![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What virus is driving the Tb epidemic? Where is this localized to?
|
HIV/AIDS
Africa |
|
|
What stain is used for a histologic diagnosis of Mycobacterium?
|
Acid-fast
|
|
|
What is the morphology of Mycobacterium?
|
Bacilli
|
|
|
What are the three unusual features of Mycobacterium?
|
Slow growing; take 8 weeks to grow!
Obligate aerobes Mycolic acid in the cell wall; gives resistance |
|
|
What occurs when Mycobacterium is in a low oxygen state?
|
Enter a quiescent state and are resistant to cidal antimicrobials
|
|
|
What are the layers within the M. tuberculosis cell wall?
|
Outer to inner:
Capsule Mycolic acid Peptidoglycan/Arabinogalactan Inner membrane |
|
|
What are the two enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of the mycolic acid in Mycobacterium that are targeted by antibiotics?
|
KatG
InhA |
|
|
What is the activity of KatG?
|
Catalase/peroxidase
Required for clinical activity of Isonazid |
|
|
What is the activity of InhA?
|
Synthesis of long chain mycolic fatty acids.
Targeted by Isoniazid |
|
|
What type of immunity is essential in controlling Tb infections?
|
Cell-mediated immunity
|
|
|
Primay Tb will show what signs on PPD and xray?
|
PPD: +
Xray: - |
|
|
Where is the first place that Mycobacteria localizes to in the body?
|
Albeolar macrophages (dust cells)
|
|
|
What is the mechanism by which Mycobacterium tuberculosis survives within macrophages?
|
Blocking of P-L fusion.
No acidification; the cells can't be killed. |
|
|
What does Mycobacterium tuberculosis do while inside the phagolysosome?
|
Shed lipids that are presented to the body.
Are able to get out of the cell and stimulate the immune system. |
|
|
What response is mycolic acid alone able to generate?
|
Granuloma formation in the host.
Sufficient for virulence. |
|
|
What is the function of TNF-alpha in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection?
|
Recruitment of macrophages
Stabilization of the granuloma |
|
|
What kind of lymphocyte is active in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection?
|
CD4 TH1 cells
|
|
|
What interleukin is produced by this T cell in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection?
What is its activity? |
IL-2
Stimulation of CD8 cytotoxic T-cell development |
|
|
What lymphokine is released by CD4 cells in T-cell Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection?
What is its activity? |
INF-gamma
Activation of macrophages |
|
|
What molecules are released by activated macrophages in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections?
What is their activity? |
IL-1
TNF-alpha Activation of a general immune response |
|
|
What type of hypersensitivity reaction is active in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections
|
Type IV
Delayed; involves macrophages |
|
|
What is the activity of CD8 T cells in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection?
|
Recognition and killing of infected macrophages
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of dispersion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the lungs?
|
Through regional lymph node
|
|
|
That is the appearance on PPD/Xray for latent/dormant Tb?
|
PPD +
Xray - |
|
|
What is the most common form of Tb in the US?
|
Latent Tb
|
|
|
What is the effect of a weakening immune system on latent Tb?
|
RELEASE OF THE BACTERIA!!!
|
|
|
What are the Xray/PPD findings for active Tb?
|
PPD +
Xray + SPUTUM + |
|
|
Who are effected by disseminated/miliary Tb?
|
Immunocompromised
Old Young |
|
|
What is the mechanism of antigen presentation with Tb?
What is a complication with this? |
MHCI
Can't really use vaccines |
|
|
What type of secretion system do Mycobacterium tuberculosis use?
|
Type VI
|
|
|
What is used for a Tb vaccine?
|
Bacille Calmette Guerin
Avirulent strain of Tb from cows. NOT SAFE IN IMMUNOCOMPROMISED |
|
|
What disease does Mycobacterium leprae cause?
|
Leprosy
|
|
|
What is the reservoir for Mycobacterium leprae?
|
Humans
|
|
|
What is the transmission of Mycobacterium leprae?
|
Person to person via secretions, aersols.
Significant amounts of contact necessary |
|
|
What is the appearance of a Mycobacterium leprae infection?
|
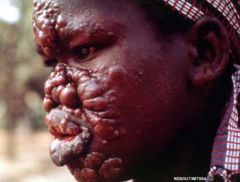
Skin lesions.
|
|
|
What type of Mycobacterium is found all over the place and has been implicated in infections in severely immunocompromised hosts?
|
Mycobacterium avium complex
|

