![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ketones will be evident in which diabetes?
Type I or Type II |
Type I
|
|
|
One S/S of esophageal varices' bleeding:
|
distended abdomen
|
|
|
Phobias involve:
|
Projection & displacement
|
|
|
S/S of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
|
low birth rate
small head circumference undeveloped cheekbones |
|
|
S/E of Dilaudid 15 mg IM:
photosensitivity, constipation or HypOtension, resp depression |
HypOtension
respiratory depression |
|
|
Blood glucose in the elderly:
how is it different in the urine? |
the renal threshold for glucose is elevated in the elderly; it may read high, which is a false-negative
|
|
|
The purpose of ultrasound in pregancy is to determine
|
gestational age
|
|
|
Head lice shampoo directions:
|
repeat 7-10 days
Kwell is toxic; |
|
|
Enema administration:
position in Left Sims' position or adjust the temp of the solution |
Position Left side-lying Sims' position with knees flexed
|
|
|
Lung sounds r/t laryngotracheobronchitis:
|
Inspiratory stridor
restlessness |
|
|
Thorazine S/E: Antipsychotic, tranquilizer, antiemetic
|
may be used for restlessness & apprehension B4 surgery
SE = HOTN; May cause tardive dyskinesia |
|
|
Purpose of fetal monitor:
|
To assess baby's O2 status
|
|
|
Normal Sodium levels:
|
136 - 145
|
|
|
Lithium toxicity S/S:
|
Fine tremors
N/V/D |
|
|
Alcohol abuse warning signs
|
tremors
incr temp nocturnal leg cramps pain intolerance |
|
|
Rinne test includes
|
tuning fork
mastoid bone auditory canal |
|
|
NSAID S/E (not tinnitis)
|
HA
dizz GI distress pruritis rash |
|
|
Pre-eclampsia early S/S:
Treatment: |
facial swelling
proteinuria HTN Treatment: delivery |
|
|
Lithium toxicity S/S:
|
Fine tremors
N/V/D |
|
|
Alcohol abuse warning signs
|
tremors
"I think I have a fever!" "My legs cramp at night" pain intolerance |
|
|
Rinne test includes
|
tuning fork, mastoid bone, auditory canal
|
|
|
NSAID S/E (not tinnitis)
|
HA, dizz, GI distress, pruritis, rash
|
|
|
Apraxia: definition
|
loss of ability to carry out learned purposeful movements, despite having to previously performed the movements (show me how you brush your teeth)
|
|
|
Ataxia: definition
|
Gross lack of muscle coordination and movements.
|
|
|
Autonomic Dysreflexia S/S
|
HA
sweats Nasal congestion piloerection (goose bumps) bradycardia HTN |
|
|
Amniocentesis will detect what condition?
|
hemolytic disease;
maternal antibodies destroy fetal RBCs; bilirubin secreted r/t hemolysis |
|
|
daily iron needs for females (mg/day)
|
15 mg
|
|
|
hemolytic reaction to blood transfusion
|
HOTN
backache low back pain fever |
|
|
Anorexics have problems with what feelings?
|
self-identity & self-esteem
|
|
|
Positive Trousseau's sign is indicative of:
|
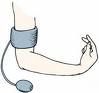
HypOcalcemia; BP cuff inflated 1-4 mins causes hand & fingers to undergo spasm & flexion
|
|
|
Lithium depends upon what body chemical to be normal for lithium to be effective?
|
Sodium
|
|
|
Miller-Abbott tube is for the purpose of:
|
removing fluid & gas from the small intestine
|
|
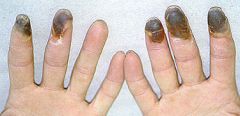
sensitivity to cold; claudication; more severe at night; decreased pulses
|
Buerger's disease
|
|
|
CBI (Continuous Bladder Irrigation) is to:
|
prevent formation of clots (obstructions) and spasms
|
|
|
Meniere's syndrome S/S (triad)
|
Vertigo
tinnitus hearing loss |
|
|
Hep A is infectious in what body outputs:
|
Feces
Saliva Blood |
|
|
Narcan:
Short or long half-life? |
Short
|
|
|
Haldol affects which of the following:
Hearing - nystagmus - blood abnormalities - EPS - changes in LOC |
blood abnormalities & EPS
|
|
|
Tofranil facts:
Tofranil S/E: |
Anti-depressant that also treats neuropathic pain
Postural HOTN Sore throat fever increased fatigue V/D |
|
|
Aminophylline used for:
Aminophylline contraindicated: |
bronchodilator; it relaxes respiratory muscles. Good 4 asthma, bronchitis, emphysema
Contraindicated in presence of stomach ulcer, seizures, HTN, thyroid condition |
|
|
IV pyelogram contraindicated when:
|
Kidney disease
DM HTN Heart disease Always draw BUN & creatinine B4 to indicate good function |
|
|
Captropril (Capoten) is in the class of:
|
antihypertensives; monitor B/P before administration
|
|
|
Mini Mental Status Exam
|
Assessment tool for determining severity of aggression;
|
|
|
Pedi immunization schedule!
|
needs an answer
|
|
|
tetracycline is what type of drug?
S/E? |
Antibiotic for bacterial infections
S/E photosensitivity Can stain teeth Don't take with milk/yogurt or antacids or at HS |
|
|
propanolol
|
Monitor HR & BP
Assess for SOB, wheezing Assess for insomnia, dizz May cause bradycardia, decr B/P, bronchospasm |
|
|
verapamil (Calan) is a:
|
CCB
When used w/other HTNsives can caust HOTN & HF |
|
|
decelerations: early vs late
|
Early are normal; occurs in response to compression of fetal head; does not indicate fetal distress
|
|
|
CF diet includes;
|
High protein
High calories Low carbs |
|
|
for men, PSA test is now used for:
|
PCa
(Prostate Cancer) |
|
|
Coombs Test is used for:
|
used for blood typing
The direct test detects the presence of antibodies against RBCs that may be attached to a person's RBCs. Although healthy people can make these antibodies, in certain diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, mononucleosis, lymphomas) these antibodies are directed against the client's own RBCs. The presence of these antibodies usually causes a hemolytic anemia. The indirect Coombs' test detects the presence of circulating antiglobulins. The test is used to determine whether the client has serum antibodies to the type of RBCs that he or she is about to receive by blood transfusion. |
|
|
Cushing syndrome affects blood glucose & sodium which way? (-ER or -O)
|
HypERglycemia
HypERatremia |
|
|
Nardil is what type of drug?
Should NOT be taken with what foods? |
MAO inhibitor
Antidepressent & anxiolytic DONT TAKE W/TYRAMINE FOOD S/E = dizz, blurred vision, dry mouth, HA, lethargy, the gamut |
|
|
STD - Syphilis early S/S:
|
Chancre (papule-like lesion) develops within 2-6 weeks. Starts as small papule, develops into PAINLESS ulcer
|
|
|
STD - Syphilis early S/S:
|
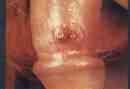
Chancre (papule-like lesion) develops within 2-6 weeks. Starts as small papule, develops into painless ulcer
|
|
|
Nurse should encourage pt to NOT push until fully dilated d/t:
|
may cause fetal hypoxia and maternal exhaustion
|
|
|
Albumin levels (normal)
|
3.5 - 5
|
|
|
Digoxin therapeutic levels
|
0.5 - 2.0
|
|
|
Magnesium levels (normal)
|
1.6 - 2.6
|
|
|
Calcium levels (normal)
|
8.6 - 10.0
|
|
|
Benzodiazepines used for:
|
anxiety reduction
Acute ETOH withdrawal Muscle relaxant |
|
|
Benzodiazepines contraindicated with:
|
narrow angle glaucoma, pregnancy
|
|
|
Benzodiazepines:
Ativan? or Haldol? or Valium? |
Ativan
Valium |
|
|
Cardiac glycosides (digoxin)
Don't use in what heart dysrhythmias? |
V-Tach, V-Fib, 2nd & 3rd heart block
|
|
|
Lopressor - Beta blocker S/E:
|
laryngospam
bradycardia cardiac arrest |
|
|
Digoxin is used for which dysrhythmias / disease?
|
CHF, A-Fib, A-flutter, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
|
|
|
Digoxin maintenance dose:
|
0.125 - 0.5 mg/day
administer over at least 5 min Check apical pulse |
|
|
Regular Insulin onset:
Peak: |
Onset - 30 minutes
Peak: 2 - 4 hrs Duration: 6 - 8 hrs |
|
|
Med to give in a transfusion reaction:
|
Benadryl
|
|
|
Peak of Regular insulin:
Peak of NPH insulin: |
Regular: 2.5 - 5 hr
NPH: 4 - 12 hr |
|
|
Cool skin, respiratory crackles, pulse 88 and bounding are S/S of what condition?
|
Fluid volume excess
|
|
|
Strabismus presents with:
|
Crossed eyes,
double vision child covers one eye to see |
|
|
Sickle cell priority
|
hydration
|
|
|
Dietary considerations for pts with ascites
|
Low sodium 200-300 mmol NA
|
|
|
Addison's DZ pts need:
More salt, or Less salt? |
More salt
|
|
|
Talipes equinovarus Interventions:
|
Casting; changed Q1-2 wks for 8-12 wks w/progressive correction
|
|
|
Talipes equinovarus: Monitor
|
circulation / skin integrity
encourage normal G & D phys therapy |
|
|
To diagnose developmental dysplasia of the hip perform what assessment:
|
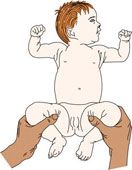
Ortolani's sign.
An audible click on hip manipulation |
|
|
Developmental hip dysplasia Intervention
|
Pavlik harness 0-6 months;
holds the hips in abduction & flexion. Worn 24 hrs/qday MONITOR FOR: skin breakdown |
|
|
Juvenile Rheumatoid arthritis:
When parents of a preschooler asks 4 info about the dz, the nurse should advise: |
Long periods of spontaneous remission are typical. Often, JRA improves or goes into remission at puberty. Approx. 75% of JRA pts enter remission with minimal functional loss & deformity
|
|
|
Oliguric phase of renal failure:
Daily urinary output < ? |
400 ml/day
|
|
|
Diuretic / Recovery phase of Acute Renal Failure
Urinary output > ? |
4-5 liters/day
|
|
|
During low-output stage of Acute Renal Failure, should fluids be limited, or encouraged?
|
Limit fluids
|
|
|
Treatment for Low-Output Stage of Acute Renal Failure:
|
Dialysis
|
|
|
Kernig's sign: describe
What does it indicate? |
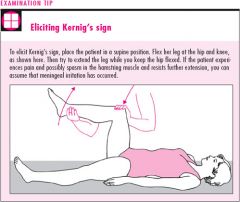
When the leg is bent at the hip and knee & subsequent extension at the knee is painful. Indicates subarachnoid hemorrhage or meningitis
|
|
|
Glucophage is best taken when?
With meals, or AC / HS |
With meals
|
|
|
Some of these foods are high in potassium:
White bread apple potato cantaloupe corn flakes scramble egg |
potato & cantaloupe
|
|
|
Normal serum albumin level
|
3.5 - 5.-0
|
|
|
Normal therapeutic digoxin administration range
|
0.5 - 2.0
|
|
|
Which drug given to prevent eclampsia:
Terbutaline Magnesium Sulfate Brethine Oxytocin |
Mag Sulfate
|

