![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What area of the pterygoid fascia do you have to be careful of when doing a maxillary nerve block?
|
pterygopsinous ligament which is continuous with the stylogmandibular ligament and could become calcified and block the needle
|
|
|
If you fracture your mandible what arteries/nerve would you be worried about and why?
|
Maxillary artery/vein and the auriculotemporal nerve pass between the sphenomandibular ligament and neck of mandible so a fracture to mandible could effect these vessels
|
|
|
What is the arterial supply to the muscles of mastication?
What are the muscles of mastication? |
branches of the second part (pterygoid) of the maxillary a and named by what muscle it goes to
- termporalis, masseter, medial and lateral pterygoid with assistance from buccinator |
|
|
What is the innervation of the mastication muscles?
|
CNV mandibular division
|
|
|
Masseter muscle...
a. innervation b. insertion c. clinically significant? d. what runs parallel |
a. masseteric nerve branch of mandibular nerve (V3)
b. inserts on lateral surface of angle of mandible c. fracture dislocations of mandible anterior to angle of mandible will cause proximal portion to displace upward and forward d. parallel with medial pterygoid |
|
|
Medial pterygoid and lateral pterygoid are for what?
|
medial close mouth and lateral opens mouth
|
|
|
Lateral pterygoid muscle:
a. insertion of upper and lower head b. relationships of the pterygoids with neurovascular structures |
a.upper: articular disk of temporomandubular joint (TMJ)
lower: pterygoid fossa of mandible b. between two head of lateral pterygoid maxillary and buccal nerve (buccal branch of V) |
|
|
What vessels pass through medial and lateral pterygoids
|
inferior alveolar and lingual nerves
|
|
|
What branch of maxillary artery supplies the chin and lower teeth?
|
inferior alveolar artery
|
|
|
Describe the component s of the masseteric reflex and how do you test it?
|
Test to see if motor and sensory of V is in tact. (only psuedo unipolar neuron in CNS)
- Monosynaptic reflex done by depression of chin, which stretches neuro spindles in masseter muscle sending signal to mesencephalic nucleus of V, and then resends to motor neuron in trigeminal motor nucleus masseter muscle to contract and close mouth |
|
|
Actions of the mouth...(name muscles that cause this)
a. normal opening b. wide opening c. closing |
a. lateral pterygoid
b. lateral pterygoid, suprahyoid muscles c. temporalis, masseter, medial pterygoid |
|
|
What ligament associated with the Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) that changes the transverse axis of rotation from a line between the mandibular condyles to a line between the lingulae
|
stylomandibular ligament
|
|
|
What are the 2 most important aspects of the development of the face?
|
1. dentitian development decreases the mental angle
2. air sinus development |
|
|
Describe the changes in the mandible from the newborn to adult...
|
Newborn mental angel with 175 deg, 4 year old- 140 degrees, adult 110-120, old persion 140
|
|
|
Fractures of the face what two things are most important for doctors?
|
1. orbits in correct position
2. dental arches lining up |
|
|
Three areas of the mandibular fractures and clinical considerations...
|
a. neck fracture- maxillary a. v. or auriculo temporal n.
b. ramus- lingual n., inferior alveolar c. body- inferior alveolar n. and vessels |
|
|
NAme the structures in the infratemporal fossa
|
1. tendon of temporalis muscle, medial and lateral pterygoid musces, maxillary a and branches, pterygoid venous plexus and mandibular branches of V
|
|
|
Two most important branches from the maxillary a?
|
a. middle meningeal
b. post sup. alveolar |
|
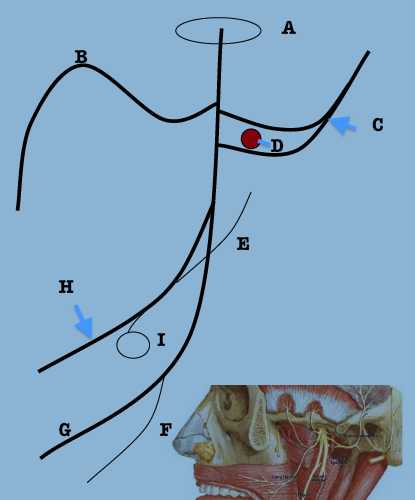
label the schematic of the mandibular nerve branches
|
a. foramen ovale
b. long buccal n. c. auriculotemporal n. d. middle meningeal a. e. chorda tympani n. f. nerve to mylohyoid g. inferior alveolar n. h. lingual n. i. submandibular ganglion |
|
|
What artery are we thinking of with epidural hematoma?
Where does this enter the skull? |
middle meningeal artery - foramen spinosum
|

