![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an ion?
|
An atom with more or less than its normal number of electrons.
|
|
|
What is an electrostatic field?
|
The space between and around charged bodies.
|
|
|
In what direction are electrostatic lines of force drawn?
|
Leaving positive, entering negative.
|
|
|
The effects of directed drift take place at what rate of speed?
|
The speed of light (186,000 miles per second, 300,000,000 meters per second).
|
|
|
What is the relationship of current to voltage in a circuit?
|
Current increases as voltage increases.
|
|
|
What term describes a material whose resistance remains relatively constant with changes in temperature?
|
Zero temperature coefficient.
|
|
|
What is the relationship between conductance and resistance?
|
They are reciprocals of each other.
|
|
|
What does the wattage rating of a resistor indicate?
|
Its ability to dissipate heat.
|
|
|
Q4. According to Ohm’s law, what happens to circuit current if the applied voltage
(a) increases, (b) decreases? |
(a) Current increases
(b) Current decreases |
|
|
According to Ohm’s law, what happens to circuit current if circuit resistance
(a) increases, (b) decreases? |
(a) Current decreases
(b) Current increases |
|
|
What is the equation used to find circuit resistance if voltage and current values are known?
|
R=I/E
|
|
|
What is the term applied to the rate at which a mechanical or electrical force causes motion?
|
Power.
|
|
|
How can the amount of current be changed in a circuit?
|
By changing the circuit resistance or the voltage of the power source.
|
|
|
What are the three formulas for electrical power?
|

Always in Watts
P=(I^2)R P=(E^2)/R P=IE |
|
|
Define direct current.
|
An electrical current which flows in one direction only.
|
|
|
Define alternating current.
|
An electrical current which is constantly varying in amplitude, and which changes direction at regular intervals.
|
|
|
What is a disadvantage of a direct-current system with respect to supply voltage?
|
The dc voltage must be generated at the level required by the load.
|
|
|
What disadvantage of a direct current is due to the resistance of the transmission wires?
|
The I 2R power loss is excessive.
|
|
|
What kind of electrical current is used in most modern power distribution systems?
|
Alternating current (ac).
|
|
|
When placed in the vicinity of a current-carrying conductor, the needle of a compass becomes
aligned at what angle to the conductor? |
The needle aligns itself at right angles to the conductor.
|
|
|
The "left-hand rule" for a conductor is used for what purpose
|
It is used to determine the relation between the direction of the magnetic lines of force around a conductor and the direction of current through the conductor.
|
|
|
In what direction will the compass needle point when the compass is placed in the magnetic field
surrounding a wire? |
The north pole of the compass will point in the direction of the magnetic lines of force.
|
|
|
When two adjacent parallel wires carry current in the same direction, the magnetic field about one wire has what effect on the magnetic field about the other conductor?
|
It combines with the other field.
|
|
|
When two adjacent parallel conductors carry current in opposite directions, the magnetic field about one conductor has what effect on the magnetic field about the other conductor?
|
It deforms the other field.
|
|
|
What is the shape of the magnetic field that exists around (a) a straight conductor and
(b) a coil? |
(a) The field consists of concentric circles in a plane perpendicular to the wire
(b) the field of each turn of wire links with the fields of adjacent turns producing a two-pole field similar in shape to that of a simple bar magnet. |
|
|
What happens to the two-pole field of a coil when the current through the coil is reversed?
|
The polarity of the two-pole field reverses.
|
|
|
What rule is used to determine the polarity of a coil when the direction of the electron current flow in the coil is known?
|
Use the left-hand rule for coils.
|
|
|
When a conductor is rotated in a magnetic field, at what points in the cycle is electromotive force
(a) at maximum amplitude and (b) at minimum amplitude? |
(a) When the conductors are cutting directly across the magnetic lines of force (at the 90º and 270º points).
(b) When the conductors are moving parallel to the magnetic lines of force (at the 0° and 180° points). |
|
|
One cycle is equal to how many degrees of rotation of a conductor in a magnetic field?
|
360° .
|
|
|
State the left-hand rule used to determine the direction of current in a generator.
|
Extend your left hand so that your thumb points in the direction of conductor movement, and your forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic flux (north to south). Now point your middle finger 90° from the forefinger and it will point in the direction of electron current flow in the conductor.
|
|
|
How is an ac voltage produced by an ac generator?
|
Continuous rotation of the conductor through magnetic fines of force produces a series of cycles of alternating voltage or, in other words, an alternating voltage or a sine wave of voltage.
|
|
|
Define Frequency.
|
Frequency is the number of complete cycles of alternating voltage or current completed each second.
|
|
|
What are the 3 formulas for current?
|
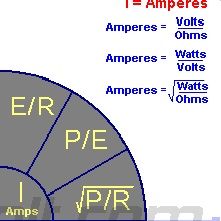
I=E/R
I=P/E I=(√P/R) |
|
|
What are the three formulas for voltage?
|
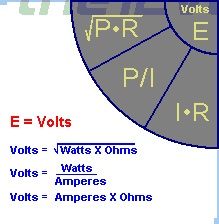
Think PRE,PIE,IRE
(√PR)=E P/I=E IR=E |

