![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
acculturatione
|
process of learning norms, beliefs, and behavioral expectations of a group other than one's own group.
|
|
|
Roman Catholicism
|
Avoid meat on Ash Wednesday and Fridays of Lent
|
|
|
Judaism
|
Fish that have scales and find are allowed. Animals allowed include animals that are vegetable eaters. During Passover, only unlearned bread is eaten.
|
|
|
yin and yang
|
cold and hot
|
|
|
Aloe
|
Anti- inflammatory and antimicrobial effects
|
|
|
Angelica
|
antispasmodic and vasodilator; balance the effects of estrogen
|
|
|
Chamomile
|
Antispasmodic and Anti-inflammatory; produces a mild sedatives
|
|
|
Garlic
|
Antioxidant; used to lower cholesterol levels
|
|
|
Ginger
|
Antiemetic
|
|
|
Gingko Biloba
|
Antioxidant; used to improve memory
|
|
|
Ginseng
|
Increases physical endurance and stamina; used for stress and fatigue
|
|
|
Kava
|
Antianxiety and Skeletal muscle relaxant; produces a sedatives affect
|
|
|
St. John Worts
|
Antibacterial, antiviral, and antidepressant
|
|
|
frontal lobe
|
controls emotions, judgements, controls motor aspects of speech, primary motor cortex for voluntary muscle activation
|
|
|
parietal lobe
|
sensory information about touch, proprioception, temperature, and pain
|
|
|
temporal lobe
|
responsible for auditory information, and language comphrension
|
|
|
Occipital Lobe
|
Visual information
|
|
|
Cerebellum
|
coordination and muscle balance
|
|
|
Brainstem (midbrain, pons, and medulla)
|
respiratory and cardiac center, nerve pathways to the brain
|
|
|
thalamus
|
touch, pain, and temperature
|
|
|
Hypothalamus
|
maintain body homeostasis, help regulate body temp, help regulate appetite control, thirst center, sleeping cycle, and control hormone secretio
|
|
|
Glasgow Coma scAle
|
+Eye opening
+Best motor Response +Best verbal Response Total score (3-15) score less than 8 equal a Coma |
|
|
Sympathetic (Fight or Flight)
|
Dilated pupils
^ HR and RR Sweating Epinephrine and Norepinephrine secreted ^ BP Construction of skin and abdominal |
|
|
Parasymathetic
|
Constructed pupils
Lower HR and RR Increase peristalsis Acetycholine screted Decrease BP Relax of skin and abdominal |
|
|
Cranial Nerves (Eye Function)
|
III Oculomotor
IV Trochlear VI Abducens |
|
|
Decorticate
|
Upper limbs flex toward the body and lower limbs in extension
|
|
|
Decerebrate
|
Increase time with all limbs in a position of extension
|
|
|
Apraxia
|
inability to perform purposeful movements
|
|
|
Agnosia
|
inability to recognize familiar objects by various senses
|
|
|
Spasticity
|
Increase tone, hyperactive reflexes, Clomid, babinski
|
|
|
Ataxia
|
General term to describe uncoordinated movements. (gait, posture, and patterns of movements)
|
|
|
Chorea
|
involuntary, rapid, irregular, jerky movements. clinical feature Huntington disease
|
|
|
Flaccidity
|
Absent tone
|
|
|
Hypotonia
|
Decrease tone
|
|
|
Aphasia
|
inability to speak or difficulty
|
|
|
Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) Stroke
|
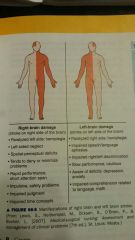
Syndrome in which cerebral circulation is interrupted, causing neurological deficits.
|
|
|
CVA, Stroke...Risk Factors
|
Diabetes
Atherosclerosis HTN Cardiac disease Transient Ischemic Attacks |
|
|
CVA, Stroke...Causes
|
Thrombosis
Embolism Hemorrhage from rupture of a vessel |
|
|
Aneurysm Precautions
|
Avoid rectal temperature
Limit visitor Avoid Valsalva's Maneuver HOB should b/w 30-45 degrees |
|
|
Valsalva's Maneuver
|
Occurs when attempting to forcibly exhale with the mouth and nose closed. It causes an increase intrathoracic pressure with an accompanying collapse of the vein of the chest wall
Slowing the pulse Decrease return of blood to the heart Increase Intrathoracic Pressure |
|
|
Elevated ICP
|
Most cases you should:
Maintain proper fluid Volumes Quiet environment Elevate HOB 30 degree Limit Sunctioning |
|
|
Horner's Syndrome
|
Sympathetic innervation to the face is interrupted by a lesion in the brain stem resulting in pupillary constrictionctions, dry and red face with no sweaty ptosis(drooping)-Mueller's muscle, problem located symathetic ascending fibers
|
|
|
Autonomic Dysreflexia
|
Caused by a lesion in the high thoracic or cervical cord. Severe HTN, sweating and headache noted. May occur with a blockage of catheter
|
|
|
Parkinson's Disease and S/S
|
Degenerative disease with primary involvement of the basal ganglia; characterized by the following:
Bradykinesia (slow movements) Resting Tremor Impaired postural reflexes Rigidity Loss of inhibitory dopamine Emotional lability |
|
|
Multiple Sclerosis and S/S
|
Progressive demyelinating disease of the CNS affecting mostly young adults
Fluctuating Exacerbations (Fatigue) Confirmed with. lumbar puncture, elevated gamma globulins, CT/MRI, myelogram, EEG Mild to moderate impaired cognition common Sensory Deficits Bowel and bladder Deficits Spasticity common Ataxic Gait |
|
|
Myasthemia Gravis and S/S
|
Neuromuscular do characterized by fatigue of skeletal muscles and muscular weakness
Progressive involvement Decrease muscle membrane acetylcholine receptors Severe Weakness Facial, ocular and bulbar Weakness Possible life-threatening respiratory muscle weakness Probable use of anticholinesterase drugs for treatment |
|
|
Guallain-Barre's Syndrom and S/S
|
Poluneuropathy with progressive muscular weakness
Demyelination of peripheral and cranial nerves Motor paralysis in an ascendi g pattern 3% mortality - respiratory failure Autonomic Dysfunction-arrhythmias, BP changes, tachycardia |
|
|
ALS Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (Lou Have it's Disease) and S/S
|
Death typically IN 2-5 years
Spasticity, Hyperreflexia Dysarthria, Dysphagia Autonomic Dysfunction in aport 1/3 of patients |
|
|
Post -Polio Syndrome
|
Slowly progressive muscle weakness that occurs in patients with a history of acute poliomyelitis.
New Weakness Pain/Myalgia Abnormal Fatgiue |
|
|
Epilepsy
|
Recurrent seziures due to excessive and audden discharge of cerebral cortical neurons.
|
|
|
Tonic - Clonic Seizure (Grand Mal)
|
Patient confused and drowsy about the seizure, 2 to 5 min
|
|
|
Meningitis
|
Inflammation of the meninges of the spinal cord and brain caused by bacteria. Neisseria Meningitidies, Diplococcus Pneumoniae, and Haemophilus Influenzae
Brudzinkski Sign Kernig Sign Stiff Neck Fever Confused |
|
|
Tidal Volume
|
Amount of air that is inhaled and echaled during normal resting ventilation
|
|
|
Residual Volume
|
The amount air remaing in the lungs following a maximal expiration
|
|
|
Friction Rub
|
Caused by the rubbi g of pleural surfaces against one another, usually as the result of inflammation processes
|
|
|
Rales (Crackles)
|
Adventitious breath sounds associated with pathology. Rales can be the result of air bubbles in secretion or movement of fibrotic tissue during breathing. Basilar rales are often accompanied with left ventricular congestive HF. (Atelectasis, Fibrosis, and PE)
|

