![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
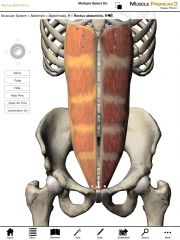
What is the origin and insertion of the Rectus Abdominis?
|
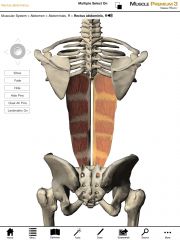
Origin: Pubic symphysis of the pelvis.
Insertion: Ribs 5-7 and at the xiphoid process of the sternum. |
|
|
What is the isolated function of the Rectus Abdominis?
|
Concentrically accelerates spinal flexion, lateral flexion, and rotation.
|
|
|
What is the integrated function of the Rectus Abdominis?
|
Eccentrically decelerates spinal extension, lateral flexion, and rotation.
Isometrically stabilizes the lumbo-pelvic-hip complex. |
|
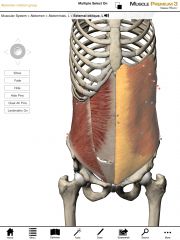
What is the origin and insertion of the External Obliques?
|
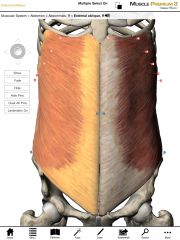
Origin: External surface of ribs 4-12
Insertion: Anterior iliac crest of the pelvis, linea alba, and contralateral rectus sheaths. |
|
|
What is the isolated function of the External Obliques?
|
Concentrically accelerates spinal flexion, lateral flexion, and contralateral rotation.
|
|
|
What is the integrated function of the External Obliques?
|
Eccentrically decelerates spinal extension, lateral flexion, and rotation.
Isometrically stabilizes the lumbo-pelvic-hip complex. |
|
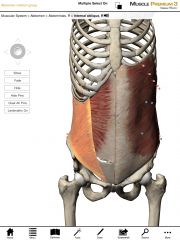
What is the origin and insertion of the Internal Obliques?
|
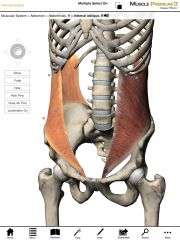
Origin: Anterior two-thirds of the iliac crest of the pelvis and thoracolumbar fascia.
Insertion: Ribs 9-12, linea alba, and contralateral rectus sheaths. |
|
|
What is the isolated function of the Internal Obliques?
|
Concentrically accelerates spinal flexion, lateral flexion, and ipsilateral rotation.
|
|
|
What is the integrated function of the Internal Obliques?
|
Eccentrically decelerates spinal extension, rotation, and lateral flexion.
Isometrically stabilizes the lumbo-pelvic-hip complex. |
|
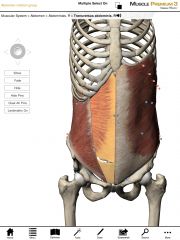
What is the origin and insertion of the Transverse Abdominis?
|
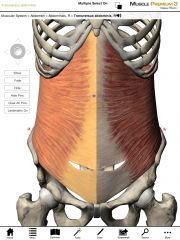
Origin: Ribs 7-12, anterior two-thirds of the iliac crest of the pelvis, and thoracolumbar fascia.
Insertion: Lineae alba and contralateral rectus sheaths. |
|
|
What is the isolated function of the Transverse Abdominis?
|
Increases intra-abdominal pressure and supports the abdominal viscera.
|
|
|
What is the integrated function of the Transverse Abdominis?
|
Isometrically stabilizes the lumbo-pelvic-hip complex.
|
|
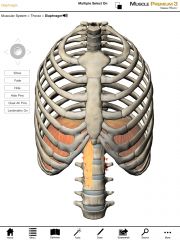
What is the origin and insertion of the Diaphragm?
|
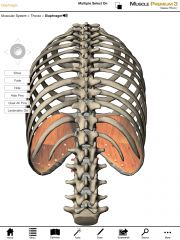
Origin:
* Costal part: inner surfaces of the cartilages and adjacent bony regions of ribs 6-12 * Sternal part: posterior side of the xiphoid process. * Crural (lumbar) part: (1) two aponeurotic arches covering the external surfaces of the quadratus lumborum and psoas major; (2) right and left crus, originating from the bodies of L1-L3 and their intervertebral disks. Insertion: Central tendon |
|
|
What is the isolated function of the Diaphragm?
|
Concentrically pulls the central tendon inferiorly, increasing the volume in the thoracic cavity.
|
|
|
What is the integrated function of the Diaphragm?
|
Stabilizes the lumbo-pelvic-hip complex.
|

