![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ASCITES |
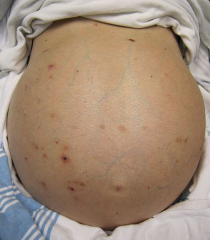
The accumulation of fluid w/in the peritoneal cavity that results from venous congestion of the hepatic capillaries, which leads to plasma leaking directly from the liver surface and portal vein |
|
|
ASTERIXIS |
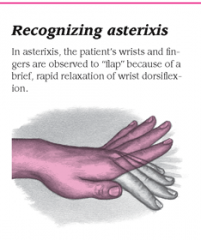
A coarse tremor characterized by rapid, nonrhythmic extensions and flexions in the wrist and fingers; also termed "liver flap"
|
|
|
Billroth I |
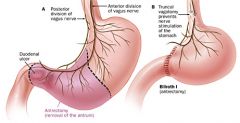
Partial gastrectomy with the remaining segment being anastomosed to the duodenum; also termed :gastroduodenostomy
|
|
|
Billroth II |
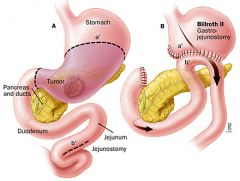
Partial gastrectomy with the remaining segment being anastomosed to the jejunum; also termed "gastrojejunostomy
|
|
|
Cholecysetectomy |
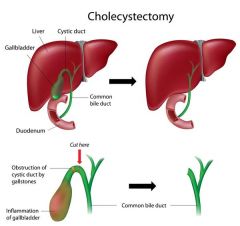
Removal of the gallbladder
|
|
|
Cholecystitis |
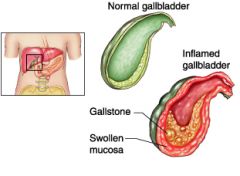
An inflammation of the gallbladder that may occur as an acute or chronic process. Acute inflammation is associated with gallstones (cholelithiasis). Chronic cholecystitis results when inefficient bile emptying and gallbladder muscle wall disease causes a fibrotic and contracted gallbladder.
|
|
|
Choledocholithotomy |
Incision into the common bile duct to remove a gallstone
|
|
|
Cirrhosis |
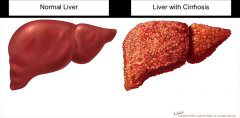
A chronic progressive disease of the liver characterized by diffuse degeneration and destruction of hepatocytes. Repeated destruction of hepatic cells causes the formation of scar tissue.
|
|
|
Crohn's Disease |
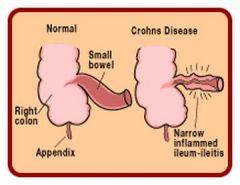
A inflammatory disease that can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract but most often affects the terminal ileum; leads to thickening and scarring, narrowed lumen, fistulas, ulcerations, and abscesses. The disease is characterized by remissions and exacerbations.
|
|
|
Cullen's Sign |
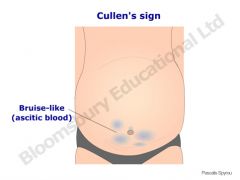
Bluish discoloration of the abdomen and periumbilical area seen in acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis.
|
|
|
Diverticulitis |
Inflammation of one or more diverticula from penetration of fecal matter through the thin-walled diverticula, resulting in local abscess formation. A perforated diverticulum can progress to intraabdominal perforation with generalized peritonitis.
|
|
|
Diverticulosis |
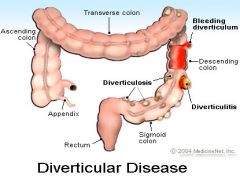
Outpouching or herniations of the intestinal mucosa that can occur in any part of the intestine but is most common in the sigmoid colon
|
|
|
Dumping Syndrome |
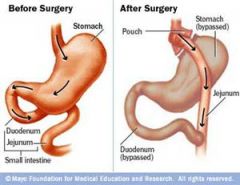
Rapid emptying of the gastric contents into the small intestine, which occurs following gastric resection
|
|
|
Esophageal varices |
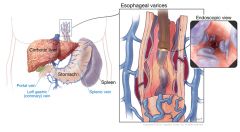
Dilated and tortuous veins in the submucosa of the esophagus caused by portal hypertension, often associated with liver cirrhosis; at high risk for rupture if portal circulation pressure rises.
|
|
|
Fetor Hepaticus |

The fruity, musty breath odor associated with severe chronic liver disease.
|
|
|
Gastrectomy |
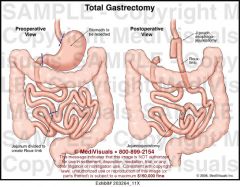
Removal of the stomach with attachment of the esophagus to the jejunum or duodenum; also termed "esophagojejunostomy" or esophagoduodenostomy.
|
|
|
Gastric resection |
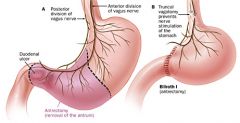
Removal of the lower half of the stomach, usually including vagotomy; also termed "antrectomy"
|
|
|
Hepatitis |
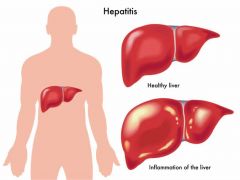
Inflammation of the liver caused by a virus, bacteria, or exposure to medications or hepatotoxins
|
|
|
Hiatal hernia |
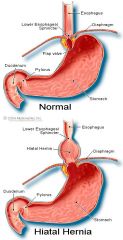
A portion of the stomach that herniates through the diaphragm and into the thorax. Herniation results fro weakening of the muscles of the diaphragm and is aggravated by factors that increase abdominal pressure, such as pregnancy, ascites, obesity, tumors, and heavy lifting; also termed "esophageal or diaphragmatic hernia
|
|
|
Melena |

Black, tarry stools as a result of bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract
|
|
|
Murphy's Sign |
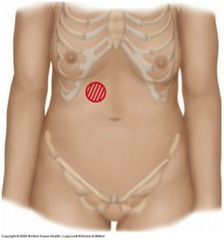
A sign of gallbladder disease consisting of pain on taking a deep breath when the examiner's fingers are on the approximate location of the gallbladder
|
|
|
Pancreatitis |
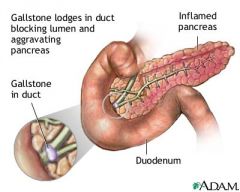
An acute or chronic inflammation of the pancreas, with associated escape of pancreatic enzymes into surrounding tissue. Acute pancreatitis can occur suddenly as one attack or can be recurrent with resolution. Chronic pancreatitis is a continual inflammation and destruction of the pancreas, with scar tissue replacing pancreatic tissue.
|
|
|
Peristalsis |
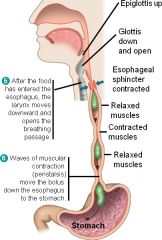
Wavelike rhythmic contractions that propel material through the gastrointestinal tract
|
|
|
Portal Hypertension |
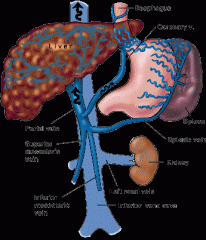
A persistent increase in pressure within the portal vein that develops as a result of obstruction to flow
|
|
|
Pyloroplasty |
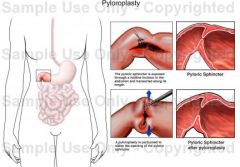
Enlarging the pylorus to prevent or decrease pyloric obstruction, thereby enhancing gastric emptying
|
|
|
Turner's Sign |
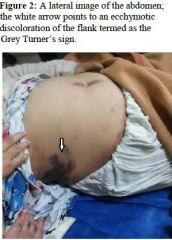
A gray-blue discoloration of the flanks seen in acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis
|
|
|
Ulcerative Colitis |
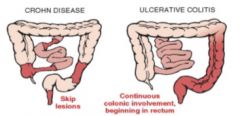
Ulcerative and inflammatory disease of the bowel that results in poor absorption of nutrients. Acute ulcerative colitis results in vascular congestion, hemorrhage, edema, and ulceration of the bowel mucosa. Chronic ulcerative colitis causes muscular hypertrophy, fat deposits, and fibrous tissue with bowel thickening, shortening, and narrowing.
|
|
|
Vagotomy |
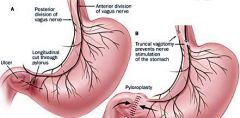
Surgical division of the vagus nerve to eliminate the vagal impulses that stimulate hydrochloric acid secretion in the stomach
|
|
|
Dumping Syndrome |

|

