![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
211 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Which astigmatism is reflected: 43.00 @ 180 / 42.50 @ 90 |
Against-the-rule |
|
|
|
What is Pleomorphism? |
When cells grow in multiple shapes or sizes; changed endothelial shape |
|
|
|
Toric Lenses: What do they correct? How are they designed? BONUS how are they designed? |
Correct myopic/hyperopic with astigmatism Have 2 correcting curves DESIGNED to be positioned/no rotation when blinking |
|
|
|
Where is the palpebral conjunctiva located? |
In the eyelids |
|
|
|
Cones vs Rods: What are they responsible for?
How many? |
Rods: night vision/ 125 million rods Comes: color and light vision/6-7 million cones |
|
|
|
Longer the ___, flatter the curve. Shorter the ____, steeper the curve. |
Radius |
|
|
|
What are the 4 types of CL tints? |
1. Visibility 2.Color enhancer 3.Opaque 4. Therapeutic |
|
|
|
What instrument measures the curve of the cornea; axis and extent of astigmatism? |
Keratometer |
|
|
|
What is neovascularization? |
Long term corneal abrasion/ edema |
|
|
|
What is the retina? |
Multi-layered sensory tissue lining the back of the eye |
|
|
|
CL’s that must be cleaned and disinfected for storage are called? BONUS: other names? |
Frequent replacement BONUS planned replacement |
|
|
|
What is the average central cornea curvature? |
7.8mm/43.25D (42-45D) |
|
|
|
What are the 3 corneal zones? |
Apical Peripheral Limbal |
|
|
|
What is the limbus? |
Circular junction; connects cornea and sclera |
|
|
|
What is the choroid? |
Lines between the retina and sclera |
|
|
|
List 3 types of CL’s: |
Soft lenses, hybrid lenses, and Gas perms |
|
|
|
Name the CL: -for presbyopia patient -concentric designs -aspheric designs -gradual power change |
Multi focal CL |
|
|
|
What focuses light onto the retina? |
Crystalline lens |
|
|
|
CL wear schedule:
Worn on daily basis/ occasional overnight use |
Flexible wear CL’s |
|
|
|
How many diopters is the crystalline les responsible for? |
15.00-16.00D |
|
|
|
What is responsible for 1/3 eyes refractive power? |
Crystalline lens |
|
|
|
Name the area where the bulbar and palpebral conjunctiva meet: |
Fornix |
|
|
|
What is consistent of the 60.00D of total eye power? How many D for each? |
Crystalline lens 15.00-16.00D Cornea 42.00 |
|
|
|
What is the sclera? |
Dense tough tissue, opaque white part of the eye |
|
|
|
What must you do to lower the range of the keratometer? |
Add -1.00 lens over aperture
Subtract 6.00D from value |
|
|
|
Another name for the Slit Lamp? |
Biomicroscope |
|
|
|
What is a keratometer?
BONUS additional name? |
Measures surface curvature of cornea
BONUS ophthalmeter |
|
|
|
List the kind of astigmatism: 42.50 @90/ 43.50 @180 |
Against-the-rule |
|
|
|
How much does the average person blink per minute? |
7-12 times |
|
|
|
PT fit with spherical GP lens; how much residual astigmatism is present? -1.00 -0.75 x 180 k’s: 42.00 @90 / 41.25 @180 |
-0.75 cyl / 0.75 difference k’s = 0.00 residual astigmatism |
|
|
|
Lens treatment that increases the mass at its bottom in order to prevent toric & bifocal CL’s is called… |
Prism ballast |
|
|
|
Minus lenticulation is called what ? |
Myoflange |
|
|
|
What increases Sagittarius depth the most? _______ diameter, _______ Base Curve. |
Increase diameter Steepen Base curve |
|
|
|
How thick is the cornea?
BONUS what comprises 90% of it’s thickness? |
0.5mm thick
BONUS the storms |
|
|
|
List the 3 layers of the precorneal tear film: |
Lipid, aqueous, and mucous |
|
|
|
What instrument accesses the quality of the tear film? What is it performed with? |
Slit lamp/ biomicroscope Fluorescin |
|
|
|
What is the average3 Break Up Time of tear film? |
20-25 seconds |
|
|
|
What does the Schirmer test acess?
What is it performed with? |
The quantity of tears normally produced
Strip of filter paper under each lid for 5 minutes. |
|
|
|
What is Nystagmus? |
Patients with eyes that oscillate constantly; lenses move with eye |
|
|
|
What is Aniridia? |
Partial or complete absence of iris |
|
|
|
What is the topogometer? |
An attachment that is movable designed to pinpoint specific locations of corneal cap measured by keratometer |
|
|
|
What is Placido’s disk? |
An instrument used for helping access regularity of cornea Shapes cocentric circles reflected from corneal surface |
|
|
|
What does biomicroscope measure? What’s another name? |
Illuminates eye to elevate cl/eye
Slit lamp |
|
|
|
Made up of the same tissue as the cornea, but opaque instead of transparent? |
Sclera |
|
|
|
When concave surface of rigid lens placed against lens stop of lensometer, measurement is of what? |
Back surface |
|
|
|
Thin transparent mucous covering front of the eye, lining inside the eyelids is called? |
Conjunctiva |
|
|
|
Which preservative is found in GP lens disinfection systems but NOT in soft lens disinfection systems? |
Benzalkonium Chloride |
|
|
|
What is the most commonly used disinfecting system used today? |
Chemical |
|
|
|
Which product is MOST responsible for removing surface debris from CL’s? |
Daily cleaner |
|
|
|
What is a phoropter? |
An instrument used testing individual lenses on each eye; determining refractive needs |
|
|
|
The lining of the eyelids is called what? |
Palpebral conjunctiva |
|
|
|
What do meiboman glands secrete? |
Lipids/oils |
|
|
|
How many icroliters is tear film volume? |
5-10microliters |
|
|
|
Which layer is responsible for keeping fluid level at proper level? |
Endothelium |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of aqueous layer of tear film? |
Delivers o2 and nutrients to cornea |
|
|
|
Opaque white part of the eye? |
Sclera |
|
|
|
Where’s is the bulbar conjunctiva located? |
On front of the eye |
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a function of tear film? |
Maintaining proper acidic level |
|
|
|
What does the oily layer of tear film do? |
Reduce evaporation of tear film |
|
|
|
The palpebral fissure averages: Width _____ Height_____ |
30Wx 15mm H |
|
|
|
Diopter to mm: 44.75D is the same as? |
7.55mm |
|
|
|
What makes up 5/6 of eyes shell? What makes the other 1/6? |
Sclera 5/6 Cornea 1/6 |
|
|
|
List the 3 zones of the cornea: |
1. Apical 2.Peripheral 3. Limbal |
|
|
|
Low pH can cause high water content, ionic CL’s to what? |
Lose hydration |
|
|
|
Which of the following care systems require neutralization? |
Oxidative |
|
|
|
Where is the anterior chamber located? |
Right behind cornea in front of iris |
|
|
|
What is average tear film pH? |
6.5-7.6 |
|
|
|
What is the pupil? Purpose? Average size? |
Opening of the eye; contracts w/help of iris Average size is 3.5mm; constantly changes size |
|
|
|
What makes up the shell of the eye? |
Cornea and sclera |
|
|
|
What instrument can help identify the power of CL’s? |
Lensometer |
|
|
|
On topography map: _____ colors are steep curves. _____ colors are flat curves. |
warm = steep Flat =cool |
|
|
|
Common misconception about saline solution: |
Disinfects CL’s |
|
|
|
What material (soft CL) delivers greater o2 without increasing water content? |
Silicone hydrogel |
|
|
|
90% of corneas thickness ______. |
Stroma |
|
|
|
Horizontal meridian is flattest, vertical meridian has steepest curve; Which astigmatism is presented? |
With-the-rule-astigmatism |
|
|
|
What reduces level of microbial contamination to safe level? |
Disinfection |
|
|
|
What is edema? |
Unclear foggy vision - When endothelium doesn’t function |
|
|
|
List the 3 types of wearing schedules: |
Daily wear Overnight/continuous wear Flexible wear |
|
|
|
What type of astigmatism has a horizontal meridian steeper than vertical meridian |
Against- the-rule |
|
|
|
What is the iris? What is it’s purpose? |
the colored part of the eye, controls light levels by contracting the pupil |
|
|
|
What is the thin mucus membrane covering the sclera? |
Bulbar conjunctiva |
|
|
|
Name the area where the cornea and sclera meet: |
Limbus |
|
|
|
CL’s worn overnight/continues wearing schedule are considered what type of wear CL? |
Flexible wear |
|
|
|
What type of astigmatism is not 90 degrees apart; due to medical physical conditions |
Irregular astigmatism |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the mucin layer? AKA tear film |
makes corneal surface hydrophilic |
|
|
|
Where is posterior chamber located? |
Behind iris in front of crystalline lens |
|
|
|
The outermost layer of the eye consists of what 4 parts? |
Cornea Sclera Conjunctiva Limbus |
|
|
|
What is steepest part of the cornea? |
Apex |
|
|
|
What do spherical lenses correct? |
Nearsightedness And farsightedness |
|
|
|
What provides the remaining 2/3 of the eyes refractive power? |
The cornea |
|
|
|
What CL type is approved to be worn during waking hours; must be removed to sleep/clean? |
Daily CL |
|
|
|
What is the vertical space between the upper and lower lid margins called? |
Palpebral fissure |
|
|
|
List the 3 types replacement schedules: |
Disposable Frequent replacement Conventional |
|
|
|
What type of CL is approved to be worn overnight from 1 week to 30 days |
Overnight/ continuous wear |
|
|
|
What type of CL is worn once then thrown away, sometimes good for 2 weeks? |
Disposables |
|
|
|
What is the height and width of the palpebral fissure in mm? |
15 mm width 30 mm wide |
|
|
|
How low can keratometer range be extended to? |
30.00-36.00 |
|
|
|
What is the IOR of cornea? |
1.376 |
|
|
|
Approved during waking hours; must be removed to sleep/ and be cleaned |
Daily wear |
|
|
|
What is polymegathism? |
Reduced # of endothelial cells |
|
|
|
What is located in the center of the retina? |
Macula; allowing finer details
@center of macula is fovea centralis |
Contains only cones |
|
|
What is the optic nerve? |
Bundle of nerve fibers; carrying visual info for retina to brain |
|
|
|
What provides 2/3 of eyes refractive power? |
The cornea |
|
|
|
CL approved to be worn overnight (1-4 weeks) is called what? |
Overnight/continuous |
|
|
|
What are the 3 GP CL presbyopic designs? |
Multi focal Bifocals Trifocals |
|
|
|
Light sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye; sending electrical impulses to the brain is called what? |
Retina |
|
|
|
A build up of fluid in cells is called what? |
Edema |
|
|
|
When describing ‘e’ values; when the value is higher, the curve _____ more |
flattens |
Steepen/flattens |
|
|
A GP lens is ordered w/ a B.C. Of 7.50mm; lens received measures 7.55mm
How much flatter/steeper in mm? |
0.25 flatter |
|
|
|
Buffers are used in solutions to keep them in range of __-__. |
6-8 |
|
|
|
What must be done to extend the upper range of keratometer? |
- place +1.25 trial les over aperture -record values +9.00d to drum reading |
|
|
|
What can the upper range of the keratometer be extended to? |
52.00D-61.00D |
In diopters |
|
|
K readings: 1.00D steeper than k Ex: 43.00 @ 180 44.00 @90 |
44.00D |
|
|
|
Fit the BC “ on K” Ex: 43.00 @ 180 44.00 @ 90 |
43.00 D |
|
|
|
What are GP CL’s? Which patients are they best for? |
Allow o2 to pass through the lens Firmer, much smaller, last 1 year+
Best for patients with myopia/hyperopia w astigmatism |
|
|
|
What is the average corneal diameter in mm? |
11.7mm |
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of GP lens fitting philosophies? |
Apical alignment Apical clearance |
|
|
|
Corneal astigmatism, full time wearer desiring excellent vision is a _______ lens candidate |
GP |
|
|
|
To achieve corneal alignment w/a 9.6mm GP lens; Where should B.C. Start? |
0.50D flatter than k |
GP larger than 9.0mm |
|
|
If fitting apical alignment lens with 0.50D flatter than flat K, what would B.C. Be if K readings are: 42.00D@ 180/ 43.00 @90 |
41.50D |
|
|
|
GP lens fit 1.00D flatter than K Rx: -3.50 -0.25 x 180 What is CL power? |
(+1.00) + (-3.50) = 2.50D |
|
|
|
When one eye is for distance and the other is for near it’s called what ? |
Mono vision |
|
|
|
Which lens corrects myopic/hyperopic w astigmatism -doesn’t rotate during blinks -double slab off/ dual back curves |
Toric CL’s |
|
|
|
What type of schedule is not commonly used due to disposable/ frequent replacement |
Conventional CL’s |
Less common RX Reused more often |
|
|
What is normal Keratometer range? |
36.00-52.00D |
|
|
|
180 degrees is the ______ meridian, while 90 degrees is the _____ meridian. |
180=horizontal 90=vertical |
|
|
|
What is 0.50D less than “k” with the given
43.00 @180/44.00 @ 90 |
“On k” is 43.00D - 0.50D = 42.50D |
|
|
|
What kind of astigmatism is present with the K readings: 43.00D @ 180 45.00D @ 90 |
With the rule astigmatism |
|
|
|
What is at the center of the iris? |
Pupil |
|
|
|
What type of lenses are available in: Spherical,Tori,Multifocal |
Soft lenses |
|
|
|
Which astigmatism has a major axis around 45-135 degrees? |
Oblique astigmatism |
|
|
|
Total refractive power of the eye in diopters? |
60D |
|
|
|
What are hybrid CL’s? |
Gas perm center, with soft lens skirts |
|
|
|
Which patients are multifocals for? List the two designs: |
Presbyopic patients Has aspheric design monovision/Dom & Non Dom |
|
|
|
CL’s not commonly used due to disposables/frequent replacement are called? |
Conventional CL’S |
|
|
|
What do the following stand for: BCR, BOZR, BCOR |
Base Curve Radius, Back Optic Zone Radius, and Back Central Optical Radius |
|
|
|
Must be cleaned/disinfected for storage |
Frequent replacement |
|
|
|
What is the spherical equivalent: -3.00 -1.00 @180 |
Cyl -1.00/2 = -0.50 Answer: -3.50 -0.50 @ 180 |
|
|
|
What would power in CL be if RX reads +6.00D |
+6.50D |
|
|
|
What does bright green flouresceine pattern present? |
Space between cornea/CL |
|
|
|
What does edge lift indicate? |
Loosely fit CL |
|
|
|
How do you loosen fit of CL? |
Reduce diameter Flatten base curve |
Diameter/BC |
|
|
What are steps to tighten fit of CL? |
Increase diameter |
|
|
|
Scleral indentation results in? |
Tightly fit CL |
|
|
|
How much overlap of sclera should be there in each direction for soft CL |
1mm |
|
|
|
Which instrument is used during CL’s fitting? |
Slit lamp |
|
|
|
@ what point should toric lens be considered for soft CL’s |
0.75D of refractive astigmatism |
|
|
|
At what point do CL’s need to be vertexed? |
+/- 4.00D |
|
|
|
_____ diameter ______ B.C. Fit of apical alignment lens? |
Large diameter Flatter BC |
|
|
|
______ diameter _______ B.C. Fit of apical clearance lens? |
Small diameter Steeper BC |
|
|
|
How much corneal astigmatism is ideal for an apical alignment GP lens fit? |
0.50-1.50D |
|
|
|
What type of astigmatism is shown? 46.00 @ 180/ 45.00 @ 90 |
Against-the-rule |
|
|
|
What is the conjunctiva? Where is it located? |
Soft, thin, mucus membrane Covers sclera/inside of eyelids |
|
|
|
K readings: 43.00 @180/42.00 @90 What kind of astigmatism is it? |
Against the rule |
|
|
|
What are the steps to tighten fit on CL? |
Increase diameter Steepen BC |
Diameter/BC |
|
|
When the concave surface of a surface lens is placed against the lens stop of the kendo meter, the measurement is _____ vertex |
Back vertex |
|
|
|
when BC # is higher, the BC of the lens is steeper? Or flatter? |
Flatter |
|
|
|
If lens does not move when patient blinks, what would you do to improve movement? |
Choose smaller diameter |
|
|
|
What is GPC? What does it stand for? |
most closely associated with wearing soiled contact lenses, it is when large bumps called papillae are seen on the palpebrae conjunctiva of the upper lid
Giant Papillary Conjunctivitus |
|
|
|
What is pinguecula? |
a raised yellowish discoloration of the nasal or temporal sides of the bulbar conjunctiva that is benign and does not invade the cornea |
|
|
|
What is Pterygium? |
wing-like thickening of the connective tissue and blood vessels of the bulbar conjunctiva that does invade the cornea |
|
|
|
What is Trachoma? |
leading cause of blindness throughout the world, it is a viral infection that causes scarring of the lids that eventually effects the cornea |
|
|
|
What is Ectropion? |
outward turning of the lid |
|
|
|
What is Entropion? |
inward turning of the eyelid |
|
|
|
What is Lagophthalmos? |
incomplete closure |
|
|
|
What is Dacryoadenitis? |
inflammation of the lacrimal gland |
|
|
|
What is Epiphoria? |
faulty drainage causing the tears to spill over lid margin onto the cheek |
|
|
|
What is Dacryocystitis? |
inflammation of the lacrimal sac |
|
|
|
What is Keratitis sicca ? How do you determine this condition? |
dry eye syndrome; corneal inflammation due to tear deficiencies - To determine a tear deficiency it is important to determine tear break up time (BUT). BUT is usually 15 seconds, which is fine since the average blink rate is 5 seconds |
|
|
|
What is the best method to determine BUT? |
through the use of fluorescein |
|
|
|
Where are the Glands of Zeis located? |
sebaceous gland that opens onto the lash follicles. Located on the temporal part of the eyelid behind the meibomian glands, it secretes the lipid layer also |
|
|
|
Where are the Glands of Moll located? |
sweat gland that opens onto the lash follicles. It is located by the glands of Zeis |
|
|
|
What and where are the Glands of Wolfring and Krause? |
accessory gland that secretes the aqueous layer of the tear film. It is on the inside surface of the lid near the conjunctival fornix. |
|
|
|
Where are goblet cells located? What do the secrete? |
They are located in the conjunctiva
They secrete the mucin layer in the tear film |
|
|
|
What muscle disorder is Suppression? |
when only one image from the retinas reach the brain |
|
|
|
What muscle disorder is Suppression? |
when only one image from the retinas reach the brain |
|
|
|
Heterophoria vs. Heterotropia: |
PHORIA-when only one image from the retinas reach the brain TROPIA-definite turning of the eye |
|
|
|
What muscle disorder is Suppression? |
when only one image from the retinas reach the brain |
|
|
|
Heterophoria vs. Heterotropia: |
PHORIA-when only one image from the retinas reach the brain TROPIA-definite turning of the eye |
|
|
|
What is strabismus? |
Definite turning of the eye |
|
|
|
What muscle disorder is Suppression? |
when only one image from the retinas reach the brain |
|
|
|
Heterophoria vs. Heterotropia: |
PHORIA-when only one image from the retinas reach the brain TROPIA-definite turning of the eye |
|
|
|
What is strabismus? |
Definite turning of the eye |
|
|
|
What is Anisometropia? |
condition in which the powers between the two eyes differ to a significant degree, |
|
|
|
WHat are the steps to keratometry readings? |
1.focus eyepiece 2.position patient 3.position keratometer 4. Focus/position internal myers 5.measure axis and power 6. Record reading |
|
|
|
When toric are generated on the posterior lens, 1.5 the amount of cyl on front surface lens is called what? |
Back surface Toric |
|
|
|
When a GP lens PT has less than -2.50 or residual astigmatism and who’s refractive power is not the same amount is called what? |
Front surface When |
|
|
|
What is the average corneal thickness? |
0.52mm |
? |
|
|
infection/corneal edema, causing blood vessels to invade the stroma results in what? |
neovascularization |
|
|
|
when corneal epithelium is deprived of o2 , it is known as what? |
corneal hypoxia |
|
|
|
in GP lenses, corneal edema is caused by many factors but only how? |
only if there is an inadequate transmission of o2 through the lens |
|
|
|
what may cause inadequate transmission of o2? |
extensive coating of deposits` |
|
|
|
What are some examples that can cause inadequate tear flow |
tight fitting lens, excessively large lens, poor blinking habit, inadequate lid closure, excessive lens thickness, low water content |
|
|
|
A flat lens indicates what? |
Central touch and diminished dye; |
|
|
|
Within smaller lenses, the diameters range from 7.8mm-___? |
8.6mm |
|
|
|
With larger lenses, the diameter is approximately 9mm-__mm |
10mm |
|
|
|
Thickness of a lens usually ranges from ____ to ____mm |
0.08mm-0.12mm |
|
|
|
Too steep/flat: When flourescine patterns are have central stagnation of dye resulting in lift of the lens edge is it too steep/flat? |
Too steep |
|
|
|
Too flat/steep: When flouresceine patterns show central touch and diminished dye, there is a greater amount of dye found under peripheral rim of lens? |
A flat lens |
|
|
|
A lens which is fit too steep results in what? |
Central stagnation of dye |
|
|
|
What does a flat lens indicate? |
Central touch and diminished dye |
|
|
|
A tight fit can result in what? |
Can result in pain and redness within just a few minutes since it causes the limbal vessels to become compressed due to tissue edema at the edge |
|
|
|
What us the meaning of HVID ? |
Horizontal visible iris diameter |
|
|
|
How long should the CL be left on the eye before making the final decision regarding parameters? |
15 minutes |
|
|
|
How much should the standard thickness move while gazing upward after a blink? |
0.5mm-1.0mm |
|
|
|
Thinner lenses are generally fit ____ and less than __mm of movement is acceptable due to the greater o2 permeability of a thinner lens |
Tighter
0.5mm |
|
|
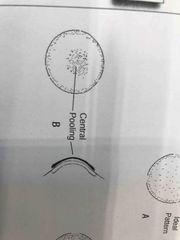
Too steep/flat: When flourescine patterns are have central stagnation of dye resulting in lift of the lens edge is it too steep/flat? |
Too steep |
|
|
|
What kind of fit does a soft lens have when the mires are distorted before the blink, clear up temporarily immediately after then become distorted again. |
An unacceptably steep fit |
|
|
|
Which anatomical part of the eye can have up to 33 diopters of optical power? |
Crystalline lens |
|
|
|
____ is inflammation of the upper tarsal conjunctiva resulting in large papillae and is associated with CL wear. |
GPC |
|
|
|
Which test can be used to measure if a patients dry eye symptoms are too severe for contact lens wear? |
BUT |
|

