![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diaphysis
|
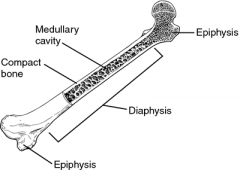
The shaft of a long bone
|
|
|
Epiphysis
|
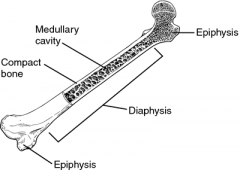
Wide ends of a long bone
|
|
|
Compact Bone
|
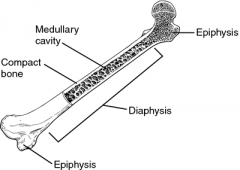
Hard bone beneath periosteum mainly found in shaft
|
|
|
Spongy Bone
|
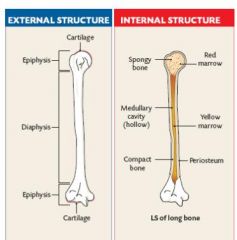
Type of bone that is light and has pores found near joints
|
|
|
Red Marrow
|
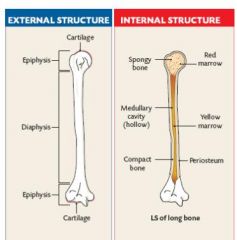
Bone marrow of children and some adult bones
|
|
|
Yellow Marrow
|
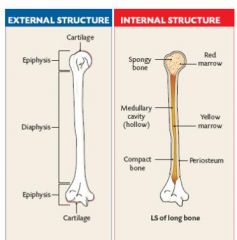
Bone marrow that is yellow with fat
|
|
|
How are bones like checking accounts?
|
-Extra Ca = deposit of calcium from blood into bones
-Need Ca = withdrawal of calcium from the bones into blood |
|
|
What are some uses of calcium in the body?
|
1. Bone strength
2. Muscle contraction 3. Neurotransmitter release 4. Blood clotting |
|
|
What are some uses of Magnesium in the body?
|
1. Relaxes muscle
|
|
|
Osteoblast
|
-Secretes gel like matrix ( which minerals bind to it)
-Use calcitonin to take Ca2+ from blood and deposits it into the bone. |
|
|
Osteoclast
|
-Breaks down the bone
-Use PTH ( parathyroid hormone) to take Ca2+ from the bone and deposits it into the blood. |
|
|
Osteocyte
|
-A mature bone cell ( osteoblast that is frozen in the matrix)
|
|
|
What are some major ways bone density could decline? (7)
|
1. Lack of Ca2+
2. Excess PTH 3. Lack of sun exposure 4. Deficiency of calcitonin 5. Stress & tissue acidity 6. Lack of weight bearing exercise 7. Lack of estrogen |
|
|
What are the functions of the skeleton?
|
-Support
-Protection -Movement -Blood and Immune function -Electrolyte Balance: bones store and release calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium. |
|
|
What is the difference between Intramembranous Ossification and Endochondral Ossification?
|
-Intramembranous ossification produces flat bones found in clavicle and skull.
-Endochondral ossification the rest of the bones in the body. |
|
|
What is interstitial growth?
|
Involves adding matrix to the interior of the bone.
Causes elongation |
|
|
What is appositional growth?
|
Involves adding matrix to the surface of the bone.
Causes widening of the bones |
|
|
What is mineral deposition?
|
When calcium and phosphorus bind to the surface of the bone.
|
|
|
What is mineral resorption?
|
The process of dissolving bone calcium and phosphorus into the blood.
|

