![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
144 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is yeast?
|
A form of fungi that is unicellular and reproduces through budding
|
|
|
What is the appearance of yeast on agar?
|
Slimy or mucoid colonies that resemble bacterial colonies
|
|
|
What is the appearance of molds on agar?
|
Downy, fluffy, cottony colonies
|
|
|
List 6 dimorphic fungi.
|
Histoplasma capsulatum
Blastomyces dermatitidis Coccidioides immitis Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Sporothrix schenckii Penicillium marneffei |
|
|
What is the definition of dimorphic fungi?
|
Mycelial fungi in nature and lab temperatures below 30 Celsius with yeast phase in human tissue or lab temperatures above 35
|
|
|
What is a cause of superficial mycoses?
|
Malassezia furfur (tinea versicolor)
|
|
|
What is a cause of subcutaneous mycoses?
|
Chromomycosis
|
|
|
What is a cause of deep or systemic mycoses?
|
Histoplasma capsulatum
|
|
|
What is a cause of opportunistic mycoses?
|
Aspergillus fumigatus
|
|
|
What is the all purpose plating media used in mycology?
|
Sabouraud's glucose agar
|
|
|
What is inhibitory mold agar?
|
It is a selective SAB agar with chloramphenicol and enrichment to inhibit bacterial growth
|
|
|
What does not grow on inhibitory mold agar?
|
Saprophytic fungi and dermatophytes
|
|
|
What agar is used for the recovery of dimorphic pathogens?
|
Inhibitory mold agar
|
|
|
Which dimorphic fungi can cause disseminated infections?
|
Histoplasma capsulatum
Blastomyces dermatitidis Coccidioides immitis Paracoccidioides brasiliensis |
|
|
What does cyclohexamide do?
|
It inhibits rapidly growing molds from overgrowing slow growing dimorphics
|
|
|
For what is blood brain heart infusion agar used?
|
To grow dimorphic pathogenic fungi such as Histoplasma capsulatum
|
|
|
What is Mycosel/Mycobiotic agar?
|
It is a selective SAB with chloramphenicol and cyclohexamide used for dermatophytes
|
|
|
What agar is used for skin, hair, and nail specimens?
|
Mycosel/Mycobiotic agar
|
|
|
Which fungi are suppressed by cyclohexamide?
|
Cryptococcus neoformans
Candida tropicalis Trichosporon beigelii Yeast of Blastomyces Yeast of Histoplasma |
|
|
Is gram stain best for the detection of yeast, mold, or both?
|
Yeast (stains a dark blue)
|
|
|
What is the calcofluor white stain?
|
Fluorescent stain that binds to keratin of both yeast and mycelial fungi
|
|
|
What does India ink stain?
|
The negative background
|
|
|
At what temperature and how long is fungus incubated?
|
30 degrees C for 4 weeks
|
|
|
What method is used to observe mold microscopically?
|
Lactophenol cotton blue prep
|
|
|
What is the geographic distribution of Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Ohio, Missouri, and Mississippi River valleys
|
|
|
What lesion is commonly seen with Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Mucocutaneous lesions
|
|
|
What percentage of Histoplasma cases are subclinical?
|
95%
|
|
|
What is the size range of Histoplasma yeast?
|
2-4 micrometers
|
|
|
Which cells contain Histoplasma yeast?
|
Macrophages
|
|
|
What is the best test for the diagnosis of Histoplasma capsulatum in immune suppressed patients?
|
Direct antigen detection in urine
|
|
|
What is the gross appearance of Histoplasma on agar?
|
White to brown, cottony mycelium that is a slow grower taking 2-8 weeks to grow
|
|
|
What is the microscopic appearance of Histoplasma?
|
Large and round (8-16 micrometer) tuberculated macroconidia with small microconidia
|
|
|
What differentiates Sepedonium species from Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Sepedonium has large rough spores (7-17 micrometers) but NO microconidia
|
|
|
Describe the budding pattern of the yeasts of Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Narrow neck budding
|
|
|
What is the cause of the appearance of a capsule in intracellular Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Staining artifact
|
|
|
What is the variant of Histoplasma capsulatum associated with skin and bone lesions in Central Africa?
|
Histoplasma capsulatum var duboisis
|
|
|
How is Histoplasma capsulatum var duboisis differentiated from classic Histoplasma capsulatum?
|
Histoplasma capsulatum var duboisis has yeast that are 8-10 micrometers (2x the size of classic Histoplasma capsulatum)
|
|
|
What is the cause of pityriasis versicolor and fungemi in neonates on IV lipid feeding?
|
Malassezia furfur
|
|
|
What causes the most superficial dermatomycoses?
|
Malassezia furfur (tenia versicolor)
|
|
|
What is needed for the growth of Malassezia furfur on culture medium?
|
Oil
|
|
|
What yeast is characterized by a collarette on wet prep?
|
Malassezia furfur
|
|
|
Is Cryptococcus sensitive to cyclohexamide?
|
Yes
|
|
|
What is the appearance of Cryptococcus neoformans on agar?
|
Mucoid colonies
|
|
|
What is a sensitive test for Cryptococcus in CSF of patients with AIDS?
|
India ink
|
|
|
What is a sensitive test for Cryptococcus in CSF of HIV-negative patients?
|
Cryptococcal antigen
|
|
|
To what is cryptococcal antigen directed?
|
Capsule of Cryptococcus
|
|
|
On what agar does Cryptococcus neoformans appear brown but other organisms appear white?
|
Birdseed agar
|
|
|
What yeast is urease positive?
|
Cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
|
What is the size range of Cryptococcus neoformans?
|
2-20 micrometers
|
|
|
How is Cryptococcus gatti distinguished from C. neoformans?
|
C. gatti turns L-canavanine glycine bromthymol blue medium blue whereas it remains yellow with C. neoformans
|
|
|
What is the most common candida?
|
C. albicans
|
|
|
Which candida are resistant to fluconazole?
|
C. glabrata
C. krusei C. tropicalis |
|
|
Which candida is a pathogen of children and IV lines?
|
C. parapsilosis
|
|
|
Which candida does not form pseudohyphae?
|
C. albicans
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Candida albicans?
|
Grows in 24-48 hours
Pasty white bacterial-like colonies |
|
|
Which candida forms chlamydospores?
|
C. albicans
|
|
|
Which candida form germ tubes?
|
Candida albicans
Candida dubliniensis |
|
|
What is the size range for Candida glabrata?
|
2-4 micrometers
|
|
|
What is the size range of Candida species?
|
8-10 micrometers
|
|
|
Which candida appears green on ChromAgar Candida?
|
C. albicans
|
|
|
Which candida appears blue on ChromAgar Candida?
|
C. tropicalis
|
|
|
Which candida appears white on ChromAgar Candida?
|
C. parapsilosis
|
|
|
Which candida appears pink on ChromAgar Candida?
|
C. glabrata
|
|
|
Which candida provides a false diagnosis of C. albicans if the germ tube test is incubated for more than 4 hours?
|
C. tropicalis
|
|
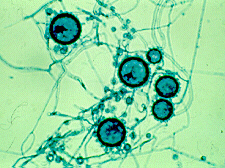
|
Histoplasma capsulatum
|
|
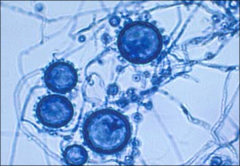
|
Histoplasma capsulatum
|
|
|
Histoplasma capsulatum
|
|
|
Histoplasma capsulatum
|
|
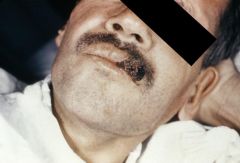
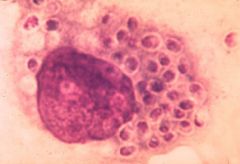
|
Mucocutaneous lesion caused by Histoplasma capsulatum
|
|
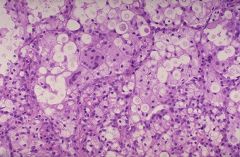
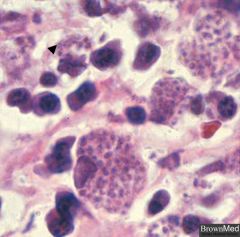
|
Cryptococcus neoformans
|
|

|
Cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
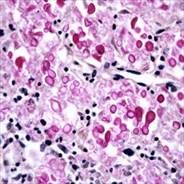
|
Cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
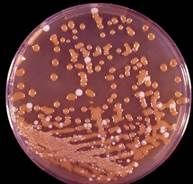
Birdseed agar
|
Cryptococcus neoformans (brown)
|
|

Urease positive yeast
|
Cryptococcus neoformans
Trichosporon species |
|
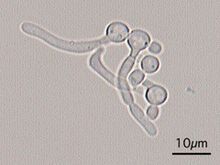
Test?
|
Germ tube test
|
|
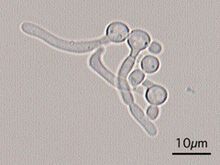
Yeast positive for germ tube test
|
Candida albicans
Candida dubliniensis Canadida tropicalis (if incubated >4 hours) |
|
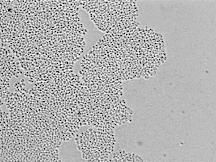
What yeast?
|
Candida glabrata
|
|
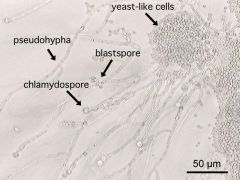
|
Candida albicans
|
|
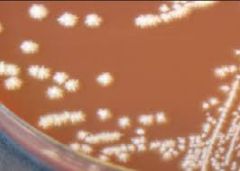
|
Candida dubliniensis
|
|
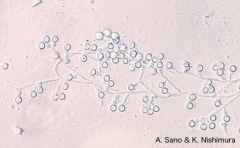
What yeast?
|
Candida parapsilosis
|
|
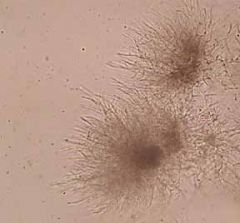
|
Candida albicans ("feet")
|
|
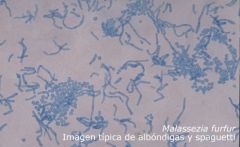
|
Malassezia furfur
|
|

|
Review
|
|
|
What is the geographic distribution of Blastomyces dermatitidis?
|
Ohio and Mississippi River valleys
|
|
|
What does Blastomyces dermatitidis cause?
|
Pulmonary disease that can disseminate to skin and bone
|
|
|
What mold is characterized by lollipop-shaped conidia?
|
Blastomyces
|
|
|
What temperature and what length of time is need to grow out the mycelial form of Blastomyces dermatitidis?
|
30 degrees C for 2-3 weeks
|
|
|
What temperature and what length of time is need to grow out the yeast form of Blastomyces dermatitidis?
|
37 degrees C for 4 weeks
|
|
|
What is a mimicker of Blastomyces?
|
Chrysosporium
|
|
|
What type of yeast budding is seen with Blastomyces dermatitidis?
|
broad-based budding with double contoured wall
|
|
|
What is the appearance of Blastomyces on agar?
|
Fluffy white and buff colored
|
|
|
What is the size range of the yeast of Blastomyces dermatitidis?
|
8-20 micrometers
|
|
|
What is the geographic distribution of Coccidioides immitis?
|
Southwest USA, Mexico, South America in Sonoran life zone (desert sands)
|
|
|
What percentage of Coccidioides immitis infections are chronic?
|
95%
|
|
|
What is the most deadly dimorphic fungi?
|
Coccidioides immitis
|
|
|
What does Coccidioides immitis cause?
|
Focal pulmonary disease, but can become disseminated
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for dissemination of Coccidioides immitis?
|
Immunodeficiency
Darker ethnic groups Pregnancy |
|
|
What temperature and what length of time is needed to grow the mycelial form of Coccidioides immitis?
|
30 degrees C for 2-3 days
|
|
|
What is the appearance of Coccidioides immitis on agar?
|
White waxy/wooly colonies
|
|
|
What is a good description for Coccidioides immitis?
|
Septated hyphae with chains of thick waled barrell shaped arthroconidia with dead cells (cleared out) in between
|
|
|
What is a mimicker of Coccidioides immitis?
|
Malbranchea
|
|
|
What is unique about Coccidioides immitis compared to other dimorphic fungi?
|
The yeast phase cannot be grown in the lab and is only seen in tissue
|
|
|
What is the appearance of Coccidioides immitis yeast in tissue?
|
10-80 micrometer spherules with endospores
|
|
|
What does Rhinosporidium seeberi cause?
|
Oral or nasal mass lesions
|
|
|
What distinguishes Rhinosporidium seeberi from Coccidioides immitis?
|
The spherules of Rhinosporidium seeberi contains endospores 2X the size of those of Coccidioides immitis
|
|
|
What is the geographic distribution of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis?
|
Brazil, Venezuela, Columbia in soil
|
|
|
Is there a male or female predominance for Paracoccidioides brasiliensis?
|
Male (95%)
|
|
|
What fungi has a marked male predominance?
|
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
|
|
|
What does Paracoccidioides brasiliensis cause?
|
Pneumonia
Disseminated infection Extrapulmonary lesions on face and oral mucosa |
|
|
What is the characteristic appearance of the yeast form of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis?
|
Large yeast (10-30 micrometer) with multiple daughter buds (2-10 micrometers) with the appearance of a mariner's wheel
|
|
|
List 4 causes of subcutaneous fungal infections
|
Mycetoma
Chromomycosis Phaeohyphomycosis Sporotrichosis |
|
|
What are other names for mycetoma?
|
Madura Foot
Maduromycosis |
|
|
What is the geographic distribution of mycetoma?
|
Hot temperate parts of the world
|
|
|
What are the criteria for diagnosing mycetoma?
|
Lesions leading to swollen extremities
Draining sinuses Sulfur granules in tissue and drainage |
|
|
What are the 2 types of mycetoma?
|
Actinomycotic
Eumycotic |
|
|
What is the most common cause of mycetoma?
|
Nocardia species
|
|
|
What causes eumycotic mycetoma?
|
Black molds
|
|
|
What type of mycetoma are 98% of cases?
|
Actinomycotic
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of actinomycotic mycetoma?
|
Nocardia species
|
|
|
What is a good description of Nocardia?
|
Gram positive filamentous branching rods
|
|
|
What is the staining pattern of Nocardia?
|
Gram positive
Modified acid-fast positive |
|
|
What is the appearance of Nocardia on agar?
|
Dry and crumbly
|
|
|
What mold has a characteristic musty smell?
|
Nocardia species
|
|
|
How long does it take to grow Nocardia on agar?
|
3-5 days
|
|
|
List 6 fungi that cause eumycotic mycetoma
|
Cladophialophora carrionii
Cladophialophora bantiana Phialophora verrucosa Fonsecaea pedrosoi Exophiala species Wangiella species |
|
|
List 6 fungi that cause chromomycosis
|
Cladophialophora carrionii
Cladophialophora bantiana Phialophora verrucosa Fonsecaea pedrosoi Exophiala species Wangiella species |
|
|
How is actinomycotic sulfur granules distinguished from eumycotic sulfur granules?
|
The edges of actinomycotic sulfur granules has thin filamentous bacteria whereas edge of eumycotic sulfur granules has thick mycelial hyphae
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of chromomycosis?
|
Wart like lesions in cutaneous tissue
Sclerotic bodies in tissue Growth of dark/pigmented fungi |
|
|
What type of infection is associated with sclerotic bodies?
|
Chromomycosis
|
|
|
What is a good description of sclerotic bodies?
|
"Copper pennies"
|
|
|
What does Prototheca wickerhamii cause?
|
Skin lesions or nodules
|
|
|
What is a characteristic finding of Prototheca wickerhamii?
|
Morula body
|
|
|
What is phaeohyphomycosis?
|
An infection caused by traumatic implantation of dark fungi into subcutaneous tissue that lacks sulfur granules and sclerotic bodies
|
|
|
What is Prototheca wickerhamii?
|
Algae without chlorophyll that can be found in immunocompromised patients
|
|
|
List 4 types of sporulation patterns of black molds
|
Rhinocladiella-like
Cladosporium-like Phialophora-like Acrotheca-like |
|
|
Describe Rhinocladiella-like sporulation
|
"Fern tree" with natural brown colors
|
|
|
Describe Phialophora-like sporulation
|
"Flower pot" with natural brown color
|
|
|
Describe Cladophialophora-like sporulation
|
"Stringy filaments"
|
|
|
What black mold causes brain infections?
|
Cladophialophoria bantiana
|
|
|
Which black mold is commonly found in showers?
|
Alternaria
|
|
|
Describe Alternaria
|
"Chain of hand grenades"
|
|
|
Describe Bipolaris
|
"Hockey stick"
|
|
|
What is a very invasive dematiaceous fungi to skin, nasal sinuses, bone, and brain?
|
Bipolaris
|
|
|
What causes the curve in Curvularia?
|
The center cell is the largest cell and causes a curve.
|

