![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are mutagens? |
Chemical agents that cause heritable changes in genes
|
|
|
What are carcinogen? |
Chemical agents that cause cancer?
|
|
|
What are teratogens? |
Chemical agents that cause birth defect? |
|
|
What types of mutations associated with Therapeutic drugs? |
Point Mutations
Alkylating Frameshift mutations Doxorubicin Chromosome rearrangements Alkylating, cisplatin Aneuploidy - drugs that affect microtubulesVinca alkaloids, taxane |
|
|
What is doxorubicin? |
Intercalating agent stacks on top of nucleotides. When DNA polymerase go over, it may skip over that area( point mutation) or insert a base where it should be |
|
|
What causes the breakage associated with DNA crosslinking agents? |
The breakage is due to DNA REPAIR. |
|
|
What is the evidence to conclude that breakage is associatd with dna repair? |
Bacteria that have mutations in mismatch repair genes are less sensitive than wild type bacteria to the effects of DNA crosslinking agents |
|
|
What is aneuploidy caused by? |
Cfhromosome nondisjunction when theres a defectine mitotic spindle checkpoint # some has more chromosomes than other uneven |
|
|
What are the methods for detectding mutagenic properties of drugs? |
Ames test Drosophilia recessive lethal test mouse domnant lethal test Micronucleus test Chromosome painting |
|
|
What is the ames test? |
You have a strain that is his - which means it can create it and add extract it liver. Known for metabolism. Then add chemical to it to see if theres any growth because the growth means there was a mutation to revert it You have to check if metabolziing the chemical by liver enzyme can create mutagens or the drug itself is a mutagen in its regular form |
|
|
What is the recessive lethal test? |
First the parent class will be a female wthat is heterozygous for bar and recessie lethal mutaion and a wild type male exposed to a suspected mutagen Therefore you hate mthe f1 bar eye females with normal males. Then you count the males, if no males were shown, mutagen wouldve been prodiced beacused it would be inherit. HOwever if its not, there should be half alive half death, the half dead should be bar eye(from mother) |
|
|
What is the dominant lethal test? |
Mutagenize males and mate with normal female Sacrifice pregnant females just before the bith of the f1 generation Examine the ratio, dead embryo means that it has domiannt mutation.. |
|
|
What is the micronucleus test? |
Exposed animals with mutagen Treat culture lympochotes with cytochalisin b( stop mitosis) Stain cells with dna binding dye and look for bi nucleate cells with a micronucleus ( look fro mono/bi nucleate want to examine the ones are undergoing division The presence of micornucleus shows that there are chromosomes that are not properly seprated therefore create their own circle You do fisih to distignuish beetween micronucleu with a whole chromosome and accentric chromosome. Naturally whole chromosome means that it was because of mutagens however accentric chromosome is due to not having a centromere for dividng |
|
|
What is chromosome paintaining? |
Painting the chromosome to see any defectes
Process: Add colchine, make them arrest in mitosis and suspend the cell in acetic /ethanol to rupture it Specifically binding unique chromosome dyes that binds to satellite dna |
|
|
What are the mutagens that suspected to being carcinogens? |
Drugs: alkylating agents, alkaloids, taxanes Foods: Saccharin |
|
|
What are the guidelines for testing for potential carcinogens? |
1. Relatively large number of animals 2. Animals must be maintained on the drug major proportion of their life 3. Two or more species 4. Tested in pregnant females and test offpsring for their lifetime 5. Route of administration in the animal should be the same as for humans 6. Dosage rage must be higher than for propose human(10-100x ) the human exposure so you can extrapolate |
|
|
What is the relationship between Initiation and Promotion? |
You need both of them to occur a tumor incidence with initatior before the promoter |
|
|
What are the features of initation and promotion? |
Iniation: mostly mutagens where the mutations occur , heritable ganes Promoters: activate cell proliferiation where now youre making cells with this mtuagens Initation must comes first . Then rpometers make carcinogen mutation Promoter may be added long after application of initatior |
|
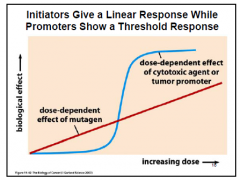
|
Initatior; Shows a linear response where as you increase the levels of them tuagen you get noticeable biological affects Promoters: Sigmoidal curve where iitially the dosage wont show any biological affect but it s biological effect increase a certain dosage and levesl off Therefore, you can possible use a promotersas long as it doesnt hit the thershold, not for mtuagen though |
|
|
What is nitrosodiethylamine |
A possible carcinogen however, by extrapolating the adta, i shows that it shows a sigmoidal curve |
|
|
How does metabolism affect carcinogencity? |
It can either increase or decrease it. In terms of benzoprene, it is not a carcinogen until p450 metabolize it it to a carcingen |
|
|
What is teratogenesis? |
Birth defect in babies/embryo 1. Time of exposure is critical: 2-10 weeks for most teratogens in humans( period of major organogensis) 2. Alteration not heritable doesnt dea with genes 3. Specific malformation depends ontime of exposure during fetal development 4. significant species difference |
|
|
What are known human teratogens? |
Thalidomide Warfarin Corticosteroids Diethylstilbestrol Phenytoin/antiepilpetics Cytoti dna damaging anticancer drugs Retinoids ACE inhibitor( teratogenic all preg) - renal pathway Ethanol |
|
|
What is Thaliomide? |
Produced as a safe drug for pregnant woman to deal with morning sickness. Has safe R and toxic S Affects include phocomelia and major organ dects Was not approved by fda but yet still on the market |
|
|
What is the approved use of Thaliomides? |
Treat : Erythema nodosum leprosum Myeloma Both patients and physcian must be enroeld in STEP before drug can be used Work as an antiogenesis inhibitor bloodcot/neuropathy |
|
|
What is Diethystilbesterol? |
DES
Used from 1940-1970 to prevent miscarriage Female offspring who used DES showed vaginal neoplasia at puberty and increased risk of vaginal /cervical cancer |

