![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the plasma membrane of muscle cells?
|
Sarcolemma
|
|
|
What is the cytoplasm for muscle cells?
|
Sarcoplasm
|
|
|
What is the fascia surrounding the entire muscle?
|
Epimysium
|
|
|
What is a bundle of muscle fibers?
|
Fasicle
|
|
|
What surrounds each fasicle?
|
Perimysium
|
|
|
What surrounds each individual muscle cell?
|
Endomysium
|
|
|
How many muscle cells make up 1 fiber?
|
1 cell
|
|
|
What is a cell that is made up of many myofibrils?
|
Myofiber
|
|
|
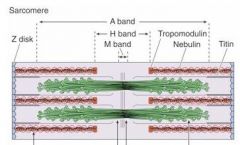
Which band is the dark band?
|
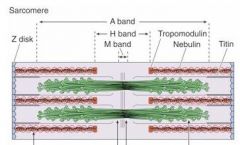
A band
|
|
|
Which band is the light band in the spaces between the A bands?
|
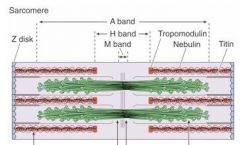
I band
|
|
|
What bisects the I bands?
|
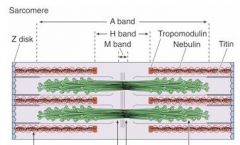
Z-disks
|
|
|
How many sarcomeres make up a muscle fiber?
|
Many
|
|
|
What is the light area in the middle of the A band?
|
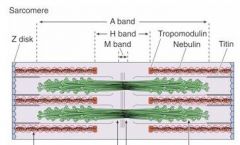
H band
|
|
|
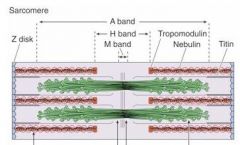
What is in the middle of the H band and sarcomere?
|
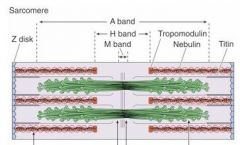
M line
|
|
|
What is a protein that fastens thin filaments to Z disks?
|
Alpha Actin
|
|
|
What is responsible for muscle contraction?
|
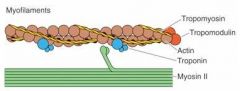
Actin & Myosin (Actomyosin)
|
|
|
What is wrapped around the actin?
|
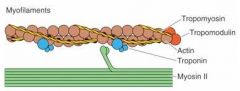
Tropomyosin
|
|
|
What forms the I bands?
|
Actin (thin filaments)
|
|
|
What shape do thin filaments have?
|
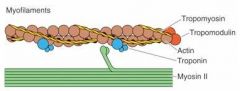
Helical shape
|
|
|
What forms the A band?
|
Myosin (thick filaments)
|
|
|
What part of the myosin is the ATPase?
|
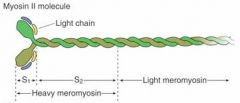
Heavy meromyosin
|
|
|
What is a rod-like protein that makes up the backbone of the thick filament?
|
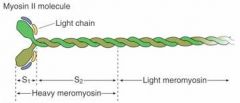
Light Meromyosin
|
|
|
What connects the thick filaments together?
|
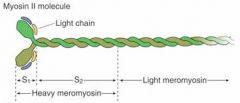
Creatine Phosphate
|
|
|
Which band disappears during contraction?
|
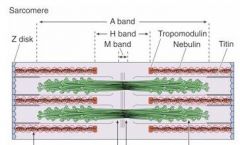
H band disappears
|
|
|
When the muscle is stretched which bands increase in width?
|
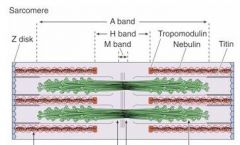
I band and H band increase
|
|
|
Where do T-tubules begin?
|
At the interface between the A & I bands
|
|
|
What is responsible for carrying a depolarization completely within a muscle fiber so that the muscle contracts all together?
|
T-tubules
|
|
|
What is the combination of two Sarcoplasmic reticulum complexes and the T-tubules?
|
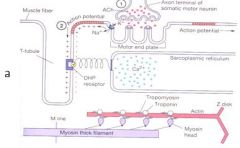
Triad
|
|
|
What is structural syncytium also known as?
|
Skeletal Muscle
|
|
|
What happens during super contractions?
|
thin filaments will bunch up in the center forming a new band
|
|
|
What hormone is especially responsible for creating white muscle?
|
Testosterone
|
|
|
What cells help regenerate skeletal muscle?
|
Satellite cells
|
|
|
What type of muscle cells are lots of individual cells held together end-to-end to form fibers?
|
Cardiac myocytes
|
|
|
What holds together the Cardiac muscle cells?
|
Intercalated Disks
|
|
|
What two configurations are cardiact myocytes found in?
|
Transverse and Longitudinal configuration
|
|
|
What holds the transverse components of Cardiac myocytes together?
|
Desmosomes and Fascia Adherens
|
|
|
What does the longitudinal component of cardiac myocytes have that allows the wave of depolarization to travel?
|
Gap Junctions
|
|
|
What do the gap junctions ability to allow the cardiac myocytes to operate as if they are a single cell called?
|
Functional Syncytium
|
|
|
Where are the nuclei of cardiac myocytes?
|
centered (not off to the side like skeletal muscle)
|
|
|
Which muscle cells are branched?
|
Cardiac myocytes
|
|
|
T/F
Satellite cells present in the heart regenerate myocytes |
False
There are no satellite cells in the heart and so there is no regeneration/division |
|
|
T/F
T-tubules are found in cardiac muscles at the A/I band junction |
False
A/I junction is skeletal muscle Cardiac is at the Z line |
|
|
T/F
Cardiac myocytes have diads |
True
Diads are only one Sarcoplasmic Reticulum associated with the T-tubule |
|
|
What is known as the wear and tear pigment in cardiac myocytes?
|
Lipofuscin is from the waste products of lysosomal digestion. It accumulates in nerves but does not seem to affect function.
|
|
|
What type of muscle consists of long Spindle-Shaped cells that taper at the end and have a nucleus in the center?
|
Smooth muscle
|
|
|
T/F
Smooth muscle cells are striated |
False
They have NO sarcomeres |
|
|
Since smooth muscle does not have sarcomeres do they lack myosin and actin?
|
No, they are just organized differently
|
|
|
How dow smooth muscle cells contract?
|
They twist and shorten like a twisted towel
|
|
|
T/F Smooth muscle have T-tubules and sarcoplasmic reticulum
|
False
Instead they have small vesicles along the membrane that hold and release Ca++ |
|
|
What muscle cells are linked by gap junctions?
|
Smooth Muscle and Cardiac Muscle
|
|
|
T/F
Smooth muscle is able to divide and it is stronger than skeletal muscle |
True
|
|
|
Which muscle cells are the smallest?
|
Smooth muscle cells
|
|
|
Which muscle cells are the largest?
|
Skeletal muscle cells
(multinucleated) |

