![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
mechanism of action |
Biological or biochemical changes with the body caused by drugs |
|
|
drug of choice |
Drug or class of drugs most frequently prescribed because of effectiveness. |
|
|
first line drugs |
Drugs that are very effective in treating a certain condition and that have an acceptable adverse effect profile. |
|
|
Absorption |
How to drug gets into the bloodstream |
|
|
Distribution |
Where the drug goes in the body |
|
|
Metabolism |
How the drug is changed in the body. Can result in the activation or elimination of the drug |
|
|
Elimination |
How the body gets rid of the drug |
|
|
ADME process |
Absorption Distribution Metabolism Elimination |
|
|
What determines the amount of drug absorbed? |
The pH of the compartment Lipid solubility Vascularity of the administration site |
|
|
Weight per volume solution |
g of drug/100 ml of solution |
|
|
Weight per weight |
grams of drug/100 grams of solid dosage form |
|
|
Volume per volume percentage |
ml/ 100 ml Used in mixing solutions |
|
|
finding % of drug in solution |
Convert g/100 ml to a percent |
|
|
Farenheit |
F = C × (9/5) +32 |
|
|
Celsius |
C = (F - 32) × 5/9 |
|
|
meniscus |
"curved" portion of liquid inside a glass cylinder -look at bottom when measuring |
|
|
1ml syringe increments |

|
|
|
3ml, 5ml, 10ml syringe increments |

|
|
|
insulin units to ml. |
order ÷ 100units/ml. |
|

|
Used for measuring small amounts |
|
|
nomogram |
chart that relates the height and weight of a person to his/her body surface area |
|
|
body surface area |
The total area of the surface of the body |
|
|
child's dose |
adult dose ÷ 1.7 |
|
|
body surface are |
recommended dosage given in mg of drug/m squared. |
|
|
individual's dose w/BSA
|
BSA × dose (m squared × mg/m squared) |
|
|
checking prescribed dose for safety |
dose ÷ BSA = amount of drug administered |
|
|
BSA formula (standard) |
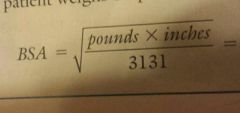
|
|
|
BSA formula (metric) |
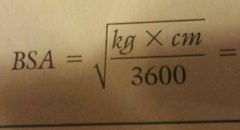
|
|
|
Troche |
Lozenge |
|
|
Information that can be added to script |

|
|
|
Sumatriptan |
Imitrex |
|
|
fexofenadine |
Telfast |
|
|
Mirtazapine |
Remeron |
|
|
hydroclorothiazide |
Diaqua |
|
|
Exforge |
amlodipine/valsartan |
|
|
Lovaza |
omega 3 fatty acid |
|
|
Janumet |
/metformin |
|
|
Atacand |
candesartan |
|
|
Aventyl, Pamelor |
nortriptyline Tricyclic antidepressant |
|
|
Adapin, Sinequan |
doxepin Tricyclic antidepressant |
|
|
Ascendin |
amoxapin Tricyclic antidepressant |
|
|
Ludiomil |
maprotiline Tetracycline Antidepressant |
|
|
nefazadone |
No brand name Heterocyclic Antidepressant |
|
|
aa |
of each |
|
|
a |
arterial |
|
|
Norvasc |
amlodipine |
|
|
Deltasone |
prednisone |
|
|
Dyrenium |
triamterene |
|
|
Darvon-N |
propoxyphene |
|
|
Prevacid |
lanpsoprezole |
|
|
Lopressor |
metoprolol tartrate |
|
|
Ativan |
lorazepam |
|
|
Plavix |
clopidogrel |
|
|
Serevent |
salmeterol |
|
|
Fosamax |
alendronate |
|
|
Zyrtec |
ceterizine |
|
|
K-Lor |
potassium chloride |
|
|
Septra, Bactrim |
trimethoprim/sulfametoxazole |
|
|
Premarin |
conjugated estrogens |
|
|
Valium |
diazepam |
|
|
Vasotec |
enalapril |
|
|
Levoxly |
levothyroxine |
|
|
Allegra |
fexofenadine |
|
|
Zantac |
rantidine |
|
|
Lotrel |
amlodipine/benazapril |
|
|
Statins |
Treat high triglycerides & cholesterol |
|
|
Concentration |
Amount / volume |
|
|
DEA |

|
|
|
BOP |

|
|
|
FDA |

|
|
|
Joint Comission |

|
|
|
DEA form 222 |

|
|
|
Drug recall class l |

|
|
|
Drug recall class ll |

|
|
|
Drug recall class lll |

|
|
|
Federal Food and Drug Act of 1906 |

|
|
|
Narcotic Tax Act of 1914 |

|
|
|
Durham - Humphrey Ammendment of 1951 |

|
|
|
Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act of 1938 |

|

