![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
placement of V1 electrode?
|
4th ICS, R SB (sternal border)
|
|
|
placement of V2 electrode?
|
4th ICS, LSB
|
|
|
placement of V3 electrode?
|
midway between V2 and V4
|
|
|
placement of V4 electrode?
|
5th ICS, L MCL (midclavicular line)
|
|
|
placement of V5 electrode?
|
horizontal with V4 position, but at L anterior axillary line
|
|
|
placement of V6 electrode?
|
horizontal with V4 position, but at L midaxillary line
|
|
|
what is a single channel monitor?
|
contains 3 monitoring wires; only one lead can be displayed at a time
|
|
|
what is a dual channel monitor?
|
contains 5 monitor wires; two of the 12 leads can be displayed simultaneously.
|
|
|
how do you monitor V1 (MCL1) if you only have 3 wires?
|
set monitor to display lead I. Place the LA (+) electrode at the V1 position and place the RA electrode under the left clavicle (-). Put your LL (ground) wire anywhere (but V6 position lets you check V6 easily if you set the monitor to show lead II). Set up like this, your monitor shows you a modified V1 (MCL1)
|
|
|
what's the best lead for distinguishing VT from SVT? best two?
|
V1 (and V6 if dual channel)
|
|
|
what's the best lead to pick up RBBB? best two leads?
|
V1 (and V6 if dual channel)
|
|
|
Best leads for anterior / anteroseptal view?
|
V1 V2 V3 V4
|
|
|
best leads for inferior view?
|
II, III, avF
|
|
|
best leads for lateral view?
|
I, avL, V5, V6
|
|
|
best leads for view of RV?
|
right sided chest leads
|
|
|
best leads for posterior view?
|
electrodes on pt's back, V7
|
|
|
benefit(s) of lead II
|
produces large, upright P waves and QRS complexes; good for determining underlying rhythm
|
|
|
benefit of lead I?
|
pts in respiratory distress (LA and RA electrodes not as sensitive to chest motion)
|
|
|
best lead to detect RCA occlusion and/or inferior wall ischemia?
|
lead II
second choice: avF third choice: lead III |
|
|
best lead to detect LAD occlusion?
|
V2 and V3
less often: V4 |
|
|
best lead to detect left circumflex occlusion?
|
in 1/3 of pts, no ST segment changes on standard 12-lead.
If lateral involved, then V5/V6 best chance of seeing ST segment changes |
|
|
if continuous 12-lead monitoring is unavailable, which two leads would you choose for pts with ACS?
|
lead III and lead V3 (unless previous ECG recorded during an ischemic event indicates anothe rlead is more sensitive)
|
|
|
what's the best lead to detect cardiac dysrhythmias?
|
V1
|
|
|
If you can view 3 leads simultaneously, which would you choose?
|
III, V3, and V5
|
|
|
in what direction is the normal flow of the electrical forces in the heart?
|
downward and to the left
|
|
|
what does the P wave represent?
|
atrial depolarization
|
|
|
what does the QRS represent?
|
ventricular depolarization
|
|
|
what does the T wave represent?
|
ventricular repolarization
|
|
|
what does the ST segment represent?
|
the brief period of time from the end of ventricular depolarization to the beginning of ventricular rest.
|
|
|
what is the J point?
|
the junction of the QRS complex with the ST segment
|
|
|
which vessels feed the SA node? in what percentage of people?
|
RCA in 55%
L circumflex in 45% |
|
|
which vessels feed the AV node? in what percentage of people?
|
RCA in 90%
L circumflex in 10% |
|
|
which vessel does the PDB come off of in most people?
|
RCA (in 90% of people)
off L circ in 10% |
|
|
what does the LAD feed?
|
anterior LV
some anterior RV posterior surface of apex IV septum |
|
|
what does the left circumflex feed?
|
LA
L lateral wall L posterior wall |
|
|
what does the RCA feed (through its branches)?
|
PDB feeds:
posterior portion of IV septum RA R posterior wall Marginal branch feeds: R anterior wall inferior wall IV septum |
|
|
which vessels feed the proximal His bundle? in what percentage of people?
|
RCA in 90%
L circumflex in 10% (same as vessels that feed AV node) |
|
|
what vessels feed the RBB?
|
RCA and
septal branches of LAD |
|
|
what vessels feed the LBB anterior fascicle?
|
LAD
|
|
|
what vessels feed the LBB posterior fascicle?
|
LAD and RCA
|
|
|
what vessel most commonly feeds the IV septum?
|
LAD
|
|
|
occlusion of which vessel would make you most concerned about dysrhythmias?
|
RCA (feeds SA node in 55%, AV node in 90%, and proximal His bundle in 90%)
|
|
|
what do flat or inverted T waves characterize?
|
myocardial ISCHEMIA
|
|
|
what does ST segment elevation characterize?
|
myocardial INJURY
|
|
|
what does ST segment depression characterize?
|
digitalis, positive stress test or NSTEMI (only tells you a smaller amt of wall is infarcted compared to STEMI)
|
|
|
what does the presence of significant Q waves characterize?
|
myocardial INFARCTION at some point. Acute MI if concurrent ST elevation; old MI if normal ST segments
|
|
|
what is indicated when there is a wide QRS complex with concordance?
|
strong indicator of VT (concordance means all the precordial leads are upright or all are inverted)
|
|
|
what is the 'silhouette sign'?
|
the loss of a normal lung/soft tissue interface or 'silhouette' caused by any pathology which either replaces or displaces normal air filled lung.
|
|
|
what is an air bronchogram? what does it commonly signify?
|
visualization of air in an airway; develops when a bronchus (air density) becomes surrounded by water density (flooded alveoli), as in pneumonia. Commonly signifies alveolar disease, but can be seen in atelectasis
|
|
|
what are Kerley A and B lines? what do Kerley B lines suggest?
|
fluid in the lung tissue collects in fine horizontal lines seen in the periphery of the lung along the chest wall. These fluid-containing lines are septae between anatomic lung lobules and are called Kerley B lines. Kerley B lines are highly suggestive of CHF.
|
|
|
what is the most common pattern of diffuse lung disease?
|
pulmonary edema in patients with congestive heart failure.
|
|
|
how does alveolar filling look on a CXR?
|
alveolar filling produces poorly defined by homogenous opacity resembling white, fluffy clouds.
|
|
|
if abnormal lung opacity changes rapidly over serial radiographs, what does that suggest?
|
it suggests pulmonary edema. Pulmonary edema can progress rapidly, while pneumonia does not.
|
|
|
how can heart size help in differentiating between cardiogenic pulmonary edema and ARDS?
|
the heart size can be normal in ARDS, but is usually enlarged in CHF. Caveat: pts with pulmonary edema from acute MI can have normal size heart.
|
|
|
what is the most common form of hyperlucency of the lung?
|
diffuse hyperlucency secondary to emphysema. the lung fields are unusually elongated and black with a flattened diaphragm, increased retrosternal space and decreased heart size.
|
|
|
what is the best indicator of emphysema on CXR?
|
a flattened diaphragm?
|
|
|
what does blunting of the costophrenic angle suggest?
|
pleural effusion.
|
|
|
in an erect patient, where does a pneumothorax usually appear?
|
in the apex of the lung
|
|
|
what is the most common location of a pneumothorax in supine or semirecumbent patients?
|
anteromedial and subpulmonic.
|
|
|
what does 'batwing' or 'butterfly' pattern refer to?
|
perihilar or central distribution of pulmonary edema suggestive of cardiogenic pulmonary edema
|
|
|
what is honeycombing? what does it suggest?
|
a pattern of coarse polygonal cystic lesions; suggests end-stage fibrotic disease
|
|
|
what can obscure the right heart border (cardiac silhouette)?
|
alveolar disease in the right middle lobe
|
|
|
what can obscure the diaphragmatic silhouette?
|
alveolar disease in the lower lobes
|
|
|
normal axis (no deviation)
|
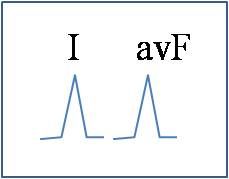
what does this signify?
|
|
|
left axis deviation
|
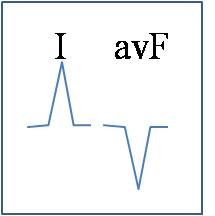
what does this signify?
|
|
|
extreme right axis deviation
|
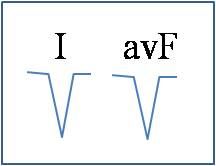
what does this signify?
|
|
|
right axis deviation
|
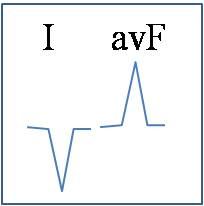
what does this signify?
|
|
|
AVL
|
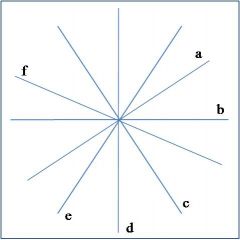
what lead is 'a' in this diagram of the hexaxial circle?
|
|
|
lead I
|
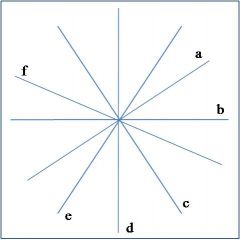
what lead is 'b' in this diagram of the hexaxial circle?
|
|
|
lead II
|
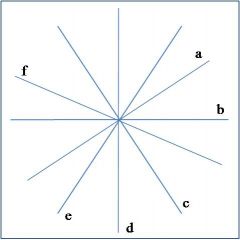
what lead is 'c' in this diagram of the hexaxial circle?
|
|
|
AVF
|
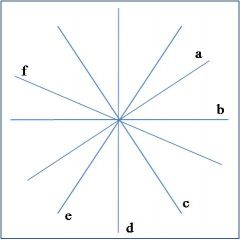
what lead is 'd' in this diagram of the hexaxial circle?
|
|
|
lead III
|
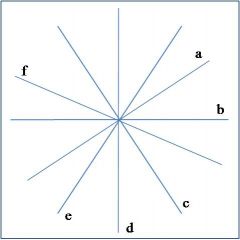
what lead is 'e' in this diagram of the hexaxial circle?
|
|
|
AVR
|
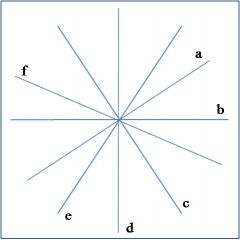
what lead is 'f' in this diagram of the hexaxial circle?
|
|
|
how can you see there's good inspiration on a CXR?
|
should see at least 8, ideally 10-11 ribs over the lung fields
|
|
|
how can you tell your film is straight?
|
medial ends of the clavicles will center on white teardrop representing spinous processes of T3
|
|
|
what is displayed in a well exposed film?
|
the soft tissues of the lung are accurately displayed and the vertebrae will be slightly visible through the heart
|
|
|
how does subcutaneous emphysema appear in a CXR?
|
multiple small, dark lines or beads
|
|
|
what is the visceral pleural stripe?
|
point of contact between pulmonary and parietal pleura
|
|
|
where would you expect to find bifurcation of the trachea on CXR?
|
somewhere around T5
|
|
|
where do you want to see the tip of the ETT when the patient's head is in a neutral position?
|
4 cm above the carina, which is between T5 and T7
|
|
|
where do you want to see the tip of a trach tube on CXR?
|
1/2 to 2/3 the distance from the stoma to the carina; normal at T3
|
|
|
where would you want to see the tip of a central line on CXR?
|
extends into the SVC with tip at right lateral border of T5/T6
|
|
|
how should the PA catheter appear on CXR?
|
goes through SVC, continues through RV, free of kinks/loops, extend into PA 3-4 cm beyond vertebral midline at T7
|
|
|
how should an NGT/OGT appear on CXR?
|
through esophagus, into stomach below L hemidiaphragm; no kinks/curls
|
|
|
how should a chest tube appear on CXR?
|
free from kinks; straight. Must be in pleural cavity with all drainage ports within the pleural cavity
|
|
|
how should an IABP appear on CXR?
|
balloon contains 30-40ml, is 8.5-10" in length. Should lie in descending aorta between L SC artery and RA branches. Visualize tip at end of aortic arch. Tip should lie just below aortic knob at L1
|
|
|
how should pacemaker wires appear on CXR?
|
extend through SVC, RA, with tip at RV apex. Appears left of midline on AP/PA
|

