Anemia, hemolysis, thrombocytopenia, confusion, fever, renal involvement, myocardial infarction
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
What is the common cause of multifocal vascular lesion
|
Vasculitis, e.g. cryoglobulinemia. SLE.
Hypercoagulable state, e.g. antiphosholipid syndrome. Endocarditis and cholesterol emboli |
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
How to manage suspected subacute endocarditis?
|
Culture three blood samples, drawn 1hr apart at separate sites. Start empirical board spectrum antibiotics once all blood sample have been obtained
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
What should be tested for culture-negative endocarditis?
|
Coxiella, Bartonella, Legionella, Clamydia species. HACEK bacteria (Haemophilus aphrophilus; Actinobacillus, cardiobacterium, Eikenella, Kingella)
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Causes of painful purple toes
|
Peripheral arterial disease;
Cellulitis; Cryoglobulinemia Phlegmasia cerulae dolens |
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Cause of painful purple toes (1)
|
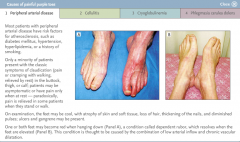
peripheral arterial disease
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Cause of painful purple toes (2)
|
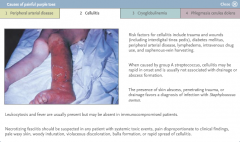
Cellulitis
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Classification of cryoglobulinemia
|
Type I: monoclonal IgG or IgM, occurs in the presence of multiple myeloma or Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
Type II: polyclonal IgG bound to monoclonal IgM. Associated with hepatitis C Type III: polyclonal IgG bound to polyclonal IgM. occurs in SLE, Sjogren's syndrome and other autoimmune diseases |
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
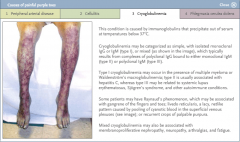
What is cryoglobulinemia?
|
Condition caused by immunoglobulins precipitate out of serum at the temperature below 37C
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
What is the common association of cryoglobulinemia?
|
MembranoProliferative GlomeruloNephritis; fever; arthralgias, neuropathy;
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
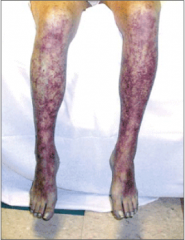
What is the diagnosis
|
Cryoglobulinemia
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
What is the diagnosis?
|
Phlegmasia cerulea dolens
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
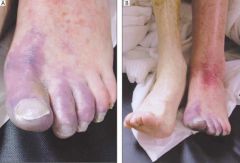
What is the diagnosis
|
Phlegmasia cerulea dolens
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
What is the diagnosis
|
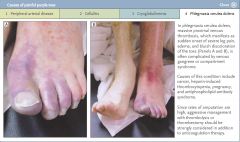
Phlegmasia cerulea dolens
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
What is the manifestation of Phlegmasia cerulea dolens
|
Severe leg pain, edema, bluish discoloration of the toes
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
What is the cause of phlegmasia cerulea dolens
|
Cancer, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, pregnancy, antiphospholipid syndrome
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Management of phlegmasia cerulea dolens
|
anticoagulation, aggressive management with thrombolysis or thrombectomy
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
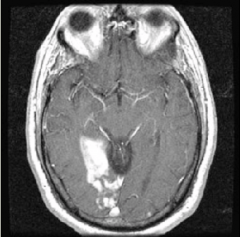
What is the most likely symptom?
|
Left homonymous hemianopia
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Risk factor: prosthetic heart valve. Casual organism for culture negative endocarditis?
|
Aspergillus species
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Risk factor: exposure to kitten. Casual organism for culture negative endocarditis?
|
Bartonella henselae
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Risk factor: homeless and body lice. Casual organism for culture negative endocarditis?
|
Bartonella quintana (urban trench fever)
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Risk factor: consumption of unpasteurized dairy product. Casual organism for culture negative endocarditis?
|
Brucella melintensis
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Risk factor: exposure to birthing animals Casual organism for culture negative endocarditis?
|
Coxiella burnetii (Q fever)
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Risk factor: poor dentition. Casual organism for culture negative endocarditis?
|
HACEK bacteria
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
Management in preventing recurrent thromboembolism in patient with active cancer and thrombosis?
|
Low-Molecular-Weight-Heparin. LMWH is superior than warfarin in preventing thrombosis (CLOT trial)
Malnutrition, drug interactions, and vomiting from chemotherapy may make dosing warfarin more problematic. |
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
What is the alternative anticoagulation in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia patient?
|
Argatroban. Direct thrombin inhibitor
|
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|
|
|
What is the cause of hypercoagulability of cancer patient?
|
1. Tissue factor driven thrombosis
2. Mucin-producing tumors 3. Chemotherapy 4. Immobility 5. Deep venous compression by tumor or lymph nodes |
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/interactive-case/361/25/e58/
|

